
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl carbon and phosphonium ylide that are needed to synthesize the given compound has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Wittig reaction:
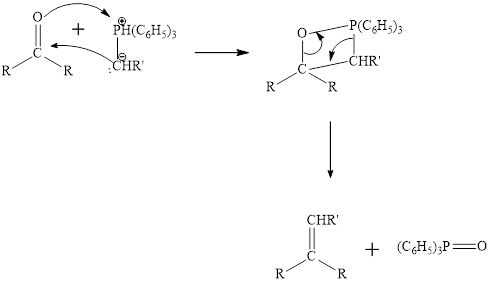
Witting reaction is the reaction between the carbonyl carbon of
Specific phosphonium ylide can be prepared for specific alkene synthesis. The triphenylphosphine is reacted with
The mechanism of the witting reaction is:
(b)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl carbon and phosphonium ylide that are needed to synthesize the given compound has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Wittig reaction:
Witting reaction is the reaction between the carbonyl carbon of aldehyde or ketone and the phosphonium ylide to give an alkene. Wittig reaction is a very useful method to synthesize the compound which can’t be synthesis easily by other methods.
Specific phosphonium ylide can be prepared for specific alkene synthesis. The triphenylphosphine is reacted with alkyl halide that has required numbers of carbon. A strong base such as sodium hydride or butyllithium is added to remove proton of carbon adjacent to the phosphorus atom. The carbon of prepared phosphonium ylide have nucleophilic character and get attached to the carbonyl carbon and carbonyl oxygen get attached to the positively charged phosphorous. Triphenylphosphine oxide gets eliminated resulting in the formation of the alkene.
The mechanism of the witting reaction is:

(c)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl carbon and phosphonium ylide that are needed to synthesize the given compound has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Wittig reaction:
Witting reaction is the reaction between the carbonyl carbon of aldehyde or ketone and the phosphonium ylide to give an alkene. Wittig reaction is a very useful method to synthesize the compound which can’t be synthesis easily by other methods.
Specific phosphonium ylide can be prepared for specific alkene synthesis. The triphenylphosphine is reacted with alkyl halide that has required numbers of carbon. A strong base such as sodium hydride or butyllithium is added to remove proton of carbon adjacent to the phosphorus atom. The carbon of prepared phosphonium ylide have nucleophilic character and get attached to the carbonyl carbon and carbonyl oxygen get attached to the positively charged phosphorous. Triphenylphosphine oxide gets eliminated resulting in the formation of the alkene.
The mechanism of the witting reaction is:

(d)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl carbon and phosphonium ylide that are needed to synthesize the given compound has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Wittig reaction:
Witting reaction is the reaction between the carbonyl carbon of aldehyde or ketone and the phosphonium ylide to give an alkene. Wittig reaction is a very useful method to synthesize the compound which can’t be synthesis easily by other methods.
Specific phosphonium ylide can be prepared for specific alkene synthesis. The triphenylphosphine is reacted with alkyl halide that has required numbers of carbon. A strong base such as sodium hydride or butyllithium is added to remove proton of carbon adjacent to the phosphorus atom. The carbon of prepared phosphonium ylide have nucleophilic character and get attached to the carbonyl carbon and carbonyl oxygen get attached to the positively charged phosphorous. Triphenylphosphine oxide gets eliminated resulting in the formation of the alkene.
The mechanism of the witting reaction is:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Use diagram to answer the following: 1.Is the overall rxn endo- or exothermic. Explain briefly your answer____________________2. How many steps in this mechanism?_____________3. Which is the rate determining step? Explain briefly your answer____________________4. Identify (circle and label) the reactants,the products and intermediate (Is a Cation, Anion, or a Radical?) Please explain and provide full understanding.arrow_forwardDraw the entire mechanism and add Curved Arrows to show clearly how electrons areredistributed in the process. Please explain and provide steps clearly.arrow_forward15) Create Lewis structure Br Brarrow_forward
- LIOT S How would you make 200. mL of a 0.5 M solution of CuSO4 5H2O from solid copper (II) sulfate? View Rubricarrow_forwardSteps and explantions pleasearrow_forwardMatch the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forward
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

