
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 70P
In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square. The charges are q1 = +Q, q2 = q3 = q, and q4 = −2.00Q. What is q/Q if the net electrostatic force or particle 1 is zero?
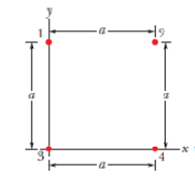
Figure 21-25
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
You are working with a team that is designing a new roller coaster-type amusement park ride for a major theme park. You are present for the testing of the ride, in which an empty 150 kg car is sent along the entire ride. Near the end of the ride, the car is at near rest at the top of a 100 m
tall track. It then enters a final section, rolling down an undulating hill to ground level. The total length of track for this final section from the top to the ground is 250 m. For the first 230 m, a constant friction force of 370 N acts from computer-controlled brakes. For the last 20 m, which is
horizontal at ground level, the computer increases the friction force to a value required for the speed to be reduced to zero just as the car arrives at the point on the track at which the passengers exit.
(a) Determine the required constant friction force (in N) for the last 20 m for the empty test car.
N
(b) Find the highest speed (in m/s) reached by the car during the final section of track length…
A player kicks a football at the start of the game. After a 4 second flight, the ball touches the ground 50 m from the kicking tee. Assume air resistance is negligible and the take-off and landing height are the same (i.e., time to peak = time to fall = ½ total flight time). (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:
Please answer.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 21 - Figure 21-11 shows 1 four situations in which five...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-12 shows three pairs of identical...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-13 shows four situations in which...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-14 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-15, a central particle of charge q is...Ch. 21 - A positively charged ball is brought close to an...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-16 shows three situations involving a...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-17 shows four arrangements of charged...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-18 shows four situations in which...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-19, a central particle of charge 2q is...
Ch. 21 - Figure 21-20 shows three identical conducting...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-21 shows four situations in which a...Ch. 21 - SSM ILW Of the charge Q initially on a tiny...Ch. 21 - Identical isolated conducting spheres 1 and 2 have...Ch. 21 - SSM What must be the distance between point charge...Ch. 21 - In the return stroke of a typical lightning bolt,...Ch. 21 - A particle of charge 3.00 106 C is 12.0 cm...Ch. 21 - ILW Two equally chained particles are held 3.2 ...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-23, three charged particles lie on an x...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-24, three identical conducting spheres...Ch. 21 - SSM WWW Two identical conducting spheres, fixed in...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square....Ch. 21 - ILW In Fig. 21-25, the particles have charges q1 =...Ch. 21 - Two particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge l.0 C and...Ch. 21 - Three particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1...Ch. 21 - GO The charges and coordinates of two charged...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-27a, particle l of charge q1 and...Ch. 21 - In Fig.21-28a, particles 1 and 2 have charge 20.0...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-29a, three positively charged particles...Ch. 21 - SSM WWW In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge q and...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-30a shows an arrangement of three...Ch. 21 - GO A nonconducting spherical shell, with an inner...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-31 shows an arrangement of four...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-32, particles 1 and 2 of charge q1 =...Ch. 21 - Two tiny, spherical water drops, with identical...Ch. 21 - ILW How many electrons would have to be removed...Ch. 21 - Prob. 26PCh. 21 - SSM The magnitude of the electrostatic force...Ch. 21 - A current of 0.300 A through your chest can send...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-33, particles 2 and 4, of charge e,...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-26, particles 1 and 2 are fixed in...Ch. 21 - ILW Earths atmosphere is constantly bombarded by...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-34a shows charged particles 1 and 2...Ch. 21 - Calculate the number of coulombs of positive...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-35 shows electrons 1 and 2 on an x...Ch. 21 - SSM In crystals of the salt cesium chloride,...Ch. 21 - Electrons and positrons are produced by the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 37PCh. 21 - GO Figure 21-37 shows four identical conducting...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-38, particle 1 of charge 4e is...Ch. 21 - In Fig, 21-23, particles 1 and 2 are fixed in...Ch. 21 - a What equal positive charges would have to be...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-39, two tiny conducting balls of...Ch. 21 - a Explain what happens to the balls of Problem 42...Ch. 21 - SSM How far apart must two protons be if the...Ch. 21 - How many megacoulombs of positive charge are in...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-40, four particles are fixed along an x...Ch. 21 - GO Point charges of 6.0 C and 4.0 C are placed on...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-41, three identical conducting spheres...Ch. 21 - A neutron consists of ore up quark of charge 2e/3...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-42 shows a long, nonconducting, massless...Ch. 21 - A charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 2.00...Ch. 21 - A particle of charge Q is Fixed at the origin of...Ch. 21 - What would be the magnitude of the electrostatic...Ch. 21 - A charge of 6.0 C is to be split into two parts...Ch. 21 - Of the charge Q on a tiny sphere, a fraction is...Ch. 21 - If a cat repeatedly rubs against your cotton...Ch. 21 - We know that the negative charge on the electron...Ch. 21 - In Fig, 21-26, particle 1 of charge 80.0C and...Ch. 21 - What is the total charge in coulombs of 75.0 kg of...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-43, six charged particles surround...Ch. 21 - Three charged particles form a triangle: particle...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-44, what are the a magnitude and b...Ch. 21 - Two point charges of 30 nC and 40 nC are held...Ch. 21 - Two small, positively charged spheres have a...Ch. 21 - The initial charges on the three identical metal...Ch. 21 - An electron is in a vacuum near Earths surface and...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge 5.00q and...Ch. 21 - Two engineering students, John with a mass of 90...Ch. 21 - In the radioactive decay of Eq. 21-13, a 238U...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square. The...Ch. 21 - In a spherical metal shell of radius R, an...Ch. 21 - An electron is projected with an initial speed vl...Ch. 21 - In an early model of the hydrogen atom the Bohr...Ch. 21 - A100 W lamp has a steady current of 0.83 A in its...Ch. 21 - The charges of an electron and a positron are e...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which detection method or methods meas...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Over time, as tributaries erode and lengthen their courses in their headwaters, what will happen to the upland ...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
1. Suppose a chloride ion and a sodium ion are separated by a center—center distance of 5 Å. Is
the interactio...
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
What is the anatomical position? Why is it important that you learn this position?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Why are the top predators in food chains most severely affected by pesticides such as DDT?
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Name the components (including muscles) of the thoracic cage. List the contents of the thorax.
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A shot putter releases a shot at 13 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees to the horizontal and from a height of 1.83 m above the ground. (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:arrow_forward"looks" like a particle.) ...32 GO In Fig. 22-55, positive charge q = 7.81 pC is spread uni- formly along a thin nonconducting rod of length L = 14.5 cm. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the electric field produced at point P, at distance R = 6.00 cm from the rod along its perpendicular bisector? R y Р + + + + + + + + +-× L Figure 22-55 Problem 32.arrow_forward1) A horizontal wire carrying current I in +x direction on the x-axis from x=0 to x=2 2) A vertical wire carrying current I upward at along the x=2 line from y=0 to y=8 3) A diagonal straight wire started at the origin and it ends at y=8 x=2 carrying a current in SE direction ( diagonally downward); y=4x In a regional magnetic field that is given in vector notation by B = ( y i - x j )/(x^2+y^2+25) As components Bx = (y+1)/x^2+y^2+25) By = (1- x )/(x^2+y^2+25) Find the integral expression for the net force for each branch carrying 5 ampere current.arrow_forward
- An electric power station that operates at 30 KV and uses a 15:1 set step-up ideal transformer is producing 400MW (Mega-Watt) of power that is to be sent to a big city with only 2.0% loss. What which is located 270 km away is the resistance of the Two wires that are being used? 52arrow_forwardSlink, from Toy Story, is a slinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed (as shown in figure A) with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again (as shown in figure C).arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forward
- Calculate the energy needed to melt 50 g of 0°C icearrow_forwardTwo very long line charges are set up along lines that areparallel to the z-axis, so they set up Electric fields strictly in the xy plane. One goes throughthe x-axis at x = −0.40 m and has charge a density λ1 = +12.0 μC/m, the other goesthrough the x-axis at x = +0.40 m has charge density λ2 = −8.0 μC/m.A. Find the Electric field at point A: (0.40, 0.80) (distances in meters). Give answersin unit vector notation and draw a graph of the x-y plane with the E-fields you justfound.B. Find a point on the x-axis at which the total E-field is 0.arrow_forwardIn order to increase the amount of exercise in her daily routine, Tara decides to walk up the four flights of stairs to her car instead of taking the elevator. Each of the steps she takes are 18.0 cm high, and there are 12 steps per flight. (a) If Tara has a mass of 77.0 kg, what is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the Tara-Earth system (in J) when she reaches her car? ] (b) If the human body burns 1.5 Calories (6.28 x 10³ J) for each ten steps climbed, how much energy (in J) has Tara burned during her climb? ] (c) How does the energy she burned compare to the change in the gravitational potential energy of the system? Eburned Δυarrow_forward
- A 4.40 kg steel ball is dropped onto a copper plate from a height of 10.0 m. If the ball leaves a dent 2.75 mm deep, what is the average force exerted by the plate on the ball during the impact? Narrow_forwardA block of mass m = 7.00 kg is released from rest from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure below. (Assume h₂ = 7.80 m.) a m ha 3.20 m 2.00 m i (a) Determine the block's speed at points ® and point B ©. m/s m/s point (b) Determine the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point J A to pointarrow_forwardA 1.10 x 10²-g particle is released from rest at point A on the inside of a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius R R B 2R/3 (a) Calculate its gravitational potential energy at A relative to B. ] (b) Calculate its kinetic energy at B. ] (c) Calculate its speed at B. m/s (d) Calculate its potential energy at C relative to B. J (e) Calculate its kinetic energy at C. ] = 26.5 cm (figure below).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY