
Concept explainers
For each amino acid: [1] draw the L enantiomer in a Fischer projection; [2] classify the amino acid as neutral, acidic, or basic; [3) give the three-letter symbol; [4] give the one-letter symbol.
- arginine
- tyrosine
- glutamic acid
- valine
(a)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of arginine in Fisher projection needs to be drawn and identified as acidic, basic or neutral. The three letter and one symbol for it needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral center of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
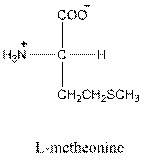
Answer to Problem 26P
- L isomer of arginine is as follows:
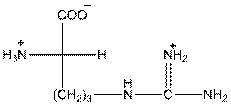
- In arginine, an additional basic nitrogen present. So, it is basic in nature.
- Three-letter symbol for arginine is 'Arg'.
- One letter symbol is 'R'.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids that have the
To draw the Fisher projection of arginine, place the
at the bottom and to draw L isomer draw
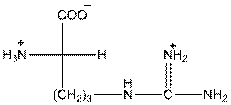
Here, R group is as follows:
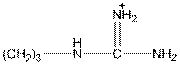
In arginine, an additional basic nitrogen present. So, it is basic in nature.
Three-letter symbol for arginine is Arg and one letter symbol is R.
(b)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of tyrosine in Fisher projection needs to be drawn and identified as acidic, basic or neutral. The three-letter and one symbol for it needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral centre of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
Answer to Problem 26P
- L-isomer of tyrosine is as follows:
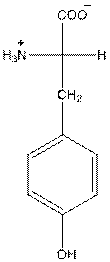
- Tyrosine is neutral in nature.
- Three-letter symbol for tyrosine is 'Tyr'.
- One letter symbol for tyrosine is 'Y'.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids that have the
To draw the Fisher projection of tyrosine by placing the
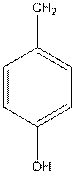
at the bottom and to draw L isomer draw
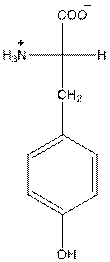
The overall charge of tyrosine is zero as there is one positive and negative charge. Hence, tyrosine is neutral in nature.
Three-letter symbol for tyrosine is 'Tyr' and one letter symbol is 'Y'.
(c)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of glutamic acid in Fisher projection needs to be drawn and identified as acidic, basic or neutral. The three-letter and one symbol for it needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral centre of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
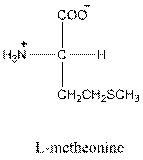
Answer to Problem 26P
- L-isomer of glutamic acid is as follows:
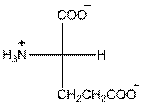
- Glutamic acid is acidic in nature.
- Three-letter symbol for glutamic acid is 'Glu'.
- One letter symbol for glutamic acid is 'E'.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids that have the
Draw the Fisher projection of glutamic acid by placing the
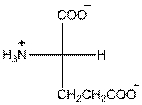
In glutamic acid, one additional acidic carboxyl group present. So, glutamic acid is acidic in nature.
Three-letter symbol for glutamic acid is 'Glu' and one letter symbol for glutamic acid is 'E'.
(d)
Interpretation:
The L-isomer of valine in Fisher projection needs to be drawn and identified as acidic, basic or neutral. The three-letter and one symbol for it needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Like monosaccharides, the prefixes D and L are used to designate the arrangement of groups to the chiral centre of amino acid, when drawn with a vertical carbon chain having
Amino acids that have the
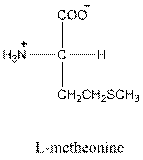
Answer to Problem 26P
- L-isomer of valine is as follows:
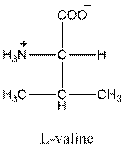
- Valine is neutral in nature.
- Three-letter symbol for valine is 'Val'.
- One letter symbol for valine is 'V'.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids that have the
Draw the Fisher projection of valine by placing the
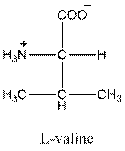
The net charge in valine is zero as there is one positive charge and negative charge in the compound. So, valine is neutral.
Three-letter symbol for valine is 'Val' and one letter symbol for valine is 'V'.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





