
Concept explainers
A muscle enzyme called ME
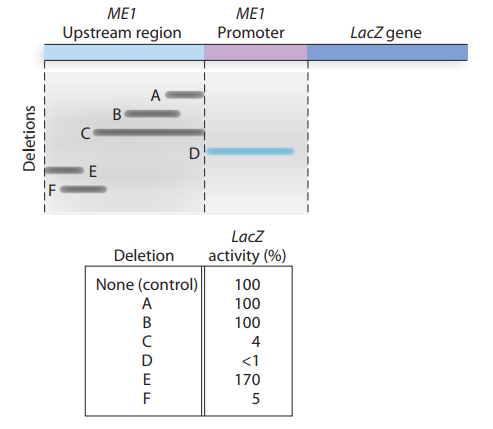
a. Does this information indicate the presence of enhancer and
b. Why does deletion D effectively eliminate transcription oflacZ?
c. Given the information available from deletion analysis, can you give a molecular explanation for the observation that ME
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- The following diagram show what is required for an active promoter of a gene of interest, where:A1 = Activator 1A2 = Activator 2Med = MediatorRep = Repressor Based on the following data, predict: Chromatin conformation Methylation state of the proximal promoter If protein A1 is present or absent If protein A2 is present or absent If the mediator is present or absent If the repressor is absence or present If this gene is likely to be transcribed or notPlease note that this is an "all or nothing" bonus question, and no partial credit will be awarded. Selecting all answers will result in zero points awarded. Selecting at least one incorrect answer will result in zero points being awarded. Question 28 options: Euchromatin Heterochromatin Methylated promoter Unmethylated promoter Activator A1 present Activator A1 absent Activator A2 present…arrow_forwardThere are similarities and differences during regulation of gene expression in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Promoters, transcription factors and RNA polymerase are essential elements in transcription but their properties and function may differ.a) Predict the outcome or consequences of mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II in eukaryote without the presence of transcription factors (TF).arrow_forwardDiscuss the following argument: “if the expression of every gene depends on a set of transcription regulators, then the expression of these regulators must also depend on the expression of other regulators, and their expression must depend on the expression of still other regulators, and so on. cells would therefore need an infinite number of genes, most of which would code for transcription regulators.” how does the cell get by without having to achieve the impossible?arrow_forward
- Gal4 is a transcription factor that activates transcription of galactose metabolism genes in yeast. These genes are ‘turned on’ when yeast cells need to metabolize galactose. To identify promoter sequences necessary for regulation of transcription of GAL1, reporter gene fusions were made and introduced into yeast cells. Deletions of GAL1 promoter were cloned upstream of LacZ gene. β-Galactosidase activity was measured in presence of galactose. Shown below is a representation of the results obtained. In the diagrams below (not to scale!): • Construct 1 contains ~ 130bp of the promoter, which is predicted to have all the predicted/putative proximal promoter elements (indicated by the solid boxes) needed to regulate transcription of GAL1.• The stippled box is the core promoter.• The arrow represents the transcriptional start site for the reporter gene Lac Z• Number of + signs represents level of transcription• Star represents a mutation in DNA sequence at that location (few nucleotides…arrow_forwardAn enhancer is surrounded by four genes (A, B, C, and D), as shown in the accompanying diagram. An insulator lies between gene C and gene D. On the basis of the positions of the genes, the enhancer, and the insulator, the transcription of which genes is most likely to be stimulated by the enhancer? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardIn the sea urchin, early development may occur even in the presence of actinomycin D, which inhibits RNA synthesis. However, if actinomycin D is present early in development but is removed a few hours later, all development stops. In fact, if actinomycin D is present only between the sixth and eleventh hours of development, events that normally occur at the fifteenth hour are arrested. What conclusions can be drawn concerning the role of gene transcription between hours 6 and 15?arrow_forward
- A strain of Arabidopsis thaliana possesses a mutation in the APETALA2 gene. As a result of this mutation, much of the 3′ UTR of the mRNA transcribed from the gene is deleted. What is the most likely effect of this mutation on the expression of the APETALA2 gene?arrow_forwardConsider this list (below) of steps involved in transcription. These steps are out of order. TRANSCRIPTION: 1. mRNA travels through a nuclear pore and enters the cytoplasm 2. the mRNA polymerase attaches at the start of a specific gene 3. RNA polymerase reads the gene surface4. a transcription factor bonds to a promoter site5. DNA molecule is unwound 6. a complimentary mRNA is produced What is the correct order of this transcription?arrow_forwardExamine Figure 17.7. What would be the effect on transcription if a mutation occurred in the gene that encodes GAL3, so that no functional GAL3 was produced?arrow_forward
- Progesterone is a steroid hormone (also described as a ligand) that prepares the body for pregnancy. It binds to the progesterone receptor (PR) protein in the cytoplasm of various cells. Ligand bound PR acts as a transcriptional activator, binds to the DNA in the promoter region of several genes and leads to transcriptional activation of these genes. Ligand bound PR has been shown to increase the expression of a gene, FKBP5. You are studying the activity of wild-type (WT) and mutant PR in cells by examining expression of FKBP5. Results are obtained as shown in the figure below, where the asterisk indicates when progesterone was (or was not) added to the cells. From the results, which of the following statements can be concluded? WT PR without progesterone WT PR with progesterone Time Time mutant PR without progesterone mutant PR with progesterone Time Time The wild-type PR is unable to increase FKBP5 expression in the absence of ligand The wild-type PR increases FKBP5 expression after…arrow_forwardCD3 is a signaling protein that is typically found only in the plasma membrane of immune system T lymphocytes. CD3 is composed of several different polypeptides, including a gamma chain, CD3γ. Scientists analyzed the promoter of the CD3γ chain gene for regulatory sequences that might have positive or negative effects on expression of the gene. The scientists cloned fragments of the CD3γ gene that included the first transcribed nucleotides plus up to 789 nucleotides of upstream regulatory sequences into plasmids in which the gene for the firefly enzyme luciferase immediately follows the fragments. The plasmids were then introduced into a line of T lymphocytes (Figure 1), and the cells were allowed to grow for a short while. Because the regulatory sequences of the CD3γ gene immediately precede the luciferase gene in the plasmids, the activity, either positive or negative, of the regulatory sequences affected the amount of luciferase gene expression by the T lymphocytes. Luciferase…arrow_forwardLack of phosporylation of the C-terminal domian of Pol Il will result in which of the following? O Assembly of the full set of general transcription factors plus Pol II at the promoter, but unphosphorylated Pol II cannot leave the promoter region No assembly of the general transcription factors at a promoter No binding of Pol II at a promoter The unphosphorylated Pol II can initiate and elongate but cannot terminatearrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





