
Fundamentals of Physics, Volume 1, Chapter 1-20
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118233764
Author: David Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 105P
In Fig. 17-35. S1 and S2 are two isotropic point sources of sound. They emit waves in phase at wavelength 0.50 m; they are separated by D = 1.60 m. If we move a sound detector along a large circle centered at the midpoint between the sources, at how many points do waves arrive at the detector (a) exactly in phase and (b) exactly out of phase?
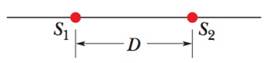
Figure 17-35 Problems 19 and 105.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
How can you tell which vowel is being produced here ( “ee,” “ah,” or “oo”)? Also, how would you be able to tell for the other vowels?
You want to fabricate a soft microfluidic chip like the one below. How would you go about
fabricating this chip knowing that you are targeting a channel with a square cross-sectional
profile of 200 μm by 200 μm. What materials and steps would you use and why? Disregard the
process to form the inlet and outlet.
Square Cross Section
1. What are the key steps involved in the fabrication of a semiconductor device.
2. You are hired by a chip manufacturing company, and you are asked to prepare a silicon wafer
with the pattern below. Describe the process you would use.
High Aspect
Ratio
Trenches
Undoped Si Wafer
P-doped Si
3. You would like to deposit material within a high aspect ratio trench. What approach would you
use and why?
4. A person is setting up a small clean room space to carry out an outreach activity to educate high
school students about patterning using photolithography. They obtained a positive photoresist, a
used spin coater, a high energy light lamp for exposure and ordered a plastic transparency mask
with a pattern on it to reduce cost. Upon trying this set up multiple times they find that the full
resist gets developed, and they are unable to transfer the pattern onto the resist. Help them
troubleshoot and find out why pattern of transfer has not been successful.
5. You are given a composite…
Chapter 17 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics, Volume 1, Chapter 1-20
Ch. 17 - In a first experiment, a sinusoidal sound wave is...Ch. 17 - In Fig. 17-25, two point sources S1, and S2, which...Ch. 17 - In Fig. 17-26, three long tubes A,B, and C are...Ch. 17 - Prob. 4QCh. 17 - In Fig. 17-27, pipe A is made to oscillate in its...Ch. 17 - Prob. 6QCh. 17 - Figure 17-28 shows a moving sound source S that...Ch. 17 - Prob. 8QCh. 17 - For a particular tube, here are four of the six...Ch. 17 - Prob. 10Q
Ch. 17 - You are given four tuning forks. The fork with the...Ch. 17 - Two spectators at a soccer game see, and a moment...Ch. 17 - What is the bulk modulus of oxygen if 32.0 g of...Ch. 17 - Prob. 3PCh. 17 - A column of soldiers, marching at 120 paces per...Ch. 17 - Prob. 5PCh. 17 - A man strikes one end of a thin rod with a hammer....Ch. 17 - SSM WWW A stone is dropped into a well. The splash...Ch. 17 - GO Hot chocolate effect. Tap a metal spoon inside...Ch. 17 - If the form of a sound wave traveling through air...Ch. 17 - Prob. 10PCh. 17 - SSM Diagnostic ultrasound of frequency 4.50 MHz is...Ch. 17 - The pressure in a traveling sound wave is given by...Ch. 17 - A sound wave of the form s = sm coskx t travels...Ch. 17 - Figure 17-32 shows the output from a pressure...Ch. 17 - GO A handclap on stage in an amphitheater sends...Ch. 17 - Two sound waves, from two different sources with...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17PCh. 17 - Prob. 18PCh. 17 - GO Figure 17-35 shows two isotropic point sources...Ch. 17 - Figure 17-36 shows four isotropic point sources of...Ch. 17 - SSM In Fig. 17-37, two speakers separated by...Ch. 17 - In Fig. 17-38, sound with a 40.0 cm wavelength...Ch. 17 - GO Figure 17-39 shows two point sources S1 and S2...Ch. 17 - Suppose that the sound level of a conversation is...Ch. 17 - A sound wave of frequency 300Hz has an intensity...Ch. 17 - Prob. 26PCh. 17 - SSM WWW A certain sound source is increased in...Ch. 17 - Two sounds differ in sound level by 1.00 dB. What...Ch. 17 - Prob. 29PCh. 17 - The source of a sound wave has a power of 1.00 W....Ch. 17 - GO When you crack a knuckle, you suddenly widen...Ch. 17 - Approximately a third of people with normal...Ch. 17 - Male Rana catesbeiana bullfrogs arc known for...Ch. 17 - GO Two atmospheric sound sources A and B emit...Ch. 17 - A point source emits 30.0 W of sound...Ch. 17 - Party hearing. As the number of people at a party...Ch. 17 - Prob. 37PCh. 17 - The water level in a vertical glass tube 1.00 m...Ch. 17 - Prob. 39PCh. 17 - Organ pipe A, with both ends open, has a...Ch. 17 - A violin siring 15.0 cm long and fixed at both...Ch. 17 - A sound wave in a fluid medium is reflected at a...Ch. 17 - SSM In Fig. 17-41, S is a small loudspeaker driven...Ch. 17 - The crest of a Parasaurolophus dinosaur skull is...Ch. 17 - In pipe A, the ratio of a particular harmonic...Ch. 17 - GO Pipe A. which is 1.20 m long and open at both...Ch. 17 - A well with vertical sides and water at the bottom...Ch. 17 - One of the harmonic frequencies of tube A with two...Ch. 17 - SSM A violin string 30.0 cm long with linear...Ch. 17 - Prob. 50PCh. 17 - The A string of a violin is a little too tightly...Ch. 17 - A tuning fork of unknown frequency makes 3.00...Ch. 17 - SSM Two identical piano wires have a fundamental...Ch. 17 - You have five tuning forks that oscillate at close...Ch. 17 - Prob. 55PCh. 17 - An ambulance with a siren emitting a whine at 1600...Ch. 17 - A state trooper chases a speeder along a straight...Ch. 17 - Prob. 58PCh. 17 - GO In Fig. 17-42, a French submarine and a U.S....Ch. 17 - A stationary motion detector sends sound waves of...Ch. 17 - GO A bat is flitting about in a cave, navigating...Ch. 17 - Figure 17-43 shows four tubes with lengths 1.0 m...Ch. 17 - ILWAn acoustic burglar alarm consists of a source...Ch. 17 - A stationary detector measures the frequency of a...Ch. 17 - GO A 2000 Hz siren and a civil defense official...Ch. 17 - GO Two trains are traveling toward each other at...Ch. 17 - SSM WWWA girl is sitting near the open window of a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 68PCh. 17 - SSMA jet plane passes over you at a height of 5000...Ch. 17 - A plane flies at 1.25 times the speed of sound....Ch. 17 - At a distance of 10 km, a 100 Hz horn, assumed to...Ch. 17 - A bullet is fired with a speed of 685 m/s. Find...Ch. 17 - Prob. 73PCh. 17 - The average density of Earths crust 10 km beneath...Ch. 17 - A certain loudspeaker system emits sound...Ch. 17 - Find the ratios greater to smaller of the a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 77PCh. 17 - A trumpet player on a moving railroad flatcar...Ch. 17 - GO In Fig. 17-46, sound of wavelength 0.850 m is...Ch. 17 - GO A detector initially moves at constant velocity...Ch. 17 - SSMa If two sound waves, one in air and one in...Ch. 17 - A continuous sinusoidal longitudinal wave is sent...Ch. 17 - SSMUltrasound, which consists of sound waves with...Ch. 17 - The speed of sound in a certain metal is vm. One...Ch. 17 - An avalanche of sand along some rare desert sand...Ch. 17 - A sound source moves along an x axis, between...Ch. 17 - SSMA siren emitting a sound of frequency 1000 Hz...Ch. 17 - Prob. 88PCh. 17 - Prob. 89PCh. 17 - Prob. 90PCh. 17 - Prob. 91PCh. 17 - You can estimate your distance from a lightning...Ch. 17 - SSMFigure 17-48 shows an air-filled, acoustic...Ch. 17 - Prob. 94PCh. 17 - SSMThe sound intensity is 0.0080 W/m2 at a...Ch. 17 - Four sound waves are to be sent through the same...Ch. 17 - Prob. 97PCh. 17 - A point source that is stationary on an x axis...Ch. 17 - You are standing at a distance D from an isotropic...Ch. 17 - Pipe A has only one open end; pipe B is four times...Ch. 17 - A pipe 0.60 m long and closed at one end is filled...Ch. 17 - A sound wave travels out uniformly in all...Ch. 17 - A police car is chasing a speeding Porsche 911....Ch. 17 - Suppose a spherical loudspeaker emits sound...Ch. 17 - In Fig. 17-35. S1 and S2 are two isotropic point...Ch. 17 - Prob. 106PCh. 17 - Kundts method for measuring the speed of sound. In...Ch. 17 - Prob. 108PCh. 17 - In Fig. 17-53, a point source S of sound waves...Ch. 17 - A person on a railroad car blows a trumpet note at...Ch. 17 - A listener at rest with respect to the air and the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Which culture uses NAD+? Use the following choices to answer questions. a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
In humans, hemophilia A (OMIM 306700) is an X-linked recessive disorder that affects the gene for factor VIII p...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Examine the graph in Figure 6.3. Note that the growth rate increases slowly until the optimum is reached and th...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
77. Write a molecular equation for the precipitation reaction that occurs (if any) when each pair of aqueous so...
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. The reason we do not have a solar ecli...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardAn electromagnetic wave is traveling through vacuum in the positive x direction. Its electric field vector is given by E=E0sin(kx−ωt)j^,where j^ is the unit vector in the y direction. If B0 is the amplitude of the magnetic field vector, find the complete expression for the magnetic field vector B→ of the wave. What is the Poynting vector S(x,t), that is, the power per unit area associated with the electromagnetic wave described in the problem introduction? Give your answer in terms of some or all of the variables E0, B0, k, x, ω, t, and μ0. Specify the direction of the Poynting vector using the unit vectors i^, j^, and k^ as appropriate. Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardAnother worker is performing a task with an RWL of only 9 kg and is lifting 18 kg, giving him an LI of 2.0 (high risk). Questions:What is the primary issue according to NIOSH?Name two factors of the RWL that could be improved to reduce risk.If the horizontal distance is reduced from 50 cm to 30 cm, how does the HM change and what effect would it have?arrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for z1z2∗. Find r and θ for z1/z2∗? Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1z2∗ Please explain all steps, Thank youarrow_forwardAn ac series circuit consists of a voltage source of frequency 60 Hz and voltage amplitude V, a 505-Ω resistor, and a capacitor of capacitance 7.2 μF. What must be the source voltage amplitude V for the average electrical power consumed in the resistor to be 236 W? There is no inductance in the circuit.arrow_forwardAn L−R−C series circuit has R= 280 Ω . At the frequency of the source, the inductor has reactance XLL= 905 Ω and the capacitor has reactance XC= 485 Ω . The amplitude of the voltage across the inductor is 445 V . What is the amplitude of the voltage across the resistor and the capacitor? What is the voltage amplitude of the source? What is the rate at which the source is delivering electrical energy to the circuit?arrow_forward
- A 0.185 H inductor is connected in series with a 98.5 Ω resistor and an ac source. The voltage across the inductor is vL=−(12.5V)sin[(476rad/s)t]vL. Derive an expression for the voltage vR across the resistor. Express your answer in terms of the variables L, R, VL (amplitude of the voltage across the inductor), ω, and t. What is vR at 2.13 ms ? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA worker lifts a box under the following conditions:Horizontal distance (H): 30 cmInitial height (V): 60 cmVertical travel (D): 50 cmTorso rotation (A): 30°Frequency: 3 times/minute for 1 hourGrip: Good Question:What is the RWL for this task?What does this value mean in terms of occupational safety?arrow_forwardCan someone helparrow_forward
- Can someone help mearrow_forward3. Four identical small masses are connected in a flat perfect square. Rank the relative rotational inertias (IA, IB, IC) about the three axes of rotation shown. Axes A and B are in the plane of the square, and axis C is perpendicular to the plane, through mass m1. ΙΑ IB m2 m1 m3 Ic m4 (a) IAarrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in the figure below. (Assume L = 5.20 m and R2 = 440 Ω.) (a) When the switch is in position a, for what value of R1 will the circuit have a time constant of 15.4 µs? (b) What is the current in the inductor at the instant the switch is thrown to position b?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What Are Sound Wave Properties? | Physics in Motion; Author: GPB Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GW6_U553sK8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY