
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Alkene among the given hydrocarbons is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the binary compounds that consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms in its structure.
Answer to Problem 21.4TC
Among the given hydrocarbons
Explanation of Solution
According to the general formula of alkenes, for 8 carbon atoms, there must be 16 hydrogen atoms. Hydrocarbon,
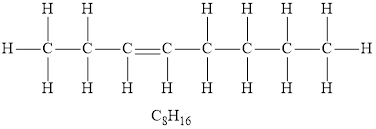
According to the general formula of alkenes, for 4 carbon atoms there must be 8 hydrogen atoms, for 7 carbon atoms there must be 14 hydrogen atoms, for 2 carbon atoms, there must be 4 hydrogen atoms. Hydrocarbons
Among the given hydrocarbons
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula of trans-difluoroethene
Concept introduction:
Isomers are the compounds which have the same molecular formula but a different structural arrangement of atoms. Alkenes have a double bond between carbon atoms. Due to the presence of a double bond, the rotation about adjacent carbon-carbon atoms is highly restricted. Hence, alkenes can exist in two forms which have the same molecular formula but a different strucutral arrangement of atoms around the double bond. This isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism which is known as geometric isomerism or cis-trans isomerism. In alkenes, when the two similar groups are present on the same side of the double bond is known as cis-isomer and when the two same groups are on the opposite side of the double bond then is known trans-isomer.
In the IUPAC name of an alkene, the Greek prefix represents the number of the substituent, the term before the Greek prefix represents the isomer of the alkene. The suffix for alkene is ‘ene’.
Answer to Problem 21.4TC
The structural formula of trans-difluoroethene
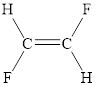
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of trans-difluoroethene
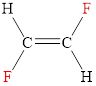
The structural formula of trans-difluoroethene

(c)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the binary compounds that consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms in its structure. Alkynes are the hydrocarbons that are unsaturated and consist of at least one carbon-carbon triple bond in its structure. The general representation of alkynes is
Answer to Problem 21.4TC
Among the given hydrocarbons
Explanation of Solution
According to the alkynes general formula, for 4 carbon atoms there must be 6 hydrogen atoms and for 7 carbon atoms, there must be 12 hydrogen atoms. Hydrocarbons
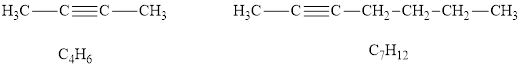
According to the alkynes general formula, for 8 carbon atoms there must be 14 hydrogen atoms and for 2 carbon atoms, there must be 4 hydrogen atoms.
Among the given hydrocarbons
(d)
Interpretation:
Straight chain isomers of pentyne and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
Isomers are the compounds which have the same molecular formula but different structural formula. Alkynes are the hydrocarbons that are unsaturated and consist of at least one carbon-carbon triple bond in its structure. The general representation of alkynes is
Answer to Problem 21.4TC
There are two straight chain isomers of pentyne:
![]()
Explanation of Solution
There are two straight chain isomers of pentyne:
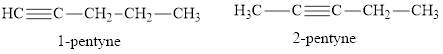
There are two straight chain isomers of pentyne:
![]()
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Bundle: Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach, 6th + LMS Integrated for OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Provide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. C6H5 CH3arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene and I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene, indicate the compound that I should add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Ο HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Select to Draw I Submitarrow_forwardFeedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forward
- If I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when chlorobenzene acid reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by reacting benzenesulfonic acid with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting ethylbenzene with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when tert-butylbenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





