
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the following organic compound is to be determined.
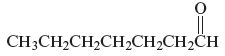
Concept Introduction :
Carbonyl compounds can be defined as the organic compounds in which carbon − oxygen double bond is present and this bond is also called a carbonyl bond. The three major carbonyl compounds are
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the following organic compound is to be determined.
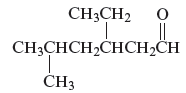
Concept Introduction :
Carbonyl compounds can be defined as the organic compounds in which carbon − oxygen double bond is present and this bond is also called a carbonyl group. The three major carbonyl compounds are aldehydes, ketenes and carboxylic acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the following organic compound is to be determined.
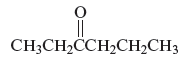
Concept Introduction :
Carbonyl compounds can be defined as the organic compounds in which carbon − oxygen double bond is present and this bond is also called a carbonyl group. The three major carbonyl compounds are aldehydes, ketenes and carboxylic acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
The name of the following organic compound is to be determined.
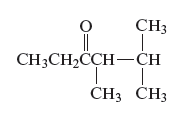
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl compounds can be defined as the organic compounds in which carbon − oxygen double bond is present and this bond is also called a carbonyl group. The three major carbonyl compounds are aldehydes, ketenes and carboxylic acid.
(e)
Interpretation:
The name of the following organic compound is to be determined.
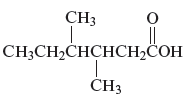
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl compounds can be defined as the organic compounds in which carbon − oxygen double bond is present and this bond is also called a carbonyl group. The three major carbonyl compounds are aldehydes, ketenes and carboxylic acid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Please handwriting for questions 1 and 3arrow_forwardIs (CH3)3NHBr an acidic or basic salt? What happens when dissolved in aqueous solution? Doesn't it lose a Br-? Does it interact with the water? Please advise.arrow_forward© Macmilla Finish resonance structure 3 Select Draw Templates More C H N 0 H H S Erase Which structure is the most stable (lowest energy) resonance contributor? The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and sulfur. All structures are equal in stability. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on sulfur and carbon. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and carbon. Q2Qarrow_forward
- Three pure compounds are formed when 1.00 g samples of element x combine with, respectively, 0.472 g, 0.630 g, and 0.789 g of element z. The first compound has the formula x2Z3. find the empricial formula of the other two compoundsarrow_forwardDraw the product and the mechanism A. excess H*; 人 OH H*; B. C. D. excess OH ✓ OH H*; H₂O 1. LDA 2. H*arrow_forwardIn reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- If the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forwardGiven the first-order reaction: aA → products. State its kinetic equation.arrow_forwardDetermine the symmetry of the combination of atomic orbitals for bf 4-arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





