Problem 1RQ: What is a half-reaction? Why must the number of electrons lost in the oxidation half-reaction equal... Problem 2RQ: Galvanic cells harness spontaneous oxidationreduction reactions to produce work by producing a... Problem 3RQ: Table 17-1 lists common half-reactions along with the standard reduction potential associated with... Problem 4RQ Problem 5RQ: The Nernst equation allows determination of the cell potential for a galvanic cell at nonstandard... Problem 6RQ Problem 7RQ Problem 8RQ Problem 9RQ: What characterizes an electrolytic cell? What is an ampere? When the current applied to an... Problem 1ALQ: Sketch a galvanic cell, and explain how it works. Look at Figs. 17-1 and 17-2. Explain what is... Problem 2ALQ Problem 3ALQ Problem 4ALQ Problem 5ALQ: Sketch a cell that forms iron metal from iron(II) while changing chromium metal to chromium(III).... Problem 6ALQ: Which of the following is the best reducing agent: F2, H2, Na, Na+, F? Explain. Order as many of... Problem 7ALQ Problem 8ALQ Problem 9ALQ: Explain why cell potentials are not multiplied by the coefficients in the balanced redox equation.... Problem 10ALQ: What is the difference between and ? When is equal to zero? When is equal to zero? (Consider regular... Problem 11ALQ Problem 12ALQ: Look up the reduction potential for Fe3+ to Fe2+. Look up the reduction potential for Fe2+ to Fe.... Problem 13ALQ Problem 14ALQ: Is the following statement true or false? Concentration cells work because standard reduction... Problem 15RORR Problem 16RORR: Assign oxidation numbers to all the atoms in each of the following: a. HNO3 b. CuCl2 c. O2 d. H2O2... Problem 17RORR: Specify which of the following equations represent oxidation reduction reactions, and indicate the... Problem 18RORR: The Ostwald process for the commercial production of nitric acid involves the following three steps:... Problem 19Q Problem 20Q Problem 21Q: When magnesium metal is added to a beaker of HCl(aq), a gas is produced. Knowing that magnesium is... Problem 22Q: How can one construct a galvanic cell from two substances, each having a negative standard reduction... Problem 23Q: The free energy change for a reaction, G, is an extensive property. What is an extensive property?... Problem 24Q: What is wrong with the following statement: The best concentration cell will consist of the... Problem 25Q: When jump-starting a car with a dead battery, the ground jumper should be attached to a remote part... Problem 26Q Problem 27Q Problem 28Q: Consider the following electrochemical cell: a. If silver metal is a product of the reaction, is the... Problem 29E: Balance the following oxidationreduction reactions that occur in acidic solution using the... Problem 30E Problem 31E Problem 32E Problem 33E: Chlorine gas was first prepared in 1774 by C. W. Scheele by oxidizing sodium chloride with... Problem 34E: Gold metal will not dissolve in either concentrated nitric acid or concentrated hydrochloric acid It... Problem 35E Problem 36E: Consider the following galvanic cell: a. Label the reducing agent and the oxidizing agent, and... Problem 37E Problem 38E: Sketch the galvanic cells based on the following overall reactions. Show the direction of electron... Problem 39E Problem 40E Problem 41E Problem 42E Problem 43E Problem 44E: Give the standard line notation for each cell in Exercises 38 and 42. Problem 45E Problem 46E Problem 47E Problem 48E Problem 49E Problem 50E: The amount of manganese in steel is determined by changing it to permanganate ion. The steel is... Problem 51E Problem 52E Problem 53E: Estimate for the half-reaction 2H2O+2eH2+2OH given the following values of Gfo: H2O(l)=237kJ/mol... Problem 54E Problem 55E: Glucose is the major fuel for most living cells. The oxidative breakdown of glucose by our body to... Problem 56E: Direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs) have shown some promise as a viable option for providing green... Problem 57E Problem 58E: Using data from Table 17-1, place the following in order of increasing strength as reducing agents... Problem 59E: Answer the following questions using data from Table 17-1 (all under standard conditions). a. Is... Problem 60E Problem 61E: Consider only the species (at standard conditions) Na+, Cl, Ag+, Ag, Zn2+, Zn, Pb in answering the... Problem 62E Problem 63E Problem 64E Problem 65E Problem 66E Problem 67E: A galvanic cell is based on the following half-reactions at 25C: Ag++eAg H2O2+2H++2e2H2O Predict... Problem 68E Problem 69E: Consider the concentration cell shown below. Calculate the cell potential at 25C when the... Problem 70E Problem 71E: The overall reaction in the lead storage battery is Pb(s)+PbO2(s)+2H+(aq)+2HSO4(aq)2PbSO4(s)+2H2O(l)... Problem 72E Problem 73E: Consider the cell described below: Zn|Zn2+(1.00M)||Cu2+(l.00M)|Cu Calculate the cell potential after... Problem 74E: Consider the cell described below: Al|Al3+(1.00M)||Pb2+(1.00M)|Pb Calculate the cell potential after... Problem 75E Problem 76E Problem 77E Problem 78E Problem 79E Problem 80E: An electrochemical cell consists of a nickel metal electrode immersed in a solution with [Ni2+] =... Problem 81E: An electrochemical cell consists of a standard hydrogen electrode and a copper metal electrode. If... Problem 82E Problem 83E: Consider a concentration cell that has both electrodes made of some metal M. Solution A in one... Problem 84E Problem 85E Problem 86E Problem 87E: Consider the following galvanic cell at 25C: Pt|Cr2+(0.30M),Cr3+(2.0M)||Co2+(0.20M)|Co The overall... Problem 88E Problem 89E Problem 90E Problem 91E Problem 92E: The solubility product for CuI(s) is 1.1 102 Calculate the value of for the half-reaction... Problem 93E: How long will it take to plate out each of the following with a current of 100.0 A? a. 1.0 kg AI... Problem 94E: The electrolysis of BiO+ produces pure bismuth. How long would it take to produce 10.0 g Bi by the... Problem 95E: What mass of each of the following substances can be produced in 1.0 h with a current of 15 A? a. Co... Problem 96E Problem 97E: An unknown metal M is electrolyzed. It took 74.1 s for a current of 2.00 A to plate out 0.107 g of... Problem 98E: Electrolysis of an alkaline earth metal chloride using a current of 5.00 A for 748 s deposits 0.471... Problem 99E: What volume of F2 gas, at 25C and 1.00 atm, is produced when molten KF is electrolyzed by a current... Problem 100E: What volumes of H2(g) and O2(g) at STP are produced from the electrolysis of water by a current of... Problem 101E Problem 102E: A factory wants to produce 1.00 103 kg barium from the electrolysis of molten barium chloride. What... Problem 103E: It took 2.30 min using a current of 2.00 A to plate out all the silver from 0.250 L of a solution... Problem 104E: A solution containing Pt4+ is electrolyzed with a current of 4.00 A. How long will it take to plate... Problem 105E: A solution at 25C contains 1.0 M Cd2+, 1.0 M Ag+, 1.0 M Au3+, and 1.0 M NiH2+ in the cathode... Problem 106E: Consider the following half-reactions: A hydrochloric acid solution contains platinum, palladium,... Problem 107E: In the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of Na2SO4, what reactions occur at the anode and the... Problem 108E: Copper can be plated onto a spoon by placing the spoon in an acidic solution of CuSO4(aq) and... Problem 109E Problem 110E Problem 111E Problem 112E: What reaction will take place at the Cathode and the anode when each of the following is... Problem 113AE: Gold is produced electrochemically from an aqueous solution of Au(CN)2 containing an excess of CN.... Problem 114AE Problem 115AE: The saturated calomel electrode. abbreviated SCE. is often used as a reference electrode in making... Problem 116AE: Consider the following half-reactions: Explain why platinum metal will dissolve in aqua regia (a... Problem 117AE: Consider the standard galvanic cell based on the following half-reactions: Cu2++2eCuAg++eAg The... Problem 118AE Problem 119AE: The black silver sulfide discoloration of silverware can be removed by heating the silver article in... Problem 120AE Problem 121AE: When aluminum foil is placed in hydrochloric acid, nothing happens for the first 30 seconds or so.... Problem 122AE Problem 123AE Problem 124AE: The overall reaction and equilibrium constant value for a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell at 298 K is... Problem 125AE: What is the maximum work that can be obtained from a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell at standard... Problem 126AE: The overall reaction and standard cell potential at 25C for the rechargeable nickel-cadmium alkaline... Problem 127AE Problem 128AE Problem 129AE Problem 130AE Problem 131AE Problem 132AE Problem 133AE Problem 134CWP Problem 135CWP: Consider a galvanic cell based on the following half-reactions: a. What is the expected cell... Problem 136CWP: Consider a galvanic cell based on the following theoretical half-reactions: What is the value of G... Problem 137CWP: Consider a galvanic cell based on the following half-reactions: a. What is the standard potential... Problem 138CWP: An electrochemical cell consists of a silver metal electrode immersed in a solution with [Ag+] =... Problem 139CWP: An aqueous solution of PdCl2 is electrolyzed for 48.6 seconds, and during this time 0.1064 g of Pd... Problem 140CP Problem 141CP Problem 142CP: The overall reaction in the lead storage battery is Pb(s)+PbO2(s)+2H+(aq)+2HSO4(aq)2PbSO4(s)+2H2O(l)... Problem 143CP: Consider the following galvanic cell: Calculate the KSP value for Ag2SO4(s). Note that to obtain... Problem 144CP Problem 145CP: A galvanic cell is based on the following half-reactions: where the iron compartment contains an... Problem 146CP Problem 147CP: The measurement of pH using a glass electrode obeys the Nernst equation. The typical response of a... Problem 148CP Problem 149CP: A galvanic cell is based on the following half-reactions: In this cell, the silver compartment... Problem 150CP Problem 151CP Problem 152CP Problem 153CP: Consider the following galvanic cell: A 15 0-mole sample of NH is added to the Ag compartment... Problem 154CP: When copper reacts with nitric acid, a mixture of NO(g) and NO2(g) is evolved. The volume ratio of... Problem 155IP: The following standard reduction potentials have been determined for the aqueous chemistry of... Problem 156IP: An electrochemical cell is set up using the following unbalanced reaction: Ma+(aq)+N(s)N2+(aq)+M(s)... Problem 157IP: Three electrochemical cells were connected in series so that the same quantity of electrical current... Problem 158IP: A silver concentration cell is set up at 25C as shown below: The AgCl(s) is in excess in the left... Problem 159MP: A galvanic cell is based on the following half-reactions: In this cell, the copper compartment... Problem 160MP format_list_bulleted

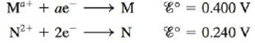

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning




