
Concept explainers
a) Acrylonitrile, C3H3N, which contains a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbon- nitrogen triple bond.
Interpretation:
Structure of acrylonitrile, C3H3N, with a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbon- nitrogen triple bond along with lone pair of electrons is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond is formed by mutual sharing of two electrons between the atoms, each atom giving one electron for sharing. Such a covalent bond, that is, a pair of shared electrons is represented as a line between the atoms, for example as A-B. The number of covalent bonds formed by an atom depends on the number of electrons that the atom requires for making the octet in its valence shell. Valence electrons that are not used for bonding are called lone-pair of electrons or nonbonding electrons.
Answer to Problem 33AP
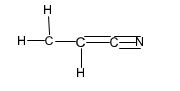
Structure of acrylonitrile, C3H3N.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of acrylonitrile, C3H3N, with a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbon- nitrogen triple bond along with lone pair of electrons is required. Carbon with four valence electrons can form four covalent bonds. Nitrogen with five valence electrons can form three covalent bonds while hydrogen with one valence electron an form one covalent bond. There are three carbons in acrylonitrile molecule. Two carbons are joined by a double bond and the third carbon is involved in forming triple bond with nitrogen and a single bond with second carbon. Out of the five valence electrons available, nitrogen has utilized only three electrons in forming the triple bond. Therefore a lone pair of electron remains on nitrogen. The hydrogen atoms are distributed on different carbon atoms depending upon their valence requirements giving the structure as

Structure of acrylonitrile, C3H3N, with a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbon- nitrogen triple bond along with lone pair of electrons.
b) Ethyl methyl ether, C3H8O, which contains an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms
Interpretation:
Structure of ethyl methyl ether, C3H8O, which contains an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms along with lone pair of electrons is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond is formed by mutual sharing of two electrons between the atoms, each atom giving one electron for sharing. Such a covalent bond, that is, a pair of shared electrons is represented as a line between the atoms, for example as A-B. The number of covalent bonds formed by an atom depends on the number of electrons that the atom requires for making the octet in its valence shell. Valence electrons that are not used for bonding are called lone-pair of electrons or nonbonding electrons.
Answer to Problem 33AP
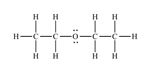
Structure of ethyl methyl ether, C3H8O, which contains an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms along with lone pair of electrons is
Explanation of Solution
Structure of ethyl methyl ether, C3H8O, with an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms along with lone pair of electrons is required. Carbon with four valence electrons can form four covalent bonds. Oxygen with six valence electrons can form two covalent bonds while hydrogen with one valence electron an form one covalent bond. There are three carbons in ethyl methyl ether molecule. Since the oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms, the third carbon must be attached to any one of the carbons bonded to oxygen atom. Hence the skeleton structure of ethyl methyl ether will be C-C-O-C. Out of the six valence electrons available, oxygen has utilized only two electrons in forming the bonds. Therefore two lone pairs of electrons remain on oxygen atom. The hydrogen atoms are distributed on different carbon atoms depending upon their valence requirements giving the structure as H3C-CH2-O-CH3.
Structure of ethyl methyl ether, C3H8O, which contains an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms along with lone pair of electrons is

c) Butane, C4H10, which contains a chain of four carbon atoms.
Interpretation:
Structure of butane, C4H10, which contains a chain of four carbon atoms along with lone pair of electrons is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond is formed by mutual sharing of two electrons between the atoms, each atom giving one electron for sharing. Such a covalent bond, that is, a pair of shared electrons is represented as a line between the atoms, for example as A-B. The number of covalent bonds formed by an atom depends on the number of electrons that the atom requires for making the octet in its valence shell. Valence electrons that are not used for bonding are called lone-pair of electrons or nonbonding electrons.
Answer to Problem 33AP
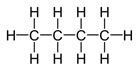
Structure of butane, C4H10.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of butane, C4H10, which contains a chain of four carbon atoms along with lone pair of electrons is

d) Cyclohexene, C6H10, which contains a ring of six carbon atoms and one carbon-carbon double bond.
Interpretation:
Structure of cyclohexene, C6H10, which contains a ring of six carbon atoms and one carbon-carbon double bond along with lone pair of electrons is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond is formed by mutual sharing of two electrons between the atoms, each atom giving one electron for sharing. Such a covalent bond, that is, a pair of shared electrons is represented as a line between the atoms, for example as A-B. The number of covalent bonds formed by an atom depends on the number of electrons that the atom requires for making the octet in its valence shell. Valence electrons that are not used for bonding are called lone-pair of electrons or nonbonding electrons.
Answer to Problem 33AP
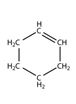
Structure of cyclohexene, C6H10, which contains a ring of six carbon atoms and one carbon-carbon double bond.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of cyclohexene, C6H10, with a ring of six carbon atoms and one carbon-carbon double bond along with lone pair of electrons is required. Carbon with four valence electrons can form four covalent bonds while hydrogen with one valence electron an form only one covalent bond. The carbons are to be arranged in the form a ring with two carbons attached through a double bond and two single bonds and others through four by single bonds. The ten hydrogen atoms are distributed on these six carbons satisfying their valence requirements. Thus no lone pair of electrons remains on either carbon or hydrogen. The structure of cyclohexene is


Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

