
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Distribution of d-electrons and the geometry of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
Complex compounds exist in following geometries - tetrahedral, square planar, octahedral etc.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of tetrahedral complex, the
In case of square planar complex, the 5 d-orbitals split into following pattern and it is given below with increasing order of energy.
(a)
Answer to Problem 22.60QP
The d-electrons are distributed in the complex ion
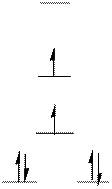
The complex has square planar geometry.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex ion

The distribution of d-electrons as shown above correlates to that of square planar geometry. Hence the complex ion
Splitting of d-orbitals determines the geometry of the complex.
(b)
Interpretation:
Distribution of d-electrons and the geometry of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
Complex compounds exist in following geometries - tetrahedral, square planar, octahedral etc.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of tetrahedral complex, the
In case of square planar complex, the 5 d-orbitals split into following pattern and it is given below with increasing order of energy.
(b)
Answer to Problem 22.60QP
The d-electrons are distributed in the complex ion
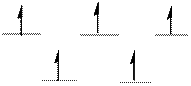
The complex has tetrahedral geometry.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex ion
Atomic number of Manganese is

The distribution of d-electrons as shown above correlates to that of tetrahedral geometry. Hence the complex ion
Splitting of d-orbitals determines the geometry of the complex.
(c)
Interpretation:
Distribution of d-electrons and the geometry of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
Complex compounds exist in following geometries - tetrahedral, square planar, octahedral etc.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of tetrahedral complex, the
In case of square planar complex, the 5 d-orbitals split into following pattern and it is given below with increasing order of energy.
(c)
Answer to Problem 22.60QP
The d-electrons are distributed in the complex ion
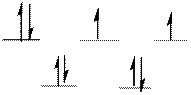
The complex has tetrahedral geometry.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex ion
Atomic number of Nickel is
The distribution of d-electrons as shown above correlates to that of tetrahedral geometry. Hence the complex ion
Splitting of d-orbitals determines the geometry of the complex.
(d)
Interpretation:
Distribution of d-electrons and the geometry of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
Complex compounds exist in following geometries - tetrahedral, square planar, octahedral etc.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of tetrahedral complex, the
In case of square planar complex, the 5 d-orbitals split into following pattern and it is given below with increasing order of energy.
(d)
Answer to Problem 22.60QP
The d-electrons are distributed in the complex ion

The complex has square planar geometry.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex ion
Atomic number of Gold is

The distribution of d-electrons as shown above correlates to that of square planar geometry. Hence the complex ion
Splitting of d-orbitals determines the geometry of the complex.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





