
Concept explainers
To graph: The
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The quadratic equation
Graph:
The graph of the quadratic equation
Consider the quadratic equation,
Rewrite the given equation:
Now put the values of
Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the value of
Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the value of
The value of
When the value of
Same as the value of
The value of
The value of
The value of
The value of
The value of
Observe that as the value of
Same as the value of
Steps to plot the graph of the equation
Step 1: Press
Step 2: Use the down arrow key to reach
Step 3: Press
Step 4: Press
Step 5: Enter the function
Step 6: Press
For better view of graph.
Step 8: Press
The result obtained on the screen is provided below,
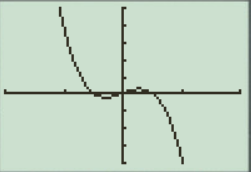
Interpretation:
The equation of the function
The equation has a wave formed graph.
The
Recall that the graphical approach to solve the equation simultaneously is observe the point where the graph of equation
Therefore, the equation
a.When the
Steps to plot the graph of the equation
Step 1: Press
Step 2: Use the down arrow key to reach
Step 3: Press
Step 4: Press
Step 5: Enter the function
Step 6: Press
For better view of graph.
Step 8: Press
The result obtained on the screen is provided below,
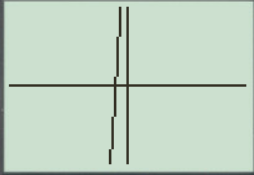
This window is not perfect viewing window.
b.
When the
Steps to plot the graph of the equation
Step 1: Press
Step 2: Use the down arrow key to reach
Step 3: Press
Step 4: Press
Step 5: Enter the function
Step 6: Press
For better view of graph.
Step 8: Press
The result obtained on the screen is provided below,
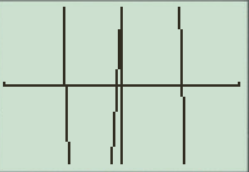
This window is not a perfect viewing window.
c.
When the
Steps to plot the graph of the equation
Step 1: Press
Step 2: Use the down arrow key to reach
Step 3: Press
Step 4: Press
Step 5: Enter the function
Step 6: Press
For better view of graph.
Step 8: Press
The result obtained on the screen is provided below,
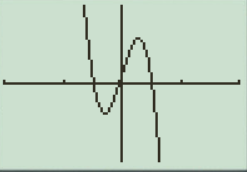
This is the perfect viewing window.
d.
When the
Steps to plot the graph of the equation
Step 1: Press
Step 2: Use the down arrow key to reach
Step 3: Press
Step 4: Press
Step 5: Enter the function
Step 6: Press
For better view of graph.
Step 8: Press
The result obtained on the screen is provided below,
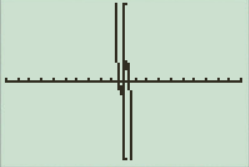
This window has large view, in this the graph points are not clear.
So the perfect viewing window of the graph
The perfect viewing window is
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS: MATHEMATICS FOR CALCUL
- #3 Find the derivative y' = of the following functions, using the derivative rules: dx a) y-Cos 6x b) y=x-Sin4x c) y=x-Cos3x d) y=x-R CD-X:-:TCH :D:D:D - Sin f) Sin(x²) (9) Tan (x³)arrow_forwardmate hat is the largest area that can be en 18 For the function y=x³-3x² - 1, use derivatives to: (a) determine the intervals of increase and decrease. (b) determine the local (relative) maxima and minima. (c) determine the intervals of concavity. (d) determine the points of inflection. b) (e) sketch the graph with the above information indicated on the graph.arrow_forwarduse L'Hopital Rule to evaluate the following. a) 4x3 +10x2 23009׳-9 943-9 b) hm 3-84 хто бу+2 < xan x-30650)arrow_forward
- Evaluate the next integralarrow_forward1. For each of the following, find the critical numbers of f, the intervals on which f is increasing or decreasing, and the relative maximum and minimum values of f. (a) f(x) = x² - 2x²+3 (b) f(x) = (x+1)5-5x-2 (c) f(x) = x2 x-9 2. For each of the following, find the intervals on which f is concave upward or downward and the inflection points of f. (a) f(x) = x - 2x²+3 (b) g(x) = x³- x (c) f(x)=x-6x3 + x-8 3. Find the relative maximum and minimum values of the following functions by using the Second Derivative Test. (a) f(x)=1+3x² - 2x3 (b) g(x) = 2x3 + 3x² - 12x-4arrow_forwardFind the Soultion to the following dy differential equation using Fourier in transforms: = , хуо, ухо according to the terms: lim u(x,y) = 0 x18 lim 4x (x,y) = 0 x14 2 u (x, 0) = =\u(o,y) = -y لوarrow_forward
- Can you solve question 3,4,5 and 6 for this questionarrow_forwardwater at a rate of 2 m³/min. of the water height in this tank? 16) A box with a square base and an open top must have a volume of 256 cubic inches. Find the dimensions of the box that will minimize the amount of material used (the surface area). 17) A farmer wishes toarrow_forward#14 Sand pours from a chute and forms a conical pile whose height is always equal to its base diameter. The height o the pile increases at a rate of 5 feet/hour. Find the rate of change of the volume of the sand in the conical pile when the height of the pile is 4 feet.arrow_forward
- (d)(65in(x)-5 cos(x) dx mins by 5x-2x² 3x+1 dx -dx 20 Evaluate each the following indefinite integralsarrow_forward19 Evaluate each the following definite integrals: a) લ b) (+3) 6) (2-2)(+33) dxarrow_forward#11 If a snowball melts so its surface area decreases at a rate of 1cm²/min, find the rate at which the diameter decreases when the diameter is 6 cm.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





