
Concept explainers
a.
Interpretation:
Given monosaccharides has to be classified based on the number of carbon atoms present in the chain and also the carbonyl group.
Concept Introduction:
Simplest carbohydrates are known as monosaccharides. They contain three to six carbons generally in a chain form with a carbonyl group present in the terminal or the adjacent carbon atom from the terminal. Monosaccharides that have the carbonyl group at the terminal carbon atom
The number of carbon atoms present in the chain characterize the monosaccharide. They are given below.
- Carbon chain with three carbon atoms is triose.
- Carbon chain with four carbon atoms is tetrose.
- Carbon chain with five carbon atoms is as pentose.
- Carbon chain with six carbon atoms is as hexose.
a.
Explanation of Solution
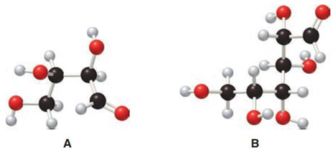
Structure of monosaccharide A is drawn as shown below.
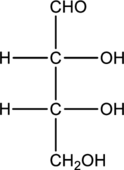
The carbonyl group is present on the terminal carbon atom
Structure of monosaccharide B is drawn as shown below.
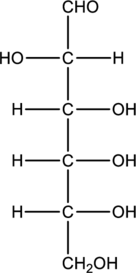
The carbonyl group is present on the terminal carbon atom
b.
Interpretation:
Chiral centers has to be located in the given compounds.
b.
Explanation of Solution
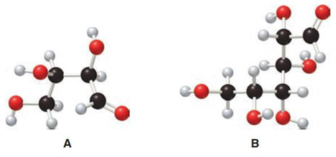
Structure of monosaccharide A is drawn as shown below.
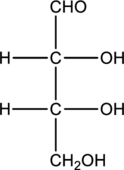
The two carbon atoms that are present in the middle is found to be bonded with four different groups. Thus, there are two chiral centers present in monosaccharide A. This is depicted as follows.
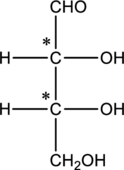
Structure of monosaccharide B is drawn as shown below.
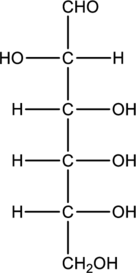
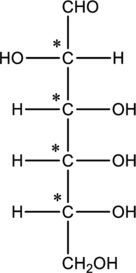
The four carbon atoms that are present in the middle is found to be bonded with four different groups. Thus, there are four chiral centers present in monosaccharide B. This is depicted as follows.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
- Can I please get help with identifying these?arrow_forward4. Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M acetic acid (CH3COOH) solution if the Ka of acetic acid = 1.8 x 10-5arrow_forwardDraw the Zaitsev product of the dehydration of this alcohol. + I X 5 OH ざ~ TSOH Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Please help with identifying these.arrow_forwardFor the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forwardCan I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





