
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 2Q
Figure 21-12 shows three pairs of identical spheres that are to be touched together and then separated. The initial charges on them are indicated. Rank the pairs according to (a) the magnitude of the charge transferred during touching and (b) the charge left on the positively charged sphere, greatest first.
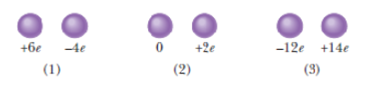
Figure 21-12 Question 2.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The cylindrical beam of a 12.7-mW laser is 0.920 cm in diameter. What is the rms value of the electric field?
V/m
Consider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...?
a. Both rods have less mass
b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass
c. both rods have more mass
d. the masses of both rods are unchanged
e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe mass
8) 9)
Chapter 21 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 21 - Figure 21-11 shows 1 four situations in which five...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-12 shows three pairs of identical...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-13 shows four situations in which...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-14 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-15, a central particle of charge q is...Ch. 21 - A positively charged ball is brought close to an...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-16 shows three situations involving a...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-17 shows four arrangements of charged...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-18 shows four situations in which...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-19, a central particle of charge 2q is...
Ch. 21 - Figure 21-20 shows three identical conducting...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-21 shows four situations in which a...Ch. 21 - SSM ILW Of the charge Q initially on a tiny...Ch. 21 - Identical isolated conducting spheres 1 and 2 have...Ch. 21 - SSM What must be the distance between point charge...Ch. 21 - In the return stroke of a typical lightning bolt,...Ch. 21 - A particle of charge 3.00 106 C is 12.0 cm...Ch. 21 - ILW Two equally chained particles are held 3.2 ...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-23, three charged particles lie on an x...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-24, three identical conducting spheres...Ch. 21 - SSM WWW Two identical conducting spheres, fixed in...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square....Ch. 21 - ILW In Fig. 21-25, the particles have charges q1 =...Ch. 21 - Two particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge l.0 C and...Ch. 21 - Three particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1...Ch. 21 - GO The charges and coordinates of two charged...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-27a, particle l of charge q1 and...Ch. 21 - In Fig.21-28a, particles 1 and 2 have charge 20.0...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-29a, three positively charged particles...Ch. 21 - SSM WWW In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge q and...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-30a shows an arrangement of three...Ch. 21 - GO A nonconducting spherical shell, with an inner...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-31 shows an arrangement of four...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-32, particles 1 and 2 of charge q1 =...Ch. 21 - Two tiny, spherical water drops, with identical...Ch. 21 - ILW How many electrons would have to be removed...Ch. 21 - Prob. 26PCh. 21 - SSM The magnitude of the electrostatic force...Ch. 21 - A current of 0.300 A through your chest can send...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-33, particles 2 and 4, of charge e,...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-26, particles 1 and 2 are fixed in...Ch. 21 - ILW Earths atmosphere is constantly bombarded by...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-34a shows charged particles 1 and 2...Ch. 21 - Calculate the number of coulombs of positive...Ch. 21 - GO Figure 21-35 shows electrons 1 and 2 on an x...Ch. 21 - SSM In crystals of the salt cesium chloride,...Ch. 21 - Electrons and positrons are produced by the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 37PCh. 21 - GO Figure 21-37 shows four identical conducting...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-38, particle 1 of charge 4e is...Ch. 21 - In Fig, 21-23, particles 1 and 2 are fixed in...Ch. 21 - a What equal positive charges would have to be...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-39, two tiny conducting balls of...Ch. 21 - a Explain what happens to the balls of Problem 42...Ch. 21 - SSM How far apart must two protons be if the...Ch. 21 - How many megacoulombs of positive charge are in...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-40, four particles are fixed along an x...Ch. 21 - GO Point charges of 6.0 C and 4.0 C are placed on...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-41, three identical conducting spheres...Ch. 21 - A neutron consists of ore up quark of charge 2e/3...Ch. 21 - Figure 21-42 shows a long, nonconducting, massless...Ch. 21 - A charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 2.00...Ch. 21 - A particle of charge Q is Fixed at the origin of...Ch. 21 - What would be the magnitude of the electrostatic...Ch. 21 - A charge of 6.0 C is to be split into two parts...Ch. 21 - Of the charge Q on a tiny sphere, a fraction is...Ch. 21 - If a cat repeatedly rubs against your cotton...Ch. 21 - We know that the negative charge on the electron...Ch. 21 - In Fig, 21-26, particle 1 of charge 80.0C and...Ch. 21 - What is the total charge in coulombs of 75.0 kg of...Ch. 21 - GO In Fig. 21-43, six charged particles surround...Ch. 21 - Three charged particles form a triangle: particle...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-44, what are the a magnitude and b...Ch. 21 - Two point charges of 30 nC and 40 nC are held...Ch. 21 - Two small, positively charged spheres have a...Ch. 21 - The initial charges on the three identical metal...Ch. 21 - An electron is in a vacuum near Earths surface and...Ch. 21 - SSM In Fig. 21-26, particle 1 of charge 5.00q and...Ch. 21 - Two engineering students, John with a mass of 90...Ch. 21 - In the radioactive decay of Eq. 21-13, a 238U...Ch. 21 - In Fig. 21-25, four particles form a square. The...Ch. 21 - In a spherical metal shell of radius R, an...Ch. 21 - An electron is projected with an initial speed vl...Ch. 21 - In an early model of the hydrogen atom the Bohr...Ch. 21 - A100 W lamp has a steady current of 0.83 A in its...Ch. 21 - The charges of an electron and a positron are e...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
49. The tabulated data show the concentration of AB versus time for this reaction:
Time(s) [AB] (M)
0 0.950
5...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Which type of cartilage is most plentiful in the adult body?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Flask A contains yeast cells in glucose-minimal salts broth incubated at 30C with aeration. Flask B contains ye...
Microbiology: An Introduction
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
A tank contains l0ft3 of air at 15psia,540R . A pipe of flowing air at l50psia,540R is connected to the tank an...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Lab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY