
a.
To find the radius of the
a.
Answer to Problem 40WE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given equation is
Calculation:
The radius of the circle can be obtained as
The standard form of the equation of a circle with center is
Where
Comparing the given equation to the standard form of the equation
The first equation is
And the second equation is
Hence,
The value of
b.
To find the distance between the centers of the circle
b.
Answer to Problem 40WE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given equation is
Calculation:
The distance between the centers of the circle can be obtained as
The standard form of the equation of a circle with center is
Where
Comparing the given equation to the standard form of the equation
The first equation has center is
And the second equation has center is
Therefore,
Hence,
The value of
c.
To explain the circle must be externally tangent
c.
Answer to Problem 40WE
The circle must be externally tangent because the distance between the centers of the circle is equal to difference of the radius
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given equation is
The circle must be externally tangent can be explain as
In previous part of the question we find the values of
The circle must be externally tangent because the distance between the centers of the circle is equal to difference of the radius
Hence,
The circle must be externally tangent because the distance between the centers of the circle is equal to difference of the radius
d.
To sketch the graph of the circle
d.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given equation is
Graph : Sketch the graph using graphing utility.
Step 1: Press WINDOW button to access the Window editor.
Step 2: Press
Step 3: Enter the expression
Step 4: Press GRAPH button to graph the
The graph is obtained as:

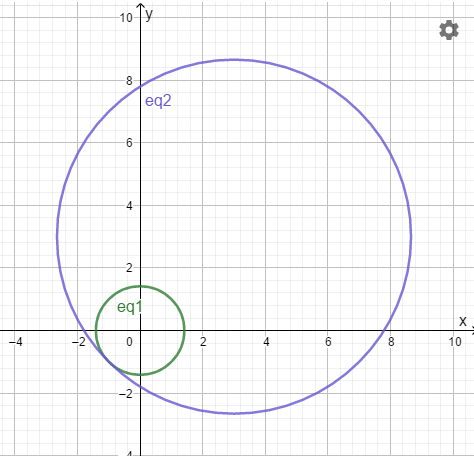
Interpretation :
From the above graph, it can be observed that the radius of the circle are
Chapter 13 Solutions
McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

