
(a)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-3-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
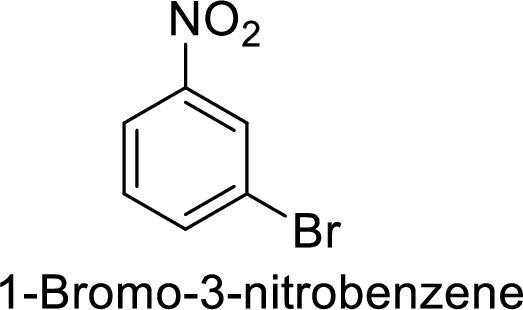
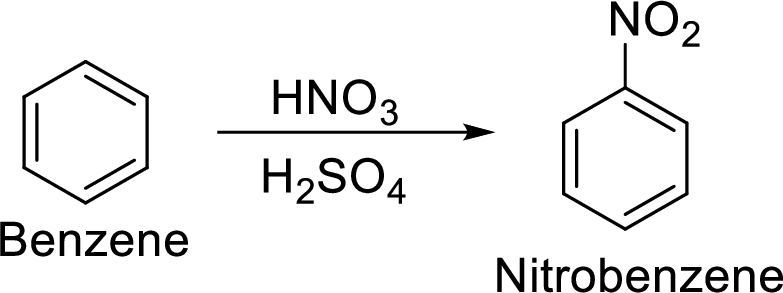
Step 1: Nitration of benzene ring by the reaction of benzene with nitrating mixture.
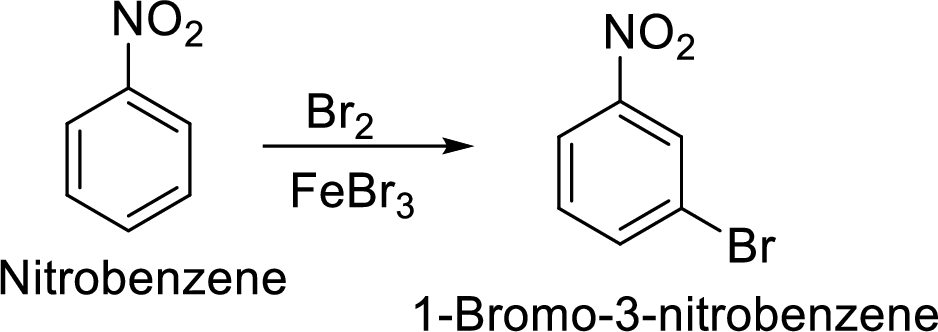
Step 2: Halogenation of nitrobenzene by the reaction of nitrobenzene with bromine in the presence of Lewis acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-4-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
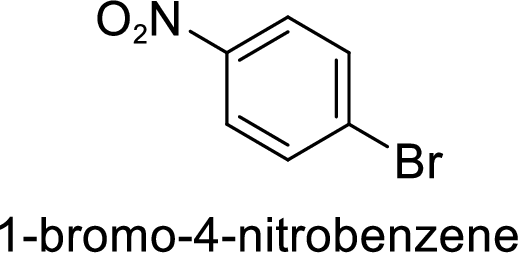
Step 1: Halogenation of benzene by the reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of Lewis acid.
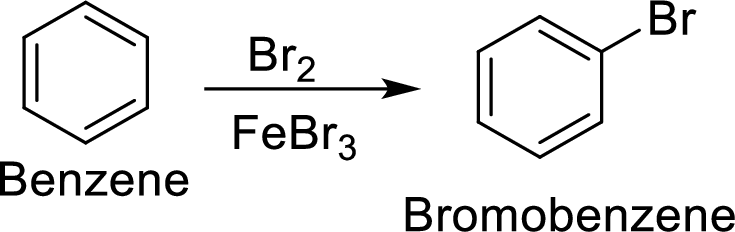
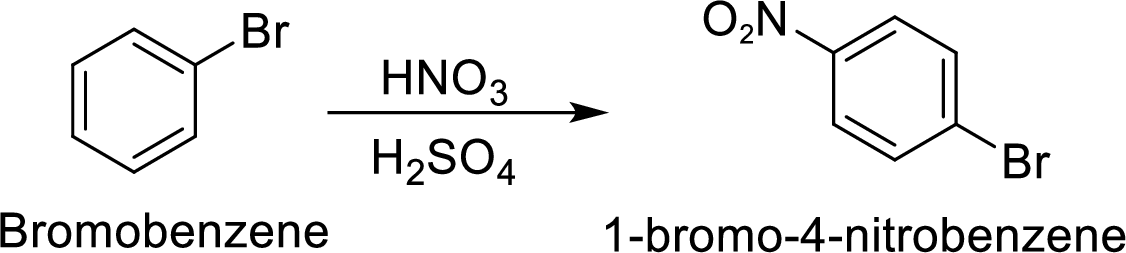
Step 2: Nitration of bromobenzene by the reaction of bromobenzene with nitrating mixture.
(c)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 2,4-6-trinitrotoluene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
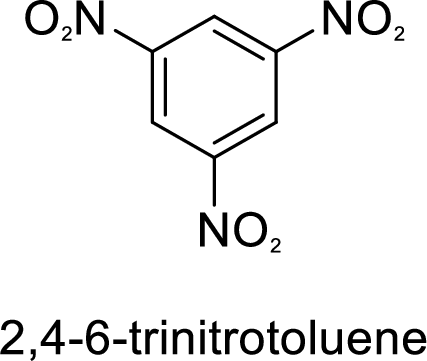
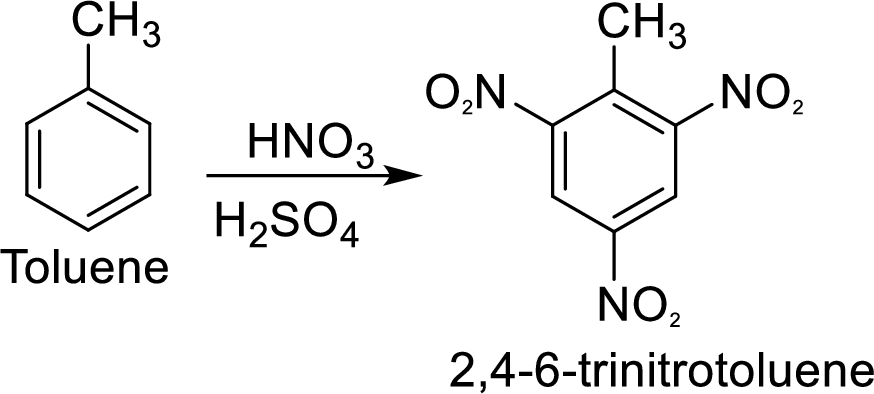
Methyl group in toluene is an activating and ortho-para directing group, so three times nitration of toluene gives the target compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the m-chlorobenzoic acid from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
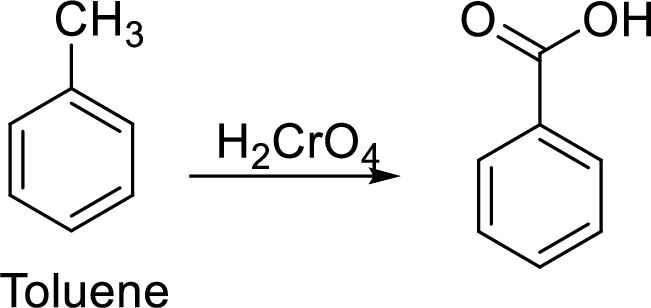
Step 1: Oxidation of toluene with chromic acid gives the benzoic acid.
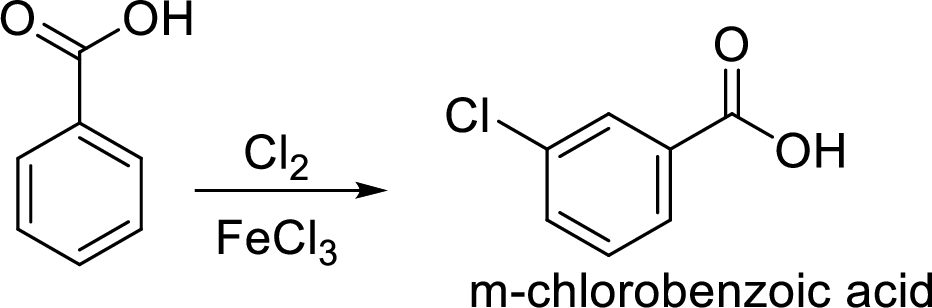
Step 2: Carboxyl group is a deactivating and meta directing group so the chlorination takes place at the meta position.
(e)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the p-chlorobenzoic acid from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
Step 1: Halogenation of toluene by the reaction of toluene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
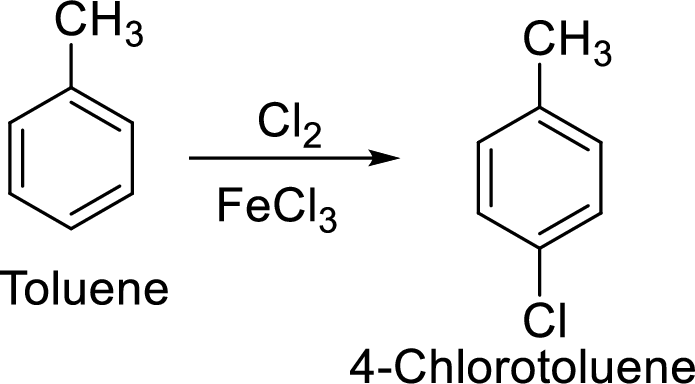
Step 2: Oxidation of 4-chlorotoluene by chromic acid gives the target compound.
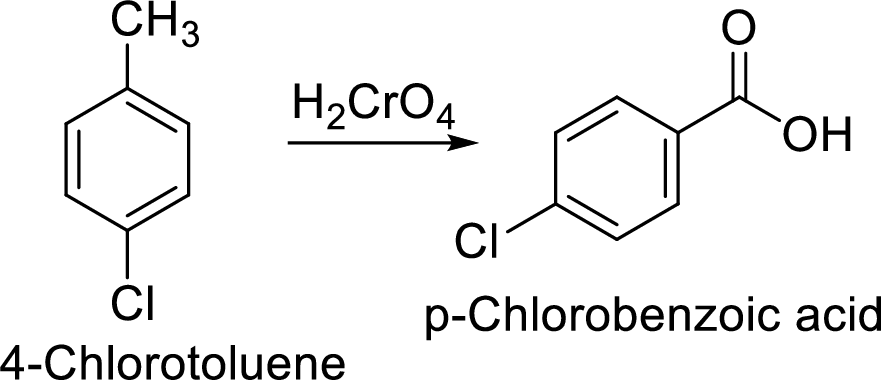
(f)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the p-dichlorobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
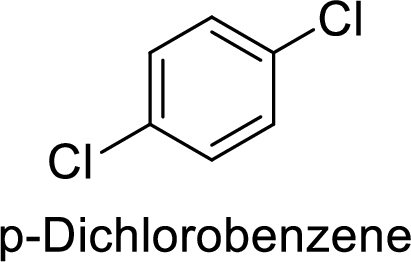
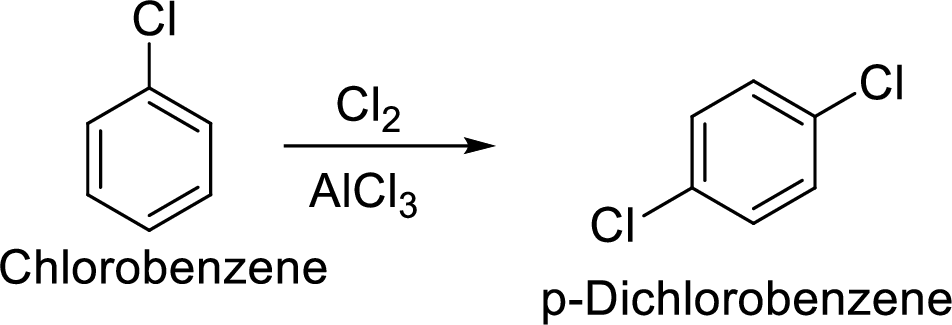
Step 1: Halogenation of benzene by the reaction of benzene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
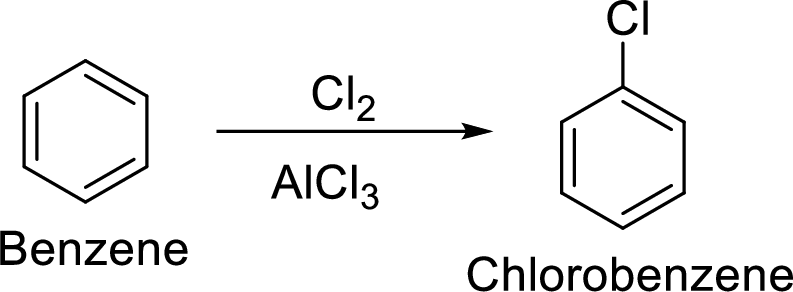
Step 2: Second halogenation of chlorobenzene by the reaction of chlorobenzene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
(g)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-4-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
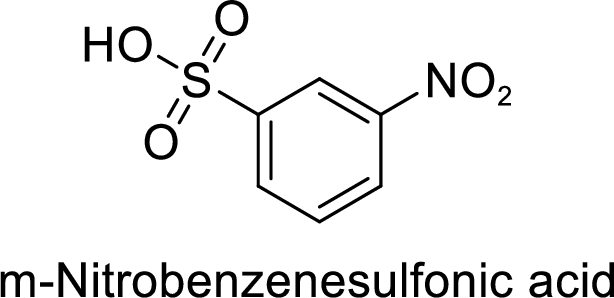
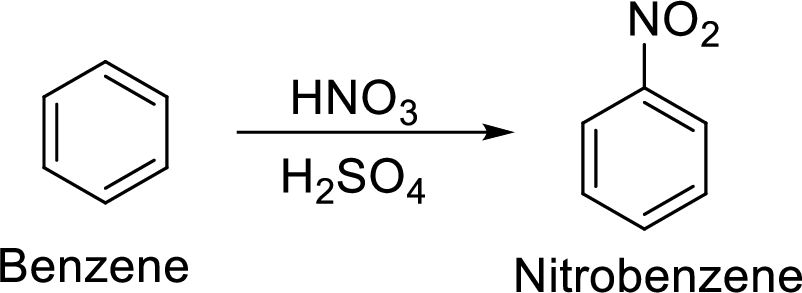
Step 1: Nitration of benzene by the reaction of benzene with nitrating mixture.
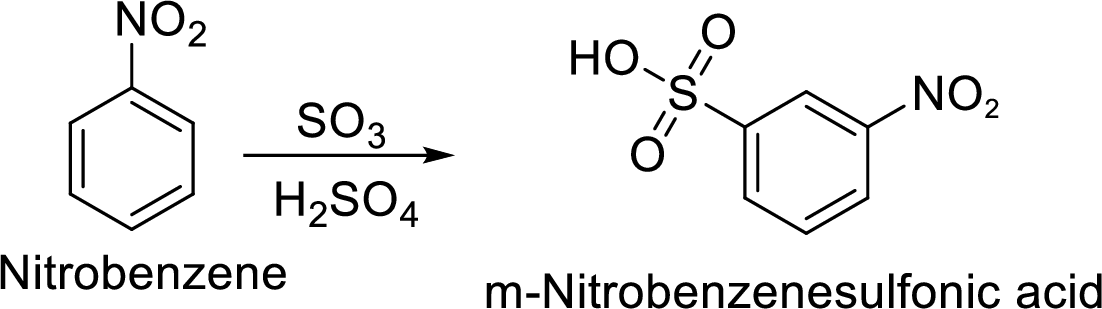
Step 2: Sulfonation of nitrobenzene by the reaction with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- How many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forward
- H H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forward
- choose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forward
- OH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning

