
Concept explainers
A hereditary disease is inherited as an autosomalrecessive trait. The wild
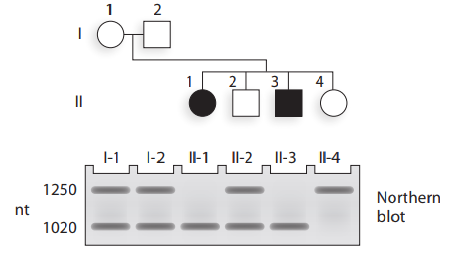
a. Identify the genotype of each family member, using the sizes of mRNAs to indicate each allele. (For example, a person who is homozygous wild type is indicated as
b. Based on your analysis, what is the most likely molecular abnormality causing the disease allele?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- a protein with a molar mass of 3800 g/mol is given. determine the number of nucleotides contained in the gene that encoded this protein, knowing that: 20% of it are introns, the mass of a nucleotide is 300 g/mol and the mass of an amino acid is 110 g/molarrow_forwardThe protein encoded by the cystic fibrosis gene is 1480amino acids long, yet the gene spans 250 kb. How is thisdifference possible?arrow_forwardA double mutant produced by uneven crossing-over contains two single nucleotide mutations that result in frame shifts and are separated by about 20 base pairs. The first is an insertion, while the second is a deletion. The amino acid sequences of the wildtype and mutant polypeptide in this region of the protein are as follows: Wildtype: Lys – Lys – Tyr – His – Gln – Trp – Thr – Cys – AsnDouble Mutant: Lys – Gln – Ile – Pro – Pro – Val – Asp – Met – Asn a) What are the original and double mutant mRNA sequences. You may find it useful to use the conventional symbols Y for pyrimidine, R for purine, N for any nucleotide, and H for A,C, or T. 2. b) Which nucleotide was inserted? 3. c) Which nucleotide was deleted?arrow_forward
- The mRNA sequence 5' AUG AAA CAG GGA UAA 3' encodes a particular peptide of interest to your research team. You have identified a new alternate allele of the sequence 5' AUG AAG CAG GGA UAA 3'. What type of mutation does this alternate sequence illustrate?arrow_forwardA gene encodes a protein with the following amino acid sequence: Met-Trp-His-Arg-Ala-Ser-Phe A mutation occurs in the gene. The mutant protein has the following amino acid sequence: Met-Trp-His-Ser-Ala-Ser-Phe An intragenic suppressor mutation restores the amino acid sequence to that of the original protein: Met-Trp-His-Arg-Ala-Ser-Phe Give at least one example of base changes that could produce the original mutation and the intragenic suppressor.arrow_forwardA gene encodes a protein with the following amino acid sequence: Met-Trp-His-Arg-Ala-Ser-Phe A mutation occurs in the gene. The mutant protein has the following amino acid sequence: Met-Trp-His-Ser-Ala-Ser-Phe An intragenic suppressor mutation restores the amino acid sequence to that of the original protein: Met-Trp-His-Arg-Ala-Ser-Phe Give at least one example of base changes that could produce the original mutation and the intragenic suppressor. (Consult the genetic code in Figure 15.10.)arrow_forward
- A gene contains 30% thymine. What is the percentage of pyrimidines present in this segment? Explain.arrow_forwardTay Sachs disease is an autosomal recessive disease in which a protein – Hex A - is abnormal. To make the Hex A protein: The promoter and transcription termination sites are 33,000 base pairs apart. The Hex A protein has 600 amino acids 5’ and 3’ UTR’s are each 500 bp long. a)How many base pairs would you expect in the final mRNA? Show your work b)How many bases were spliced out? Show your workarrow_forwardA normal hemoglobin protein has a glutamic acid at position 6; in sickle-cell hemoglobin, this glutamic acid has been replaced by a valine. List all the possible mRNA codons that could be present for each type of hemoglobin. Can a single base change result in a change from Glu to Val in hemoglobin?arrow_forward
- Here is a eukaryotic gene. The numbers given are base pairs of exon and intron. How long in bases will the pre mRNA transcript be? Explain briefly. What is the maximum number of amino acids that could make up the protein product from the final mRNA? Explain briefly.arrow_forwardGiven the following Wild Type and Mutated DNA sequences: 1.) Identify where the base pair change occurs ( what letter changed?) 2.) For BOTH sequences, write the mRNA strands, define the codon regions and amino acid sequences. 3.) Describe what kind of mutation has occurred (missense, nonsense, or silent), and what effect this may have on the protein. Wild Type DNA Sequence: 3' - AGGCTCGCCTGT - 5' Mutated DNA Sequence: 3' - AGTCTCGCCTGT - 5'arrow_forwardYou have created three different mutations in the histoneH1 protein (HISmut1, HISmut2, HISmut3), and each of these mutations eliminate a stretch of 5 amino acids from the primary sequence. Based on the description of where you find the mutant histoneH1 proteins when you look inside a cell in each of the cases below, describe 1) what the function is of the amino acids that were removed, and 2) what is not happening with the mutant histoneH1 protein that does happen with wild type H1: 1. HISmut2 protein is found in the cytoplasm, and never in the nucleus. 2. HISmut1 protein is found in only briefly in the cytoplasm because it is very quickly sent to the proteasome. 3. HISmut3 protein is found floating freely throughout the nucleoplasm.arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
