
Concept explainers
For each amino acid: [1] draw the L enantiomer in a Fischer projection; [2] classify the amino acid as neutral, acidic, or basic; [3] give the three-letter symbol; [4] give the one-letter symbol.
- leucine
- tryptophan
- lysine
- aspartic acid
(a)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of leucine in Fisher projection needs to be drawn and should be identified as acidic, basic or neutral. The three letter and one symbol for it needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
Answer to Problem 25P
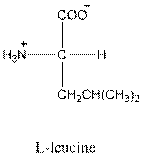
- L-isomer of leucine is as follows:
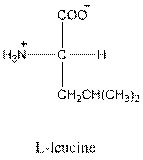
- Leucine is neutral.
- Three-letter symbol for leucine is Leu.
- One-letter symbol for leucine is L.
Explanation of Solution
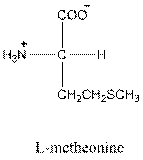
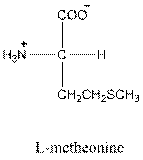
For leucine the R group is
The amino acid leucine has one positive charge on amino group
One letter symbol for leucine is L and three-letter symbol for leucine is Leu.
(b)
Interpretation:
To draw L-isomer of tryptophan (amino acid) in Fisher projection, to identify it is acidic, basic or neutral and to give three letter and one symbol for it
Concept Introduction : :
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
Answer to Problem 25P
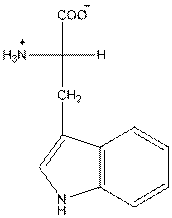
- L-isomer of tryptophan is as follows:
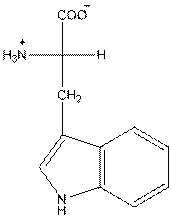
- Amino acid tryptophan is neutral.
Explanation of Solution
For tryptophan the R group is as follows:
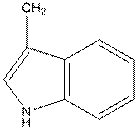
And in L-isomer the amino group
The amino acid tryptophan has one positive charge on amino group
One letter symbol for tryptophan is W and three-letter symbol for tryptophan is Trp.
(c)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of lysine in Fisher projection needs to be drawn, whether it is acidic, basic or neutral needs to be determined and the three-letter and one symbol for it needs to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
Answer to Problem 25P
- L-isomer of lysine is as follows:
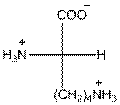
- The amino acid lysine is basic in nature.
- The three letter symbol for lysine is Lys.
- The one letter symbol for lysine is K.
Explanation of Solution
For lysine the R group is
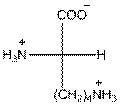
The amino acid lysine has one positive charge on amino group
The three letter symbol for lysine is Lys and one letter symbol for lysine is K.
(d)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of aspartic acid in Fisher projection needs to be drawn, whether it is acidic, basic or neutral needs to be determined and the three-letter and one symbol for it needs to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
Answer to Problem 25P
- L-isomer of aspartic acid is as follows:
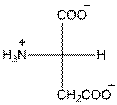
- The aspartic acid is acidic in nature.
- The three letter symbol for aspartic acid is Asp.
- The one letter symbol for aspartic acid is D.
Explanation of Solution
For aspartic acid the R group is
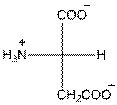
The aspartic acid has one positive charge on amino group
The three letter symbol for aspartic acid is Asp and the one letter symbol for aspartic acid is D.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- personality of each of them in terms of nucleophile vs. electrophile (some can be considered acids/bases but we are not looking at that here). Note you may have to use your growing intuition to figure out the personality of one of the molecules below but I believe in you! Rationalize it out based on what we have called strong versus weak electrophiles in past mechanisms. Consider using the memes below to help guide your understanding! A OH O B CH3 C Molecule A: [Select] Molecule B: [Select] Molecule C: [Select] Molecule D: [Select] > H D OHarrow_forward4) Which oxygen atom in the structure below is most basic / nucleophilic? Please explain by discussing the electron density around each oxygen atom. Show at least three resonance structures for the compound. оогоarrow_forwardCan you show me this problem. Turn them into lewis dot structures for me please and then answer the question because I cant seem to comprehend it/ The diagrams on the picture look too small I guess.arrow_forward
- The fire releases 2.80 x 107 Joules of heat energy for each liter of oil burned. The water starts out at 24.5 °C, raising the water's temperature up to 100 °C, and then raises the temperature of the resulting steam up to 325 °C. How many liters of water will be needed to absorb the heat from the fire in this way, for each 1.0 liter of crude oil burned? 4186 J/(kg°C) = heat of water 2020 J/(kg°C) = heat of steam 2,256,000 (i.e. 2.256 x 106) J/kg = latent heat of vaporization for water (at the boiling point of 100 °C).arrow_forward6 Which of the following are likely to be significant resonance structures of a resonance hybrid? Draw another resonance structure for each of the compounds you select as being a resonance form. (A Br: Br: A B C D Earrow_forwardWrite the systematic (IUPAC) name for the following organic molecules. Note for advanced students: you do not need to include any E or Z prefixes in your names. Br structure Br Br Oweuarrow_forward
- Conservation of mass was discussed in the background. Describe how conservation of mass (actual, not theoretical) could be checked in the experiment performed.arrow_forwardWhat impact would adding twice as much Na2CO3 than required for stoichiometric quantities have on the quantity of product produced? Initial results attachedarrow_forwardGiven that a theoretical yield for isolating Calcium Carbonate in this experiment would be 100%. From that information and based on the results you obtained in this experiment, describe your success in the recovery of calcium carbonate and suggest two possible sources of error that would have caused you to not obtain 100% yield. Results are attached form experimentarrow_forward
- 5) Calculate the flux of oxygen between the ocean and the atmosphere(2 pts), given that: (from Box 5.1, pg. 88 of your text): Temp = 18°C Salinity = 35 ppt Density = 1025 kg/m3 Oxygen concentration measured in bulk water = 263.84 mmol/m3 Wind speed = 7.4 m/s Oxygen is observed to be about 10% initially supersaturated What is flux if the temperature is 10°C ? (2 pts) (Hint: use the same density in your calculations). Why do your calculated values make sense (or not) based on what you know about the relationship between gas solubility and temperature (1 pt)?arrow_forwardFind a molecular formula for these unknownsarrow_forward(ME EX2) Prblms 8-11 Can you please explain problems 8 -11 to me in detail, step by step? Thank you so much! If needed color code them for me.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





