
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The optical activity of the given structure of tartaric acid should be determined.
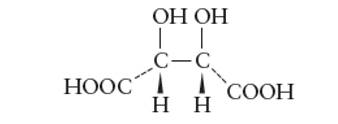
Concept Introduction: The organic compounds with same molecular formula and different structural formula are known as isomers of each other.
Stereoisomers are type of isomers with same molecular formula and structural formula but they have different optical activity towards plane polarized light.
The optical isomers have certain essential conditions such as they must have asymmetric C atoms and should not have plane of symmetry in the molecule.
(b)
Interpretation: The optical active forms of tartaric acid should be determined.
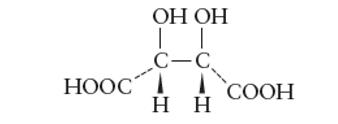
Concept Introduction: The organic compounds with same molecular formula and different structural formula are called as isomers of each other.
Stereoisomers are type of isomers with same molecular formula and structural formula but they have different optical activity towards plane polarized light.
The optical isomers have certain essential conditions such as they must have asymmetric C atoms and should not have plane of symmetry in the molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- 2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward
- 3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). H-Br CH2Cl2arrow_forwardWrite the aldol condensation mechanism and product for benzaldehyde + cyclohexanone in a base. Then trans-cinnamaldehyde + acetone in base. Then, trans-cinnamaldehyde + cyclohexanone in a base.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





