
Concept explainers
Catalytic antibodies catalyze a reaction by forcing the conformation of the substrate in the direction of the transition state. The synthesis of the antibody is carried out in the presence of a transition state analog—a stable molecule that structurally resembles the transition state. This causes an antibody to be generated that recognizes and binds to the transition state, thereby stabilizing it. For example, the following transition state analog has been used to generate a catalytic antibody that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the structurally similar ester:
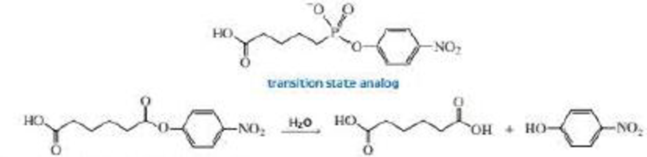
a. Draw a possible transition state for the hydrolysis reaction.
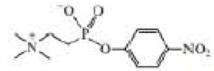
b. The following transition state analog is used to generate a catalytic antibody for the catalysis of ester hydrolysis. Draw the structure of an ester whose rate of hydrolysis would he increased by this catalytic antibody.
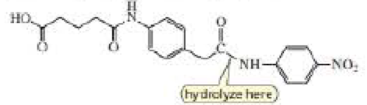
c. Design a transition state analog that catalyzes amide hydrolysis at the amide group indicated.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- List two ways that enzyme catalysis of a reaction is superior to normal conditions.arrow_forwardAmylase’ is an enzyme in our saliva that digests the ‘amylose’ protein in mouth. How could you justify the mechanism of enzymatic action using enzyme-catalyzed reaction models?arrow_forwardDraw a reaction coordinate diagram in which the structure of the transition site is more similar to the product of the reaction than to the reactant.arrow_forward
- The Michaelis-Menten equation is an expression of the relationship between the initial velocity Vo of an enzymatic reaction and substrate concentration [S]. There are three conditions that are useful for simplifying the Michaelis-Menten equation to an expression from which the effect of [S] on the rate can be more readily determined. Match the condition (e.g., [S] = Km) with the statement or statements that describe it. Doubling [S] will almost double the rate. Half of the active sites are occupied by substrate. About 90% of the active sites are occupied by substrate. Doubling [S] will have little effect on the rate. Less than 10% of the active sites are occupied by substrate. This condition will result in the highest rate. Answer Bank [S] = 0.1 Km [S] = Km [S] = 10 Kmarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forwardDraw the complete electron pushing mechanism that is enzyme catalyzed.arrow_forward
- If a fast step precedes a slow step in a two-step mecha-nism, how is the fast step affected? How is this effect used to determine the validity of the mechanism?arrow_forwardLet's try similar things with another enzyme! Here's one with a cool mechanism that makes an interesting product. Cys157 Cys157 Cys157 His296 His296 His296 OH HNN: HN, HN -CO2 CH2 Asn329 Asn329 Asn329- Cys157 His296 OH OH HNNH HC. Asn329 N Note that this figure is typical of those found in the biochemical literature in that it provides a somewhat abbreviated view of what is happening. For example, the arrows I have circled in red above for the fırst step need some sorting out. What mechanism is represented by these arrows? O a two step, addition/elimination reaction O an SN2 reaction O an SN1 reaction O nucleophilic aromatic substitution O electrophilic aromatic substitutionarrow_forwardChorismate mutase is an enzyme that promotes a pericyclic reaction by forcing the substrate to assume the conformation needed for the reaction. The product of the pericyclic reaction is prephenate that is subsequently converted into the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. What kind of a pericyclic reaction does chorismate mutase catalyze?arrow_forward
- Chemistry Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Suppose a sequence of enzymatically catalyzed reactions converts substrate A to final product D through a sequem reactions involving the production of intermediate products B and C as shown. Product D inhibits enzyme E₁. If the enzymes E₁-E3 are all present in a test tube and substrate A is added to the reaction mixture, how will the concentration of product D change? E₁ E₂ E3 A B C D increase to a fixed value first increase, then decrease remain at zero oscillate between zero and the concentration of A added increase to the concentration of A added Submit Answer Try Another Version 1 item attempt remainingarrow_forwardUnder acidic conditions (such as in your stomach) benzyl penicillin (BP) breaks down to three products which we will call A, B, and C in a parallel reaction with the following A BP B. values for the rate constants: ka = 7.0 × 10-4 sec-1; ks = 4.1 x 10-3 sec-1; and ke 5.7 x 10-3 sec-1. What is the yield of product A? In other words, after the reaction has reached completion what fraction of the product is present as compound-A?arrow_forwardReview the structure of the standard amino acids and listthose that are capable of acting as acids or bases in enzymecatalysis. Are there any that can function as either acids orbases?arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





