
(a)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the compound
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The compound,
Explanation of Solution
Pentanoic acid combines with methyl amine to give corresponding amides. By addition reaction, nitrogen of amino group of methyl amine attaches to carbonyl carbon of pentanoic acid. Amide obtained is reduced with a suitable reducing agent like sodium in ethanol or
The amines can be prepared by the reaction of carboxylic acid with ammonia and its derivatives. The amides obtained are reduced to required amine by a suitable reducing agent.
(b)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the compound, pentylamine from pentanoic acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid reacts with ammonia and its derivatives to give ammonium salts of primary secondary and tertiary amines. On heating, this ammonium salts dehydrate to form amides. The amides can be reduced to amines with
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The compound pentylamine can be synthesized from pentanoic acid as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
When pentanoic acid is treated with ammonia, the pentonamide is obtained. In this by addition reaction of ammonia to carboxylic acid amide is formed. This pentonamide gets reduced with sodium in ethanol or
Reaction product is a primary amine, pentyl amine. To prepare the given compound acid is treated with ammonia as shown below.
(c)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the compound,
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid reacts with ammonia and its derivatives to give ammonium salts of primary secondary and tertiary amines. On heating this ammonium salts dehydrate to form amides. The amides can be reduced to amines with
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The compound,
Explanation of Solution
The compound
The tertiary amine
(d)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the compound butylamine from pentanoic acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids when treated with ammonia give primary amines. This reaction is known as Schmidt reaction. Under acidic conditions ammonia is added to acid by nucleophilic addition. One molecule of carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas each is removed and amine is formed with one carbon less than parent acid.
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The compound, butylamine can be synthesized from pentanoic acid as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The pentanoic acid, when treated with ammonia undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction. First ammonia is added to acid with elimination of a nitrogen molecule and amide is formed. Under acidic condition this amide breaks to give primary amine and a carbon dioxide molecule is evolved. The reaction is known as Schmidt reaction and is given below.
The pentanoic acid can be converted to butylamine as shown below.
(e)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the compound hexylamine from pentanoic acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The no of carbon atoms in acid can be increased by its esterification. Acid is treated with alcohol to obtain desired ester. The ester gets reduced to
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The compound, hexylamine can be synthesized from pentanoic acid as shown below
Explanation of Solution
In this reaction, the number of carbon atom is more in the desired product than in given compound. To increase the carbons first the esterification of acid is done with methyl alcohol. As methyl group is introduced, the ester is reduced to alkane. Halogenation of this hexane is done and then with any hydrogen halide. The obtained halide is treated with ammonia to get the required amine as in Hofmann’s method.
The hexylamine is having more carbon than pentanoic acid, therefore number of carbon atoms is increased first, and then it is converted to desired amine.
(f)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the given quaternary ammonium salt from butyraldehyde is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The given quaternary ammonium salt can be synthesized from butyraldehyde as given below.
Explanation of Solution
The compound butyraldehyde, in presence of nickel and hydrogen, gets hydrogenated and give alcohol. This butyl alcohol reacts with hydrogen bromide to give the corresponding bromobutane. Bromobutane when comes in contact with tertiary amine
The desired quaternary ammonium salt can be prepared from butyraldeyd as shown below.
(g)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the given compound
Concept introduction:
Wurtz reaction is used to increase the numbers of carbon atoms in an alkane. Two alkyl halides according to required compound are taken. Sodium metal in dry ether solution is used for the coupling reaction, to form the higher alkane. The halides of these alkanes can go under controlled substitution reaction with amines, to give primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The compound
Explanation of Solution
The toluene is first halogenated with bromine to give bromotoluene. This bromotoluene reacts with ethyl bromide in presence of sodium metal and dry ether, to produce the phenyl propane (wurtz reaction). This is again halogenated with bromine to get the substituted bromo propane. When this substituted bromo propane reacts with ethyl amine, the desired product,
The compound,
(h)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the given compound,
Concept introduction:
By substitution reaction the alky groups can be introduced to active methylene carbon of diethyl malonate. Further on its hydrolysis corresponding acid is obtained which can be converted into amide and then reduced to amine.
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The given compound
The amide is reduced to final product as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The diethyl malonate has an active methylene group
The amide is reduced to final product as shown below.
The substituted
The amide is reduced to final product as shown below.
(i)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the given compound, isobutyl amine from acetone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
When
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The given compound is butyl amine can be synthesized from acetone as given below.
Explanation of Solution
The given acetone is treated with Grignard’s reagent. The result is addition product. This upon hydrolysis gives the corresponding isobutyl alcohol. Obtained isobutyl alcohol is treated with hydrogen bromide to get the corresponding halide, isobutyl bromide. The isobutyl bromide gives substituted tertiary amine upon treatment with ammonia. The reactions are given below.
The isobutyl amine, a tertiary amine can be prepared from acetone by the reaction sequences as shown below.
(j)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the compound isopentylamine from acetone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
When ketones are treated with Grignard reagents, the addition product, tertiary alcohol is formed. This alcohol can be reduced to corresponding alkane. Alkanes react with halogens to produce halides. This halide can be substituted with amine group to get the required compound.
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The compound isopentylamine can be synthesized from acetone as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The acetone gives an addition product with Grignard’s reagent. This product is hydrolyzed to get the isopentyl alcohol. The isopentyl alcohol, in presence of aluminium chloride gets reduced and then hydrogenated to get the parent alkane that is pentane. The pentane is treated with bromine, to produce the bromo pentane. This, when treated with ammonia, produces the required compound isopentyl amine. The corresponding reactions are shown below.
Reaction product is the required primary amine, isopentyl amine. To prepare the given compound acetone is subject to treatment with Grignard’s reagent and other reactants as shown.
(k)
Interpretation:
The synthesis for the compound,
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by another electrophile is known as electrophilic
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The synthesis of
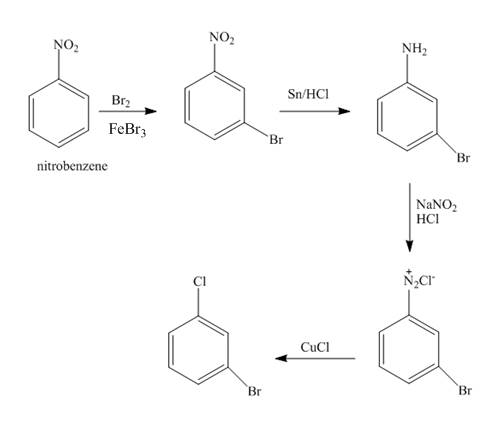
Explanation of Solution
The nitro group is meta directing group. The nitrobenzene undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction with
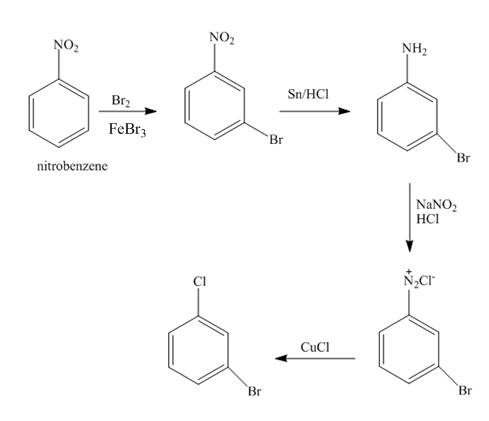
Figure 1
The synthesis of
(l)
Interpretation:
The synthesis for the compound
Concept introduction:
In presence of mixed acids, conc.
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The synthesis for the compound
Explanation of Solution
The nitro group of nitrobenzene get reduced to amino group with help of reagents

Figure 2
The synthesis for the compound
(m)
Interpretation:
A synthesis for the compound
Concept introduction:
The alcohol group of phenol is ring activating and para directing group. The oxygen shares its lone pair of electron with the ring. The increased electron density makes the ring prone to electrophilic substitution reactions. In presence of a base the phenols give ether with alkyl halides.
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The compound,
Explanation of Solution
The phenol is treated with a base. It gives sodium salt of phenoxide ion. This reacts with methyl bromide to produce methoxybenzene. This methoxybenzene is treated with potassium cyanide in presence of cuprous cyanide to give required
The compound,
(n)
Interpretation:
The synthesis for the given amine from given alcohol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
When alcohols undergo substitution nucleophilic reaction with
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The synthesis for the given amine from given alcohol is shown below.
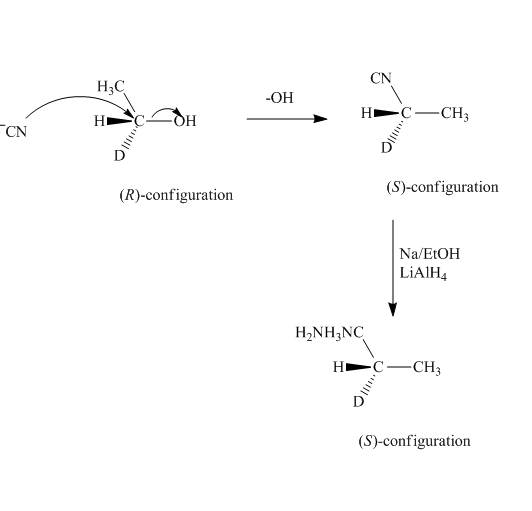
Explanation of Solution
First the alcohol is treated with

Figure 3
The synthesis for the given amine from given alcohol is shown in Figure 3.
(o)
Interpretation:
The synthesis for the given substituted pyrrole from levulinic acid is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The acids when react with amines they give corresponding amides. These amides can be reduced to get higher amines. The amines with ketone group in vicinity, undergo nucleophilic addition reaction to give cyclic compounds.
Answer to Problem 23.66AP
The synthesis for the given substituted pyrrole from levulinic acid is shown below.
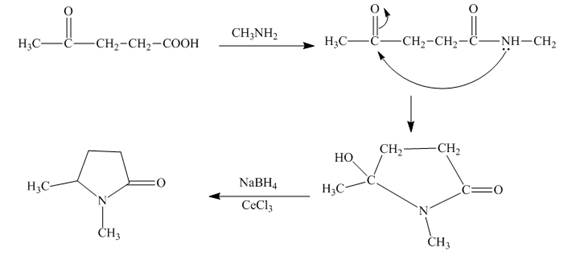
Explanation of Solution
The given keto acid is first treated with methyl amine. The corresponding amide is obtained. This amide is now undergoes cyclisation reaction to form the pyrrole ring. The alcoholic group can be reduced by the selective reduction with sodium borohydride and cerium chloride ( luche reduction ). The reactions are given below.

Figure 4
The substituted pyrrole can be prepared from levulinic acid as shown in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forwardΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forward
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





