
Interpretation:
Synthesis of the given compound Darvon, starting with ethyl phenyl
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagent reactions with carbonyl groups are treated as acid–base reactions.
The reaction of Grignard reagents with carbonyl groups yields secondary and tertiary alcohols. These reactions are two-step reactions. In the first step, nucleophilic addition of carbonyl group takes place because Grignard reagent, being nucleophilic, uses its lone pair of electrons to form a bond with a carbon atom. This results in the formation of an alkoxide ion which remains associated with
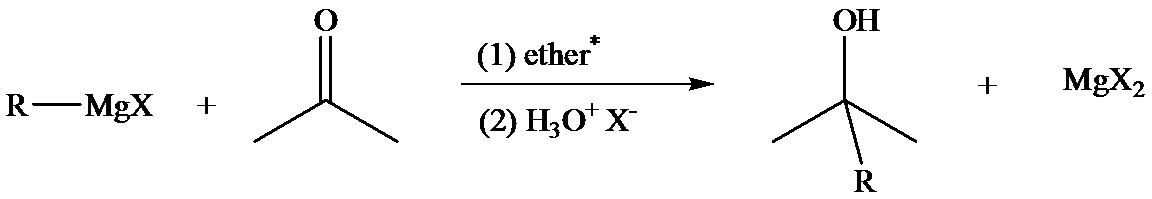
In the second step, addition of aqueous HX causes the protonation of the alkoxide ion, which leads to the formation of the alcohol and
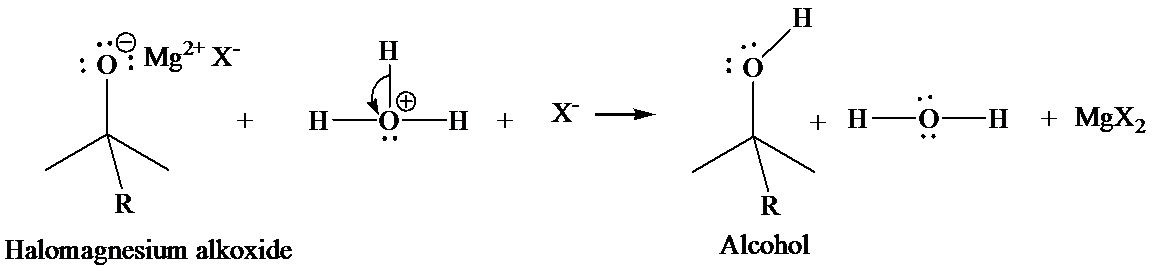
Mannich reaction: Carbonyl groups capable of forming enol react with primary or secondary
Alcohols react with acetic anhydride to form esters via nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Part C A solution that is 0.040 M in HCIO4 and 0.046 M in HCI Express your answer numerically to two decimal places. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? pH = Submit Request Answer Part D A solution that is 1.08% HCl by mass (with a density of 1.01 g/mL) Express your answer numerically to three decimal places. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ -> 0 ? pH =arrow_forwardPredict the equilibrium arrows for the following reaction:*see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information for each of the two following reacitons: *see imagearrow_forward
- Draw an example of the following functional groups: *see imagearrow_forwardAldehydes and Ketones: Show the reaction conditions, and molecules, that connect the reactant to the product. A protecting group will be needed. *see imagearrow_forwardAldehydes and Ketones: Show the reaction conditions, and molecules, that connect the reactant to the product. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information for each of the four reactions: *see imagearrow_forward6. Chlorine dioxide (CIO) is used as a disinfectant in municipal water-treatment plants. It decomposes in a first-order reaction with a rate constant of 14 s. How long would it take for an initial concentration of 0.06 M to decrease to 0.02 M? [6 pts]arrow_forwardIf possible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a methyl group substituent, and replace an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. If one of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substituent can be added, check the box under the drawing area. en HO OHarrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the intermediate and product of this hydrohalogenation reaction. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Br Select to Draw 51°F Sunny esc F1 HBr Select to Draw 1,2-hydride shift Br Select to Draw Q Search F2 F3 F4 1 2 # # 3 DII L F5 F6 F tA $ % Λarrow_forwardplease help i cant find the article to even startarrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
