
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula and name of the organic product is to be determined as well as the type of the expected product is to be indicated.
Concept Introduction :
The structural formula of an organic compound is representing the chemical bond location between the atoms of the molecule. It is also consist of the atom’s symbol which is connected by the
(a)
Answer to Problem 67A
The structure is
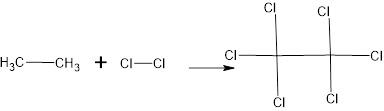
The major product is
Explanation of Solution
The complete reaction is,
Structural formula:
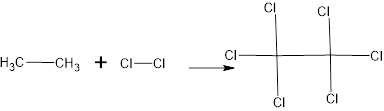
The name of the product is
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula and name of the organic product is to be determined as well as the type of the expected product is to be indicated.
Concept Introduction :
The structural formula of an organic compound is representing the chemical bond location between the atoms of the molecule. It is also consist of the atom’s symbol which is connected by the chemical bonds.
(b)
Answer to Problem 67A
The structure is,
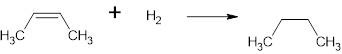
And the product name is butane
Explanation of Solution
The complete reaction is,
Structural formula:
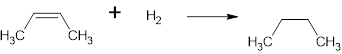
The name of the product is Butane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula and name of the organic product is to be determined as well as the type of the expected product is to be indicated.
Concept Introduction :
The structural formula of an organic compound is representing the chemical bond location between the atoms of the molecule. It is also consist of the atom’s symbol which is connected by the chemical bonds.
(c)
Answer to Problem 67A
The structure is,
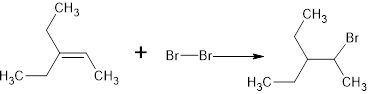
And the product is
Explanation of Solution
The complete reaction is,
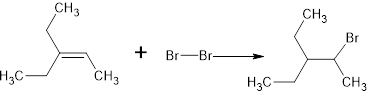
The name of the product is
Chapter 20 Solutions
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
- Pls help.arrow_forward13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward
- 11) The Ksp expression for copper (II) sulfate is: a. [Cu2+][SO4²¯] b. [Cu²+]² [SO4²]² c. [Cu²+]²[SO4²] d. [CuSO4] 12) Which of the following is true about a chemical system in equilibrium? a. All chemical reactions have stopped b. The concentration of reactants is equal to the concertation of products c. The forward and reverse reaction rates become equal d. The system will remain at equilibrium regardless of any external factorsarrow_forward21) Explain the difference between the rate of a reaction and the extent of a reaction. Why are both of these concepts important, if you are a chemical engineer that is trying to develop a process to produce a large volume of a specific type of chemical compound?arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





