
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of
Concept Introduction:
Molecular orbital theory is a method that shows that how atomic orbitals combine with other or with each other to form bonding and antibonding orbitals. It is used to determine the molecular structure of a molecule. The
(a)
Answer to Problem 48E
The electronic configuration of
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
The molecular orbital diagram for
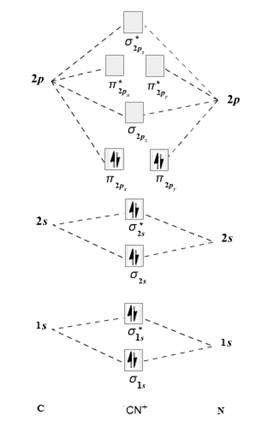
Therefore, the electronic configuration of
The bond order is calculated as follows:
Substitute electrons in antibonding MO and bonding MO for
Therefore, the bond order of
(b)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of
Concept Introduction:
Molecular orbital theory is a method that shows that how atomic orbitals combine with other or with each other to form bonding and antibonding orbitals. It is used to determine the molecular structure of a molecule. The atomic number represents the number of electrons in an atom.
(b)
Answer to Problem 48E
The electronic configuration of
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
The molecular orbital diagram for
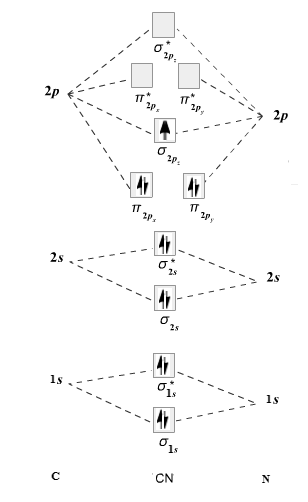
Therefore, the electronic configuration of
The bond order is calculated as follows:
Substitute electrons in antibonding MO and bonding MO for
Therefore, the bond order of
(c)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of
Concept Introduction:
Molecular orbital theory is a method that shows that how atomic orbitals combine with other or with each other to form bonding and antibonding orbitals. It is used to determine the molecular structure of a molecule. The atomic number represents the number of electrons in an atom.
(c)
Answer to Problem 48E
The electronic configuration of
The order of increasing bond length is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
The molecular orbital diagram for
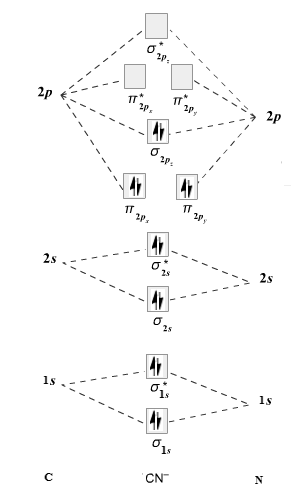
Therefore, the electronic configuration of
The bond order is calculated as follows:
Substitute electrons in antibonding MO and bonding MO for
Therefore, the bond order of
The relationship among bond energy, bond length and bond order is as follows:
The bond order of
The bond order is directly proportional to bond energy. Therefore, the order of increasing bond energy is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- > H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardThe answer is shown. What is the reaction mechanism to arrive at the answer?arrow_forward
- no Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardConsider the following nucleophilic substitution reaction. The compound listed above the arrow is the solvent for the reaction. If nothing is listed over the arrow, then the nucleophile is also the solvent for the reaction. Part 1 of 2 Br CH,CN + I¯ What is the correct mechanism for the reaction? Select the single best answer. @SN2 ○ SN 1 Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Draw the products for the reaction. Include both the major organic product and the inorganic product. If more than one stereoisomer is possible, draw only one stereoisomer. Include stereochemistry where relevant. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X હૈarrow_forward20.33 Think-Pair-Share (a) Rank the following dienes and dienophiles in order of increasing reactivity in the Diels-Alder reaction. (i) CO₂Et (ii) COEt || CO₂Et MeO MeO (b) Draw the product that results from the most reactive diene and most reactive dienophile shown in part (a). (c) Draw a depiction of the orbital overlap involved in the pericyclic reaction that oc- curs between the diene and dienophile in part (b). (d) Is the major product formed in part (b) the endo or exo configuration? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





