
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 15, Problem 61P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
To predict the products obtained upon the hydrolysis of aspartame in an aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid.
Concept introduction:
Amides are generally very stable compounds however upon acid or base catalyzed hydrolysis the amide bond
The general mechanism for the acid hydrolysis of amides is given as,
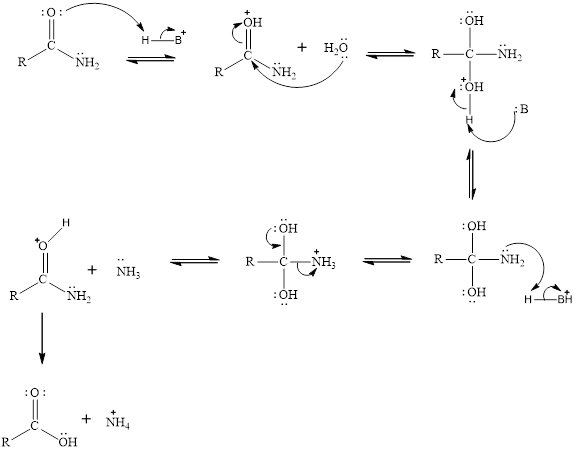
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
LIOT
S
How would you make 200. mL of a 0.5 M solution of CuSO4 5H2O from solid copper (II) sulfate?
View Rubric
Steps and explantions please
Match the denticity to the ligand.
Water
monodentate
✓
C₂O2
bidentate
H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate
x
EDTA
hexadentate
Question 12
Partially correct
Mark 2 out of 2
Flag question
Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below:
Na NC-Ag-CN]
Number of ligands:
20
Coordination number: 2✔
Geometry: linear
Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x
in 12
correct
out of 2
question
Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below.
Na NC-Ag-CN]
Number of ligands:
20
Coordination number: 2
Geometry: linear
0
Oxidation state of transition metal ion:
+3X
Chapter 15 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 15.1 - The aromas of many flowers and fruits are due to...Ch. 15.1 - Name the following:Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 3PCh. 15.2 - Which is longer, the carbon-oxygen single bond in...Ch. 15.2 - There are three carbon-oxygen bonds in methyl...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 6PCh. 15.4 - a. What is the product of the reaction of acetyl...Ch. 15.4 - What is the product of an acyl substitution...Ch. 15.5 - a. Which compound has the stretching vibration for...Ch. 15.5 - Using the pKa values listed in Table 15.1, predict...
Ch. 15.5 - Is the following statement true or false? If the...Ch. 15.6 - Starting with acetyl chloride, what neutral...Ch. 15.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 15.7 - Starting with methyl acetate, what neutral...Ch. 15.7 - We saw that it is necessary to use excess amine in...Ch. 15.7 - Prob. 17PCh. 15.7 - Which ester hydrolyzes more rapidly? a. methyl...Ch. 15.7 - a. state three factors that cause the uncatalyzed...Ch. 15.8 - Prob. 21PCh. 15.8 - Using the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed...Ch. 15.8 - Prob. 23PCh. 15.8 - Show the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed...Ch. 15.8 - Prob. 25PCh. 15.8 - Write the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed...Ch. 15.8 - Write the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed...Ch. 15.9 - Prob. 28PCh. 15.9 - Prob. 29PCh. 15.10 - Show how each of the following esters could he...Ch. 15.10 - Prob. 32PCh. 15.11 - Prob. 33PCh. 15.11 - Which of the following reactions leads to the...Ch. 15.12 - Prob. 35PCh. 15.12 - Prob. 36PCh. 15.13 - Prob. 37PCh. 15.14 - Prob. 38PCh. 15.14 - Prob. 39PCh. 15.15 - Prob. 40PCh. 15.15 - Which alkyl halides from the carboxylic acids...Ch. 15.16 - Prob. 43PCh. 15.16 - Prob. 44PCh. 15.16 - Prob. 45PCh. 15.17 - Prob. 46PCh. 15.18 - How could you synthesize the following compounds...Ch. 15 - Prob. 48PCh. 15 - Name the following:Ch. 15 - Prob. 50PCh. 15 - What compound are obtained from the fallowing...Ch. 15 - a. Rank the following esters in order of...Ch. 15 - Because bromocyclohexane is a secondary alkyl...Ch. 15 - a. Which compound would you expect to have a...Ch. 15 - How could you use 1H NMR spectroscopy to...Ch. 15 - Rank the following compounds in order of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 57PCh. 15 - Prob. 58PCh. 15 - Prob. 59PCh. 15 - A compound with molecular formula C5H10O2 gives...Ch. 15 - Prob. 61PCh. 15 - Prob. 62PCh. 15 - Prob. 63PCh. 15 - Prob. 64PCh. 15 - Prob. 65PCh. 15 - Prob. 66PCh. 15 - Two products, A and B, are obtained from the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 68PCh. 15 - Prob. 69PCh. 15 - Prob. 70PCh. 15 - Prob. 71PCh. 15 - Prob. 72PCh. 15 - When treated with an equivalent of methanol,...Ch. 15 - a. Identify the two products obtained from the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 75PCh. 15 - Prob. 76PCh. 15 - a. When a carboxylic acid is dissolved in...Ch. 15 - Prob. 78PCh. 15 - Identity the major and minor products of the...Ch. 15 - When a compound with molecular formula C11H14O2...Ch. 15 - Prob. 81PCh. 15 - Prob. 82PCh. 15 - Prob. 83PCh. 15 - The 1H NMR spectra for two esters with molecular...Ch. 15 - Show how the following compounds could be prepared...Ch. 15 - Prob. 86PCh. 15 - Prob. 87PCh. 15 - The intermediate shown here is formed during the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 89PCh. 15 - Propose a mechanism that accounts for the...Ch. 15 - Catalytic antibodies catalyze a reaction by...Ch. 15 - Prob. 92P
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole