
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Using crystal field theory, the energy level diagram of d-orbitals of the complex ion
Concept Introduction:
There are five d-orbitals in a metal ion. They have similar energy levels that they are degenerated. Under the influence of ligands during complex formation, the degeneracy in d-orbitals is destroyed that they are split into two sets of orbitals - one set having lower energy and the another set is higher in energy. Crystal field splitting refers to the difference in energy levels between these two sets of d-orbitals.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of octahedral complex, the
(a)
Answer to Problem 22.57QP
The energy level diagram of d-orbitals of the complex ion

Two unpaired electrons are present in this complex ion.
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of

(b)
Interpretation:
Using crystal field theory, the energy level diagram of d-orbitals of the high-spin complex ion
Concept Introduction:
There are five d-orbitals in a metal ion. They have similar energy levels that they are degenerated. Under the influence of ligands during complex formation, the degeneracy in d-orbitals is destroyed that they are split into two sets of orbitals - one set having lower energy and the another set is higher in energy. Crystal field splitting refers to the difference in energy levels between these two sets of d-orbitals.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of octahedral complex, the
(b)
Answer to Problem 22.57QP
The energy level diagram of d-orbitals of the high-spin complex ion
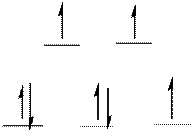
There are three unpaired electrons in the complex ion
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number of Cobalt is
The electronic configuration of

From the above arrangement we could say there are three unpaired electrons in the complex ion
(c)
Interpretation:
Using crystal field theory, the energy level diagram of d-orbitals of the low-spin complex ion
Concept Introduction:
There are five d-orbitals in a metal ion. They have similar energy levels that they are degenerated. Under the influence of ligands during complex formation, the degeneracy in d-orbitals is destroyed that they are split into two sets of orbitals - one set having lower energy and the another set is higher in energy. Crystal field splitting refers to the difference in energy levels between these two sets of d-orbitals.
When ligands approach the metal ion the degeneracy in d-orbitals of the metal ion is destroyed and they split into two different energy levels. In case of octahedral complex, the
(c)
Answer to Problem 22.57QP
The energy level diagram of d-orbitals of the low-spin complex ion
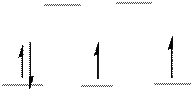
There are two unpaired electrons in the complex ion
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number of Manganese is
The electronic configuration of

From the above arrangement we could say there are two unpaired electrons in the complex ion
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
- Draw a tetramer of this alternating copolymer.arrow_forwardH I T H HH H -H C. H- Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H CIH H H H HHHH H H 0 ·H H– 冊 CH CHI HH C- H- H H- H H A. H H C H H- -H HH H B. H- -H D. H H H H • H -H E. -H H H HICH T HHH F. H-arrow_forwardPolylactic acid (shown below) is a biodegradable polymer used for food packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate pleasearrow_forwardPoly(ethylene adipate) is a biodegradable polyester (shown below). Identify the type of polymerization process used in the production of this polymer.arrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. draw two repeat units(dimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. assume there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the dimer. ignore inorganic byproducts pleasearrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardOne of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forward
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forwardProvide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





