
Interpretation:
Vapor pressure of solution is lower than pure solvent, needs to be described on particle basis.
Concept introduction:
Solution can be defined as a homogenous mixture that consist of two components solute and solvent.
Solvent: Solvent can be defined as a component that dissolves other component.
Solute: Solute can be defined as a component that is dissolved in the other component, solvent.
During solution formation, solute and solvent particles collide with each other, so that the solute gets dissolves in solvent.
Vapor pressure:
Vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a liquid particle that have entered the gaseous state in a closed container.
Answer to Problem 42SSC
Solution consists of two components- solute and solvent, so in a solution, solvent contains a solute, so lesser solventparticles occupy the surface and lesser particlesescape into the gaseous state that’s why vapor pressure of solution is lower than pure solvent
Vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a liquid particle that have entered the gaseous state in a closed container. When a non-volatile solute is added in solvent, it lowers the vapor pressure of the solvent. The particles escape the liquid phase at its surface that lowers the vapor pressure while in a pure solvent, the particles occupied the whole surface area, that is more particle will escape in gaseous state and vapor pressure increases.
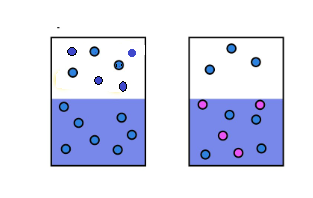
Pure solvent Solution(solute+solvent)
Explanation of Solution
Vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a liquid particle that have entered the gaseous state in a closed container. When a non-volatile solute is added in solvent, it lowers the vapor pressure of the solvent. The particles escape the liquid phase at its surface that lowers the vapor pressure while in a pure solvent, the particles occupied the whole surface area, that is more particle will escape in gaseous state and vapor pressure increases.

Pure solvent Solution(solute+solvent)
Chapter 14 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- When talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?arrow_forwardUsing the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$arrow_forwardIndicate characteristics of oxodec acid.arrow_forward
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





