
Concept explainers
Label each compound as a hydrolyzable or nonhydrolyzable lipid.
- prostaglandin
- phosphoacylglycerol
- triacylglycerol
- lecithin
- leukotriene
- cholesterol
- vitamin A
(a)
Interpretation:
Prostaglandin should be labeled as Hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable lipid.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Nonhydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Prostaglandin is a 20 carbon unsaturated carboxylic acid which contains a five-membered ring. A typical structure for prostaglandin is,
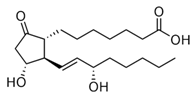
Prostaglandin does not contain an ester group. So, prostaglandin is nonhydrolyzable lipid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Triacylglycerol should be labeled as Hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Hydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Triacylglycerol is produced by reacting a glycerol molecule with three molecules of fatty acids by an ester linkage.
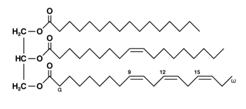
Triacylglycerol has three ester linkages. So, triacylglycerol is a hydrolyzable lipid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Leukotriene should be labeled as Hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Nonhydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Leukotrienes belong to the family of eicosanoids. Leukotrienes are synthesized by arachidonic acid. A typical structure for leukotriene is,
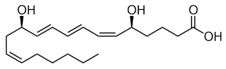
Leukotrienes have no ester linkages. So, leukotrienes are nonhydrolyzable lipids.
(d)
Interpretation:
Vitamin A should be labeled as hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Nonhydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Vitamin A is a group of several unsaturated fatty acids. It includes retinol which has an alcohol functional group, retinal which is an aldehyde and retinoic acid which is a carboxylic acid.
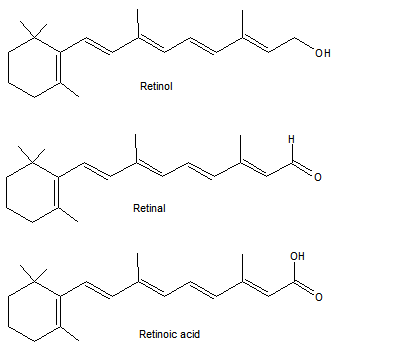
No structure has an ester linkage. So vitamin A is nonhydrolyzable lipid.
(e)
Interpretation:
Phoshoacylglycerol should be labeled as hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Hydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Phosphoacylglycerols are esterified glycerol in which, two hydroxyl groups of glycerol are esterified with fatty acids and one hydroxyl is esterified with phosphoric acid.
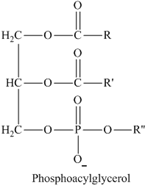
Since phosphoacylglycerol has ester linkages, it is a hydrolyzable lipid.
(f)
Interpretation:
Lecithin should be labeled as hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Hydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Lecithins are mixtures of glycerophospholipids. As glycerophospholipids are esterified form of glycerol with two fatty acids and phosphoric acid. Lecithin contains ester linkages. So, lecithin is a hydrolyzable lipid. The structure of phosphatidylcholine which is a type of phospholipid in lecithin is given below.
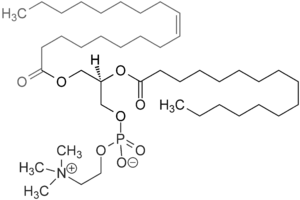
(g)
Interpretation:
Cholesterol should be labeled as hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are sub groups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Nonhydrolyzable
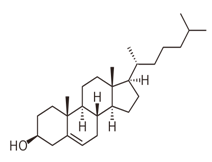
Explanation of Solution
Cholesterol is a type of sterol and has no ester linkages. So, cholesterol is nonhydrolyzable lipid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Choose the best reagent(s) for carrying out the following conversions from the list below. Place the letter corresponding to the best choice in the blank to the left of the conversion. a. KMnO4, H3O+ b. Tollens' Reagent [oxidizing reagent] C. NaBH4, ethanol d. 1. BH3 2. H3O+ e. 1. CH3MgBr, ether 2. H3O+ f. CrO3, H2SO4, H₂O g. 1. Mg, ether 2. CO2 3. H3O+ h. 1. NaCN 2. H2SO4, H2, heat i. O3, then Zn and HOAC j. CH₂I A. B. C. CH CH=CHCH2COOH Br CEN CH COOH + HOOCCH COOH COOH 010 CH3arrow_forwardDraw the structures for each of the intermediates in the boxes provided for the synthesis below. OCH3 Fe HO HNO (CHOO pynding H₂504 LHNO2 NACH-I Fa H₂O HCL HNO 180arrow_forwardProvide structure(s) for the starting material(s), reagent(s) or the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry [three only] A. o 11 (CH3)CH — C— C ether (CH3)2CH-C-O-C-CH3 B. CH3 CHy CI Staf OH C. HC OCHS + H₂Oarrow_forward
- Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following questions: EtO Compound X 1. NaOEt, EtOH OEt Br CO₂Et NaOEt, EtOH Compound Z CO₂Et Compound Y A. Compound X, diethyl propanedioate, is more commonly known as a. ethyl acetoacetate b. acetoacetic ester C. oxalic ester d. malonic ester 3. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the conversion of Compound X into Compound Y. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures.arrow_forwardClassify each of the following nitrogen atoms in the following compounds as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary [three only] CH3 HO-CHCHNHCH3 A. B. C. H&C CH3 D. HO phedrine CH2CHCH3 amphetamine NH₂ mepiquat chloride faxofenadine OH H&C CH CO₂Harrow_forwardDraw the structure of the aldol self-condensation product for each of the following compounds. If a compound does not undergo aldol self-condensation, explain why it does not. A. B. CHICHCH₂OH CH3CHCH2CH CH3 CH3 C. CH 30 H3C-C-C-H CH3 questionsarrow_forward
- . A.Propose a synthesis for propylbenzene which avoids the problems of direct Friedel-Crafts alkylation. B. Consider the reaction below to answer the following questions. A B C NO2 Febr Brz D The Lewis acid catalyst in the reaction is: a. The nucleophile in the reaction is: b. C. d. This reaction proceeds Draw the structure of product D. (faster or slower) than benzene.arrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to answer the following questions. HOCH CHOH На A B C D H₂Oarrow_forwardConsider the structures below to answer the following questions. A. Indicate the most acidic hydrogens in each of the molecules. OH CH-H CH₂C-H H&C མིངྒཱའི B. Rank the molecules above in order of increasing acidity (least acidic to most acidic). a. III, II, I b. II, III, I C. I, II, III d. II, I, IIIarrow_forward
- Consider the reaction below to answer the following questions. H H+ A B CH₂OH 5% NaOCH, CH₂OH A. Which carbonyl compound functions as the electrophile in this reaction? B. Draw the structure of the enolate ion that is generated during the course of this reaction. C. This reaction is an example of: a. a mixed Claisen condensation. b. C. d. a Dieckman condensation. a Michael reaction. a mixed aldol reaction.arrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry. [two only] CH3O (11 HC-C-C-CH3 A. CH3 12. NaOHarrow_forwardDiethyl malonate can be prepared by the following reaction sequence. Draw the structures of each of the missing intermediates in the boxes provided. 17 1. Br PBr H&C OH 2 H₂O CH3CH₂OH На NaCN H₂SO4 NC. CH CH₂OH на H₂O, heat CH₂ OCHCH3 ཝསི། ཡིཀྑཱམུདྡྷནྟ CH₂ OEtarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



