
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781292089034
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 43P
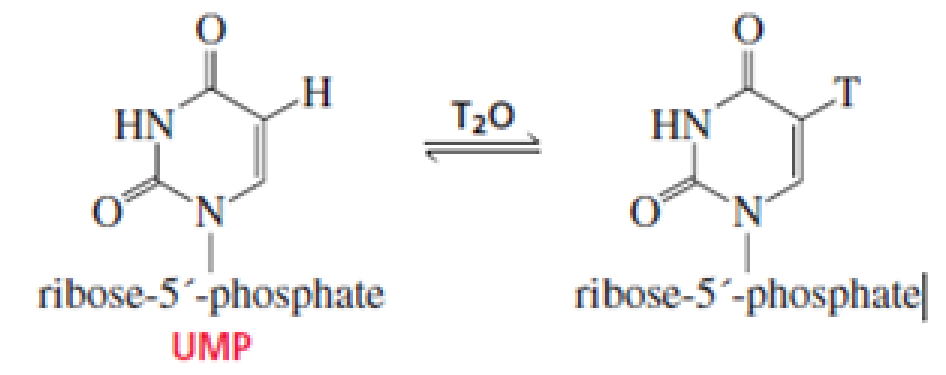
When UMP is dissolved in T2O, exchange of T for H occurs at the 5 position. Propose a mechanism for the exchange. (T is 3H, a hydrogen with two neutrons.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Steps and explanation please
Steps and explanation to undertand concepts.
None
Chapter 18 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 18.2 - If H218O were used to hydrolyze lysozyme, which...Ch. 18.3 - Which of the following amino acid side chains can...Ch. 18.3 - Arginine and lysine side chains fit into trypsins...Ch. 18.4 - Which of the following amino acid side chains can...Ch. 18.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 18.5 - Prob. 7PCh. 18.5 - Draw the mechanism for the hydroxide-ion-catalyzed...Ch. 18.5 - What advantage does the enzyme gain by forming an...Ch. 18.7 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 18.7 - Prob. 11PCh. 18.8 - How many conjugated double bonds are there in a....Ch. 18.8 - Instead of adding to the 4a-position and...Ch. 18.8 - In succinate dehydrogenase, FAD is covalently...Ch. 18.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 18.9 - Acetolactate synthase is another TPP-requiring...Ch. 18.9 - Acetolactate synthase can also transfer the acyl...Ch. 18.9 - Prob. 18PCh. 18.9 - Prob. 19PCh. 18.10 - Prob. 21PCh. 18.11 - Prob. 23PCh. 18.11 - Which compound is more easily decarboxylated?Ch. 18.11 - Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an...Ch. 18.11 - Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an...Ch. 18.12 - What groups are interchanged in the following...Ch. 18.13 - Why is the coenzyme called tetrahydrofolate?Ch. 18.13 - What amino acid is formed by the following...Ch. 18.13 - How do the structures of tetrahydrofolate and...Ch. 18.13 - What is the source of the methyl group in...Ch. 18 - Prob. 32PCh. 18 - Prob. 33PCh. 18 - From what vitamins are the following coenzymes...Ch. 18 - Prob. 35PCh. 18 - For each of the following reaction, name both the...Ch. 18 - Explain why serine proteases do not catalyze...Ch. 18 - Prob. 38PCh. 18 - For each of the following enzyme catalyzed...Ch. 18 - Trisephosphate isomerase (TIM) catalyzes the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 41PCh. 18 - What acyl groups have we seen transferred by...Ch. 18 - When UMP is dissolved in T2O, exchange of T for H...Ch. 18 - Prob. 44PCh. 18 - When transaminated, the three branched-chain amino...Ch. 18 - Aldolase shows no activity if it is incubated with...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. Draw a curved arrow mechanism for the following reaction. HO cat. HCI OH in dioxane with 4A molecular sievesarrow_forwardTry: Convert the given 3D perspective structure to Newman projection about C2 - C3 bond (C2 carbon in the front). Also, show Newman projection of other possible staggered conformers and circle the most stable conformation. Use the template shown. F H3C Br Harrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- 16. Consider the probability distribution p(x) = ax", 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 for a positive integer n. A. Derive an expression for the constant a, to normalize p(x). B. Compute the average (x) as a function of n. C. Compute σ2 = (x²) - (x)², the variance of x, as a function of n.arrow_forward451. Use the diffusion model from lecture that showed the likelihood of mixing occurring in a lattice model with eight lattice sites: Case Left Right A B C Permeable Barrier → and show that with 2V lattice sites on each side of the permeable barrier and a total of 2V white particles and 2V black particles, that perfect de-mixing (all one color on each side of the barrier) becomes increasingly unlikely as V increases.arrow_forward46. Consider an ideal gas that occupies 2.50 dm³ at a pressure of 3.00 bar. If the gas is compressed isothermally at a constant external pressure so that the final volume is 0.500 dm³, calculate the smallest value Rest can have. Calculate the work involved using this value of Rext.arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forward2010. Suppose that a 10 kg mass of iron at 20 C is dropped from a heigh of 100 meters. What is the kinetics energy of the mass just before it hits the ground, assuming no air resistance? What is its speed? What would be the final temperature of the mass if all the kinetic energy at impact is transformed into internal energy? The molar heat capacity of iron is Cpp = 25.1J mol-¹ K-1 and the gravitational acceleration constant is 9.8 m s¯² |arrow_forwardell last during 7. Write the isotopes and their % abundance of isotopes of i) Cl ii) Br 8. Circle all the molecules that show Molecular ion peak as an odd number? c) NH2CH2CH2NH2 d) C6H5NH2 a) CH³CN b) CH3OHarrow_forward
- Calsulate specific heat Dissolution of NaOH ก ง ง Mass of water in cup Final temp. of water + NaOH Initial temp. of water AT Water AH Dissolution NaOH - "CaicuraORT. AH (NaOH)=-AH( 30g (water) 29.0°C 210°C 8°C (82) 100 3.. =1003.20 Conjosarrow_forwardPlease provide throrough analysis to apply into further problems.arrow_forwardMolecular ion peak: the peak corresponding to the intact morecure (with a positive charge) 4. What would the base peak and Molecular ion peaks when isobutane is subjected to Mass spectrometry? Draw the structures and write the molecular weights of the fragments. 5. Circle most stable cation a) tert-butyl cation b) Isopropyl cation c) Ethyl cation. d)Methyl cationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

DIGESTER-35 | VITAMINS AND THEIR RELATED COENZYMES| GPAT | NIPER | PHARMACIST| DI; Author: GPAT DISCUSSION CENTER;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CGrdNYmho0s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY