
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the given alkene has to be described.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes can also be two types-
- Unbranched alkenes
- Branched alkenes
(a)
Answer to Problem 30A
The name of the above compound is 2-pentene.
Explanation of Solution
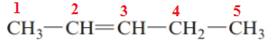
The principle chain contains five carbon atoms and one double bond between C2 and C3. So, the name of the above compound is 2-pentene.
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the given alkene has to be described.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are acyclic or cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) and the general molecular formula CnH2n (where n = number of carbon atoms). Simplest alkene among all is ethylene C2H4 which contains one carbon-carbon double bond.
Alkenes can also be two types-
- Unbranched alkenes
- Branched alkenes
(b)
Answer to Problem 30A
The name of the above compound is 2-pentene.
Explanation of Solution
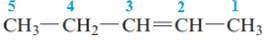
The principle chain contains five carbon atoms and one double bond between C2 and C3. So, the name of the above compound is 2-pentene.
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the given alkene has to be described.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are acyclic or cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) and the general molecular formula CnH2n (where n = number of carbon atoms). Simplest alkene among all is ethylene C2H4 which contains one carbon-carbon double bond.
Alkenes can also be two types-
- Unbranched alkenes
- Branched alkenes
(c)
Answer to Problem 30A
The name of the above compound is 2,5-dimethylhex-3-ene.
Explanation of Solution
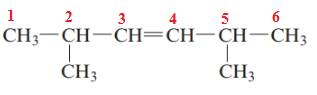
The principle chain contains six carbon atoms, two methyl substituents at C2 and C5 and one double bond between C3 and C4. So, the name of the above compound is 2,5-dimethylhex-3-ene.
(d)
Interpretation:
The name of the given alkene has to be described.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are acyclic or cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) and the general molecular formula CnH2n (where n = number of carbon atoms). Simplest alkene among all is ethylene C2H4 which contains one carbon-carbon double bond.
Alkenes can also be two types-
- Unbranched alkenes
- Branched alkenes
(d)
Answer to Problem 30A
The name of the above compound is 3,4,5-trimethylhept-1-ene.
Explanation of Solution
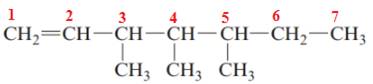
The principle chain contains seven carbon atoms, three methyl substituents at C3, C4 and C5 and one double bond between C1 and C2. So, the name of the above compound is 3,4,5-trimethylhept-1-ene.
Chapter 20 Solutions
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
- Indicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forwardPrimary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forward
- Complete the following equations hand written pleasearrow_forwardComplete the following equations please hand written pleasearrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 3+ 3Cu²+ (aq) +2Al(s) → 3 Cu(s)+2A1³* (aq) 2+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 5.29 M Cu in one half-cell and 2.49 M A1³+ in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. x10 μ ☑ 00. 18 Ar Иarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





