
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the given monosaccharide is a D or L sugar needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The configuration stereochemistry of the molecule is represented as D and L enantiomers. In the L isomer of a carbohydrate, the
All the natural sugars are D-isomers.
Answer to Problem 20.75P
D-isomer
Explanation of Solution
The given monosaccharide is as follows:
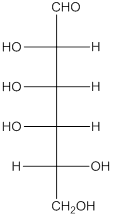
From the structure, the hydroxyl group to the carbon atom away from carbonyl group that is C-5 as hydroxyl group on right hand side thus, it is a D-isomer.
(b)
Interpretation:
The type of carbonyl and number of atoms in the chain of the given monosaccharide needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Monosaccharides are simplest sugar and basic units of carbohydrates. The monosaccharides are further hydrolyzed to form simpler chemical compounds. The general fromula of carbohydrate is
Answer to Problem 20.75P
Aldehyde group with 6 carbon atom: aldohexose.
Explanation of Solution
The given monosaccharide is as follows:
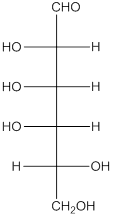
There are 6 carbon atoms present in it and there is an aldehyde group thus, it is an aldohexose.
Thus, the type of carbonyl group is aldehyde and number of atoms in chain is 6 carbon atoms.
(c)
Interpretation:
The enantiomers of the given monosaccharide need to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The configuration stereochemistry of the molecule is represented as D and L enantiomers. In the L isomer of a carbohydrate, the
Answer to Problem 20.75P
Explanation of Solution
The given monosaccharide is as follows:
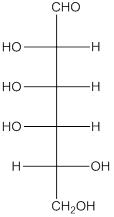
From the structure, the hydroxyl group to the carbon atom away from carbonyl group that is C-5 as hydroxyl group on right hand side thus, it is a D-isomer.
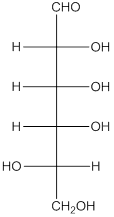
The enantiomer of the given monosaccharide will be L-isomer. The enantiomer of the D-isomer will be non-superimposable mirror image of it. Thus, the structure of L-isomer will be as follows:
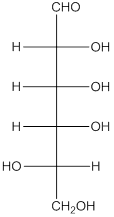
(d)
Interpretation:
The chirality centers needs to be labelled.
Concept Introduction:
The molecules in which there is one or more chiral centers are known as chiral molecules. A carbon attached to four different groups or atom is chiral in nature. The chiral molecules which are mirror images of each other are known as enantiomers. The chiral molecules are non-superimposable to each other. Non-superimposible means one molecule cannot be placed on the other molecule.
Answer to Problem 20.75P
The 4 chiral centers are represented as follows:
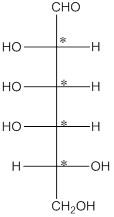
Explanation of Solution
The given monosaccharide is as follows:
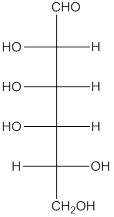
The chiral carbon atom has 4 different groups attached to it. Thus, the labelled carbon atoms are chiral in nature.
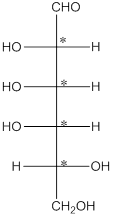
Thus, there are 4 chiral centers in the molecules.
(e)
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction:
An epimer is a stereoisomer having difference in configuration at any one chiral center. In the case of anomer, the difference in configuration takes place at the hemiacetal carbon in the cyclic form. The carbon atom is known as anomeric carbon.
Both the
Answer to Problem 20.75P
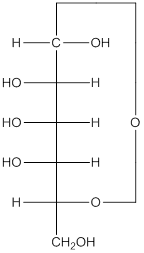
Explanation of Solution
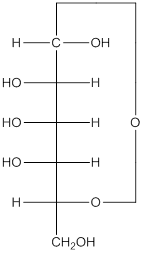
The given monosacchride is as follows:
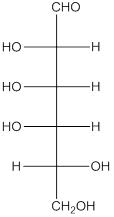
The
(f)
Interpretation:
The product from the reaction of monosaccharide with Benedict's reagent needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
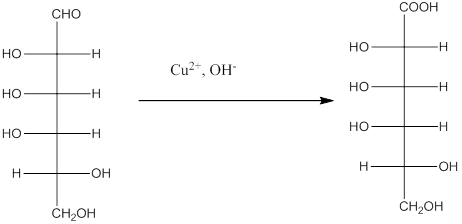
Benedict's reagent is used as a mild oxidizing agent and can oxidize aldehyde into the corresponding acid.
Answer to Problem 20.75P
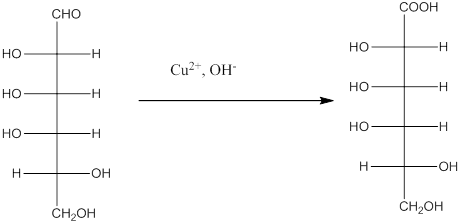
Explanation of Solution
The given monosacchride is as follows:
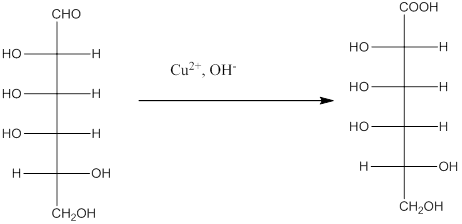
The Benedict's reagent is used as a mild oxidizing agent. Here, Cu2+ complexed with citrate and OH- are present in the Benedict's reagent which is used to identify reducing sugars. It is used as a mild oxidizing agent and can oxidize aldehyde into the corresponding acid. A hydroxyl group is added to the carbon with the carbonyl group when this reagent is added. Cu2+ is converted to Cu+ which then precipitates as Cu2O which is a brick red precipitate.
The reaction is represented as follows:
(g)
Interpretation:
The product formed on reaction of monosaccharide with
Concept introduction:
H2, Pd is used as a reducing agent to reduce compounds like
Answer to Problem 20.75P
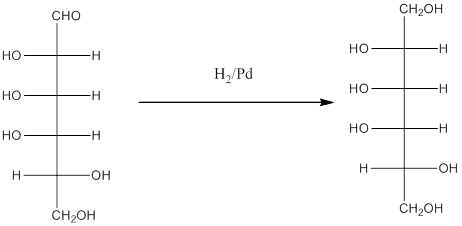
Explanation of Solution
When H2, Pd is added to aldehyde (reducing sugars), the corresponding alcohol is formed. The double bonded oxygen of the aldehyde turns to a hydroxyl group and one hydrogen atom is added to the carbon containing the respective oxygen atom. Pd is the catalyst of this reaction. H2 breaks and gets added as H atoms to oxygen atom and the carbon atom.
The given monosacchride is as follows:
Thus, the reaction with H2, Pd is represented as follows:
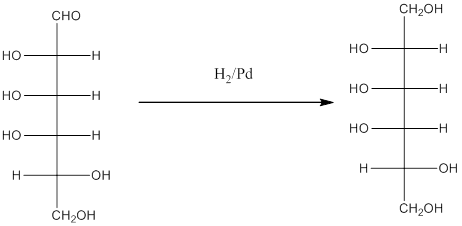
(h)
Interpretation:
The monosaccharide needs to be labelled as a reducing or non-reducing sugar.
Concept Introduction:
A reducing sugar is defined as any sugar capable of behaving as a reducing agent having a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. All monosaccharide are reducing sugars. There are some disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides which are also reducing sugars.
Answer to Problem 20.75P
The given monosaccharide is a reducing sugar.
Explanation of Solution
The given monosaccharide is represented as follows:
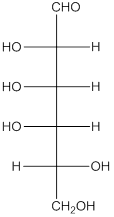
Since, all the monosaccharides are reducing sugar thus, it is also reducing sugar. A reducing sugar acts as a reducing agent. Thus, on reaction with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward8:44 PM Sun Apr 13 Earn Freecash.com O Measurement and Matter =1 Setting up a unit conversion 110 Eddie says... ✰ www-awu.aleks.com A student sets up the following equation to convert a measurement. (The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Fill in the missing part of this equation. Note: your answer should be in the form of one or more fractions multiplied together. (- 4 J kJ -7.0 × 10 ☐ = ? mmol.°C mol °C x10 μ Explanation Check □·□ torox.io Grey Hill LLC. All Rightsarrow_forward
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts please.arrow_forwardi need help with the folarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP NOW! URGENT!arrow_forward
- a. Determine whether each of the Followery Molecules is in the R- On the y- Configuration 1-01"/ 1-6-4 Br 4 I el Br b. Draw The Fisher projection For all the Meso compounds that can exist FOR The Following molenlearrow_forward1- Refer to the monosaccharides below to answer each of the following question(s): CH₂OH CHO CH₂OH CH₂OH 0 H- OH 0 0 HO- H H- -OH HO H HO H H OH HO- H CH₂OH H. OH HO H HO- H CH₂OH CH₂OH CH3 a. Sorbose b. Rhamnose c. Erythrulose d. Xylulose Classify each sugar by type; for example, glucose is an aldohexose. a. Xylulose is .. b. Erythrulose is . c. Sorbose is .. d. Rhamnose is .. 2- Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). CHO H OH CH₂OH CH₂OH HO- H HO HO + H. -OH HO OH HO. H OH OH H -OH H OH CH₂OH Q Z a. Refer to Exhibit 25-11. Place a triangle around the anomeric carbon in compound Q. Compound Z is: b. 1. the D-anomer. 2. the a-anomer. 3. the ẞ-anomer. 4. the L-anomer. c. Which anomer is the LEAST stable? d. Q and Z are cyclic examples of: a. acetals b. hemiacetals c. alditols d. hemialditolsarrow_forwardi need help identifying the four carbon oxygen bonds in the following:arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





