
EBK LOOSE-LEAF VERSION OF UNIVERSE
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781319227975
Author: KAUFMANN
Publisher: VST
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 20, Problem 74Q
To determine
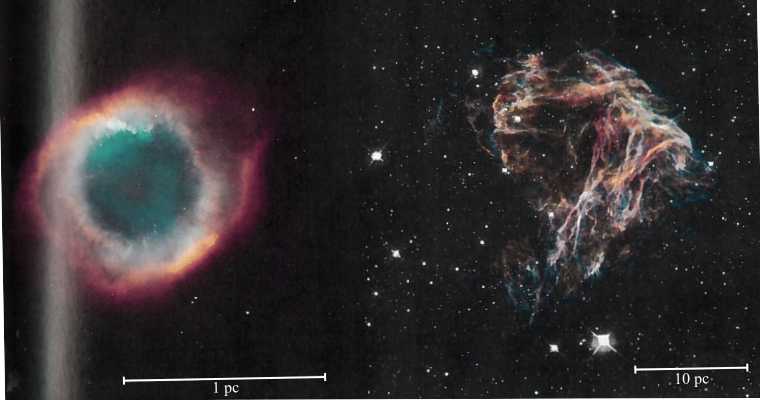
The object among the planetary nebula and the supernova remnants as shown below. The body in which the gases would expand more rapidly, away from the central star. Both bodies comprise of glowing gases and are about the same age. (Provide the reason for the answer)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Suppose there are two transformers between your house and the high-voltage transmission line
that distributes the power. In addition, assume your house is the only one using electric power.
At a substation the primary of a step-down transformer (turns ratio = 1:23) receives the voltage
from the high-voltage transmission line. Because of your usage, a current of 51.1 mA exists in
the primary of the transformer. The secondary is connected to the primary of another step-
down transformer (turns ratio = 1:36) somewhere near your house, perhaps up on a telephone
pole. The secondary of this transformer delivers a 240-V emf to your house. How much power is
your house using? Remember that the current and voltage given in this problem are rms values.
In some places, insect "zappers," with their blue lights, are a familiar sight on a summer's night. These devices use a
high voltage to electrocute insects. One such device uses an ac voltage of 3970 V, which is obtained from a
standard 120-V outlet by means of a transformer. If the primary coil has 27 turns, how many turns are in the
secondary coil?
hel
lp?
Hi,
Does Quantum physics theory means all branches for example quantum relativity, Quantum mechanics, Quantum field theory, and string theory? Can you explain each one of them?
Best
Chapter 20 Solutions
EBK LOOSE-LEAF VERSION OF UNIVERSE
Ch. 20 - Prob. 1CCCh. 20 - Prob. 2CCCh. 20 - Prob. 3CCCh. 20 - Prob. 4CCCh. 20 - Prob. 5CCCh. 20 - Prob. 6CCCh. 20 - Prob. 7CCCh. 20 - Prob. 8CCCh. 20 - Prob. 9CCCh. 20 - Prob. 10CC
Ch. 20 - Prob. 11CCCh. 20 - Prob. 12CCCh. 20 - Prob. 13CCCh. 20 - Prob. 14CCCh. 20 - Prob. 15CCCh. 20 - Prob. 16CCCh. 20 - Prob. 17CCCh. 20 - Prob. 18CCCh. 20 - Prob. 1QCh. 20 - Prob. 2QCh. 20 - Prob. 3QCh. 20 - Prob. 4QCh. 20 - Prob. 5QCh. 20 - Prob. 6QCh. 20 - Prob. 7QCh. 20 - Prob. 8QCh. 20 - Prob. 9QCh. 20 - Prob. 10QCh. 20 - Prob. 11QCh. 20 - Prob. 12QCh. 20 - Prob. 13QCh. 20 - Prob. 14QCh. 20 - Prob. 15QCh. 20 - Prob. 16QCh. 20 - Prob. 17QCh. 20 - Prob. 18QCh. 20 - Prob. 19QCh. 20 - Prob. 20QCh. 20 - Prob. 21QCh. 20 - Prob. 22QCh. 20 - Prob. 23QCh. 20 - Prob. 24QCh. 20 - Prob. 25QCh. 20 - Prob. 26QCh. 20 - Prob. 27QCh. 20 - Prob. 28QCh. 20 - Prob. 29QCh. 20 - Prob. 30QCh. 20 - Prob. 31QCh. 20 - Prob. 32QCh. 20 - Prob. 33QCh. 20 - Prob. 34QCh. 20 - Prob. 35QCh. 20 - Prob. 36QCh. 20 - Prob. 37QCh. 20 - Prob. 38QCh. 20 - Prob. 39QCh. 20 - Prob. 40QCh. 20 - Prob. 41QCh. 20 - Prob. 42QCh. 20 - Prob. 43QCh. 20 - Prob. 44QCh. 20 - Prob. 45QCh. 20 - Prob. 46QCh. 20 - Prob. 47QCh. 20 - Prob. 48QCh. 20 - Prob. 49QCh. 20 - Prob. 50QCh. 20 - Prob. 51QCh. 20 - Prob. 52QCh. 20 - Prob. 53QCh. 20 - Prob. 54QCh. 20 - Prob. 55QCh. 20 - Prob. 56QCh. 20 - Prob. 57QCh. 20 - Prob. 58QCh. 20 - Prob. 59QCh. 20 - Prob. 60QCh. 20 - Prob. 61QCh. 20 - Prob. 62QCh. 20 - Prob. 63QCh. 20 - Prob. 64QCh. 20 - Prob. 65QCh. 20 - Prob. 66QCh. 20 - Prob. 67QCh. 20 - Prob. 68QCh. 20 - Prob. 69QCh. 20 - Prob. 70QCh. 20 - Prob. 71QCh. 20 - Prob. 72QCh. 20 - Prob. 73QCh. 20 - Prob. 74QCh. 20 - Prob. 75Q
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Dear Scientist in physics , How are doing, my name is Yahya from Saudi Arabia and currently in my first semester to pursue Master's degree in physics. I have been watching all interviews of some scientists in physics on YouTube Channel and somthing has got my mind. I studied my bachelor 's degree in biology and I have been contacting Professor's Bruce Lipton many times and he explained epigenatic well. He was talking about physics many times. He said if you want to understand who we are and how we think, you need to understand Physics well. So I have decided to study physics. I have some questions : Why is the community of physics are divided? What is the difference between Quantum physics, quantum field theory, Quantim theory, and classical physics? What is quantum consciousness theory as well. What do they mean by wave function collapse? Why professor Roger's always has another opinions in quantum consciousness theory?? Best Regards, Yahyaarrow_forwardGiven water's mass of 18g/mole and the value of the fundamental charge (charge magnitude of the electron and proton), use the largest charge density from the article to determine what fraction of water molecules became ionized (charged) due to triboelectric effects when it flows through the material that causes the largest charge transfer. Give your answer in e/molecule, or electrons transferred per molecule of water. For instance, a value of 0.2 means only one in five molecules of water loses an electron, or that 0.2=20% of water molecules become chargedarrow_forwardno AI, pleasearrow_forward
- Sketch the resulting complex wave form, and then say whether it is a periodic or aperiodic wave.arrow_forwardDuring a concentric loading of the quadriceps muscle in the upper leg, an athlete extends his lower leg from a vertical position (see figure (a)) to a fully extended horizontal position (see figure (b)) at a constant angular speed of 45.0° per second. Two of the four quadriceps muscles, the vastis intermedius and the rectus femoris, terminate at the patellar tendon which is attached to the top of the tibia in the lower leg. The distance from the point of attachment of the patellar tendon to the rotation axis of the tibia relative to the femur is 4.10 cm in this athlete. a b (a) The two quadriceps muscles can exert a maximum force of 225 N through the patellar tendon. This force is applied at an angle of 25.0° to the section of the tibia between the attachment point and the rotation axis. What is the torque (in N⚫ m) exerted by the muscle on the lower leg during this motion? (Enter the magnitude.) N⚫ m (b) What is the power (in W) generated by the athlete during the motion? W (c)…arrow_forward= A hanging weight, with a mass of m₁ = 0.365 kg, is attached by a rope to a block with mass m₂ 0.835 kg as shown in the figure below. The rope goes over a pulley with a mass of M = 0.350 kg. The pulley can be modeled as a hollow cylinder with an inner radius of R₁ = 0.0200 m, and an outer radius of R2 = 0.0300 m; the mass of the spokes is negligible. As the weight falls, the block slides on the table, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table is μk = 0.250. At the instant shown, the block is moving with a velocity of v; = 0.820 m/s toward the pulley. Assume that the pulley is free to spin without friction, that the rope does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley, and that the mass of the rope is negligible. mq R₂ R₁ mi (a) Using energy methods, find the speed of the block (in m/s) after it has moved a distance of 0.700 m away from the initial position shown. m/s (b) What is the angular speed of the pulley (in rad/s) after the block has moved this…arrow_forward
- Two astronauts, each having a mass of 95.5 kg, are connected by a 10.0-m rope of negligible mass. They are isolated in space, moving in circles around the point halfway between them at a speed of 4.60 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate each of the following. CG × d (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system kg m2/s (b) the rotational energy of the system KJ By pulling on the rope, the astronauts shorten the distance between them to 5.00 m. (c) What is the new angular momentum of the system? kg m2/s (d) What are their new speeds? m/s (e) What is the new rotational energy of the system? KJ (f) How much work is done by the astronauts in shortening the rope? KJarrow_forwardA uniform horizontal disk of radius 5.50 m turns without friction at w = 2.55 rev/s on a vertical axis through its center, as in the figure below. A feedback mechanism senses the angular speed of the disk, and a drive motor at A ensures that the angular speed remain constant while a m = 1.20 kg block on top of the disk slides outward in a radial slot. The block starts at the center of the disk at time t = 0 and moves outward with constant speed v = 1.25 cm/s relative to the disk until it reaches the edge at t = 360 s. The sliding block experiences no friction. Its motion is constrained to have constant radial speed by a brake at B, producing tension in a light string tied to the block. (a) Find the torque as a function of time that the drive motor must provide while the block is sliding. Hint: The torque is given by t = 2mrvw. t N.m (b) Find the value of this torque at t = 360 s, just before the sliding block finishes its motion. N.m (c) Find the power which the drive motor must…arrow_forward(a) A planet is in an elliptical orbit around a distant star. At its closest approach, the planet is 0.670 AU from the star and has a speed of 54.0 km/s. When the planet is at its farthest distance from the star of 36.0 AU, what is its speed (in km/s)? (1 AU is the average distance from the Earth to the Sun and is equal to 1.496 × 1011 m. You may assume that other planets and smaller objects in the star system exert negligible forces on the planet.) km/s (b) What If? A comet is in a highly elliptical orbit around the same star. The comet's greatest distance from the star is 25,700 times larger than its closest distance to the star. The comet's speed at its greatest distance is 2.40 x 10-2 km/s. What is the speed (in km/s) of the comet at its closest approach? km/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)
Physics
ISBN:9781337399920
Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)
Physics
ISBN:9781337399944
Author:Michael A. Seeds
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9781938168284
Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:OpenStax

Stars and Galaxies
Physics
ISBN:9781305120785
Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:Cengage Learning