
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The series of
Concept introduction:
舧 Formation of isomers is called isomerization. Monosaccharides undergo a series of keto-enol tautomerizations and enolizations and to produce different isomeric forms. In order to preserve the stereochemical nature of the compounds, the formation of such isomeric forms needs to be prevented.
舧 Stereochemistry: A carbon atom is attached to four distinct groups is said to be a stereogenic or chirality center of that molecule. A stereocenter is that point in a molecule where any two groups exchange their positions to form stereoisomers.
舧 The pair of diastereomers that shows different configuration at the chirality center are called epimers. The aldohexoses,
舧 A carbohydrate is a
舧
舧 Carbohydrates are oxidized by
舧 Aldaric acids are carbohydrates having two
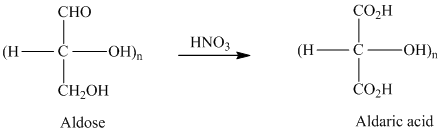
舧 Monosaccharides containing six carbon atoms and an
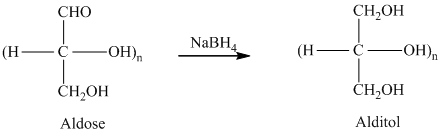
舧 Alditols are compounds produced from aldoses or ketoses on reduction with certain reagents such as sodium borohydride (
舧 Compounds formed by the reaction of reducing sugars with excess of phenyl hydrazine are called osazones. Osazones are products of oxidation and are produced by all reducing sugars.
舧 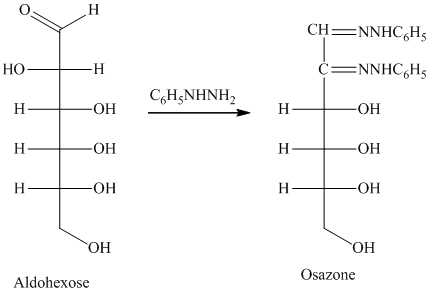
舧 Fischer projection is a way of representing the structural formulae of compounds through cross formulation of their open chain structures.
舧 Bromine water is an effective reagent that selectively oxidizes the
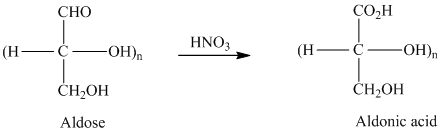
舧 While dissolved in aqueous bases such as pyridine, monosaccharides undergo complex isomerization as they form different enols and keto-enols. Aldonic acids form epimers (usually at the
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- Consider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forward
- What is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forward
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



