
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The type of isomerism that could be exhibited by the given formulas.
An example that illustrates the specific type of isomerism is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Organic compounds which have similar chemical formula but different structures, i.e., the atoms are in a different spatial arrangement, they are known as structural isomers. Cis and Trans isomers are also structural or geometrical isomers.
To determine: The type of isomerism that could be exhibited by
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The structural isomer of
The given formula,
The root word hexene indicates that six carbon atoms are present in the parent chain. Double bond is present between first and second carbon.
The structure of

Figure 1
The structural isomer of
The given formula,
The root word hexene indicates that six carbon atoms are present in the parent chain. The number
The structure of

Figure 2
The structural isomer of
The given formula,
The root word hexene indicates that six carbon atoms are present in the parent chain. The number
The structure of

Figure 3
The structural isomer of
The given formula,
The root word pentene indicates that five carbon atoms are present in the parent chain. The number
The structure of
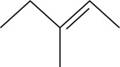
Figure 4
The structural isomer of
The given formula,
The root word butene indicates that six carbon atoms are present in the parent chain. The double bond is present between second and third carbon. Two methyl groups are attached at second and third carbon.
The structure of
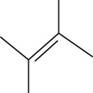
Figure 5
The geometric isomer of
The structure of cis-
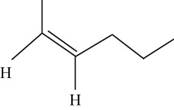
Figure 6
The structure of trans-
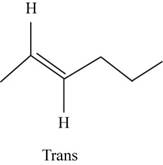
Figure 7
In the cis isomer, the two hydrogen of the double bonded carbons are adjacent to each other while in trans isomer, they are opposite to each other.
The geometric isomer of
The structure of cis-
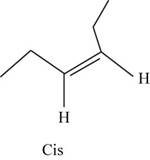
Figure 8
The structure of trans-
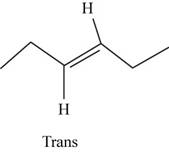
Figure 9
In the cis isomer, the two hydrogen of the double bonded carbons are adjacent to each other while in trans isomer, they are opposite to each other.
(b)
Interpretation: The type of isomerism that could be exhibited by the given formulas.
An example that illustrates the specific type of isomerism is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Organic compounds which have similar chemical formula but different structures, i.e., the atoms are in a different spatial arrangement, they are known as structural isomers. Cis and Trans isomers are also structural or geometrical isomers.
To determine: The type of isomerism that could be exhibited by
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The root word pentane indicates that five carbon atoms are present in the parent chain. Hydroxyl group is attached to first carbon.
The structure of pentan-1-ol is shown in Figure 10.
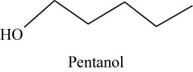
Figure 10
The structural isomer of
The root word butane indicates that four carbon atoms are present in the parent chain.
The structure of
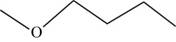
Figure 11
The structural isomer of
The root word propane indicates that three carbon atoms are present in the parent chain.
The structure of
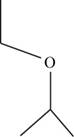
Figure 12
The structural isomer of
The root word butane indicates that four carbon atoms are present in the parent chain.
The structure of
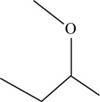
Figure 13
The structural isomer of
The root word pentane indicates that five carbon atoms are present in the parent chain. Hydroxyl group is attached to third carbon.
The structure of pentan-
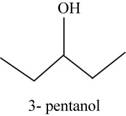
Figure 14
The structural isomer of
The root word pentane indicates that five carbon atoms are present in the parent chain. Hydroxyl group is attached to second carbon.
The structure of pentan-
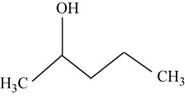
Figure 15
(c)
Interpretation: The type of isomerism that could be exhibited by the given formulas.
An example that illustrates the specific type of isomerism is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Organic compounds which have similar chemical formula but different structures, i.e., the atoms are in a different spatial arrangement, they are known as structural isomers. Cis and Trans isomers are also structural or geometrical isomers.
To determine: The type of isomerism that could be exhibited by
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The structural isomer of
In
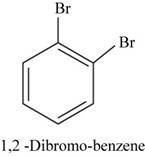
Figure 16
The structural isomer of
In
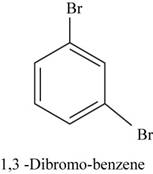
Figure 17
The structural isomer of
In
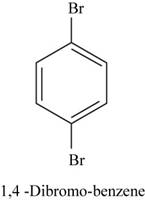
Figure 18
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: AN ATOMS FIRST APPROACH
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwardDraw the major organic product when each of the bellow reagents is added to 3,3-dimethylbutere. ✓ 3rd attempt Part 1 (0.3 point) H.C CH CH + 1. BHG THF 210 NaOH NJ 10000 Part 2 (0.3 point) HC- CH HC 2741 OH a Search 1. He|DA HO 2. NIBH さ 士 Ju See Periodic Table See Hint j = uz C H F F boxarrow_forwardSynthesis of 2-metilbenzimidazol from 1,2-diaminobenceno y propanona.arrow_forward
- Predict the product of the following reaction. 1st attempt HI 1 product 50300 Jul See Periodic Table See Hint P Br 石尚 Iarrow_forwardIndicate the substitutes in one place, if they are a diazonio room.arrow_forwardIndicate the product formed in each reaction. If the product exhibits tautomerism, draw the tautomeric structure. a) о + CH3-NH-NH2 CO2C2H5 b) + CoH5-NH-NH2 OC2H5arrow_forward
- Indicate the formula of the compound, that is the result of the N- alquilación (nucleofílic substitution), in which an additional lateral chain was formed (NH-CH2-COOMe). F3C. CF3 NH NH2 Br о OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forwardSynthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole from 1,2-diaminobenceno.arrow_forwardSynthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning


