
Concept explainers
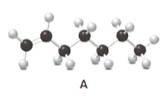
Answer the following questions about compound A, represent in the given ball-and-stick model.
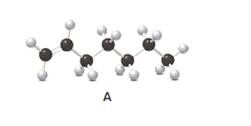
- Convert A to a condensed structure and give its IUPAC name.
- What product is formed when A is treated with H2 in the presence of metal catalyst?
- What product is formed when A is treated with H2O in the presence of H2SO4?
- What
polymer is formed when A ispolymerized ?
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of the molecule A should be converted to a condensed structure and IUPAC name of the molecule should be given.
 = (
= (
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
In alkene nomenclature, the longest C chain will be considered as the parent/ main C chain. At the end of the alkane suffix -ene is added. The longest chain which includes the carbon-carbon double bond will be considered as the main carbon chain. The numbering of the main C chain is starting from the first substituent by giving the lower number to that substituent and as well as the double bond should get the lower number. All the substituents should be numbered and named. Two or more identical substituents should be indicated by using appropriate prefixes as di-. Names of the substituents should be alphabetized. Each substituent should have a position number which is mentioned in the main C chain.
Answer to Problem 95P
Condensed structure −
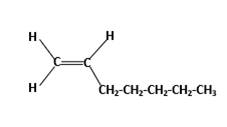
IUPAC name −Heptene
Explanation of Solution
In alkenes, there is a carbon-carbon double bond and different groups are connected to the two carbons. In most of the alkenes; out of four binding positions of carbon-carbon double bond, two of them are bind with two hydrogen atoms and the other two binding positions bind with two different alkyl groups. In this molecule, carbon atoms are represented in black and hydrogen atoms are represented in white color. The structure of a chemical compound is the arrangement of atoms and bonds in the space.
Condensed structure −
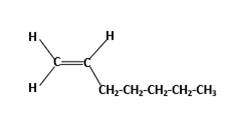
In this molecule, the main carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon double bond is a seven-membered chain and there are no substituents in this molecule. According to the numbering of the main chain double bond gets the lowest number and it is number 1. Hence, the IUPAC name of the molecule is heptene.
(b)
Interpretation:
The resulting product should be identified after reacting
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that contain a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 95P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
(c)
Interpretation:
The resulting product should be identified after reacting
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 95P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Refer to the below reaction;
(d)
Interpretation:
The resulting polymer should be identified after polymerization of
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond inside a molecule.
Polymers are high molecular weight macromolecules which formed from covalently bonded monomer molecules.
Answer to Problem 95P
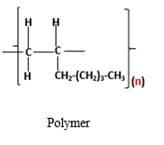
Explanation of Solution
Polymers are high molecular weight macromolecules which formed from covalently bonded monomer molecules. When forming polymers from alkene monomers, the weak bond which is in the carbon-carbon double bond is broken and new strong bond will form to connect the monomer molecules together. Hence; weak bond of the carbon-carbon double bond of

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- Q9. The insecticide DDT (in the box below) is useful in controlling mosquito populations and has low toxicity to humans, but is dangerous to birds and fish. Hoping to alleviate the dangers, little Johnny Whizbang, an aspiring chemist, proposes a new version of DDT ("Bromo-DDT") and shows his synthesis to his boss. Will Johnny Whizbang's synthesis work? Or will he be fired? Assume there is an excess of bromine and polybrominated products can be separated. Explain why. CH3 Br2, light CBR3 ok-ok Br Br Br Br CI "Bromo-DDT" CCl 3 DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) CIarrow_forwardDifferentiate the terms Monotectic, Eutectic, Eutectoid, Peritectic, Peritectoid.arrow_forwardQ5. Predict the organic product(s) for the following transformations. If no reaction will take place (or the reaction is not synthetically useful), write "N.R.". Determine what type of transition state is present for each reaction (think Hammond Postulate). I Br₂ CH3 F2, light CH3 Heat CH3 F₂ Heat Br2, light 12, light CH3 Cl2, lightarrow_forward
- a. For the following indicated bonds, rank them in order of decreasing AH° for homolytic cleavage. Based on your answer, which bond would be most likely to break homolytically? (a) (c) H3C CH3 .CH3 CH3 CH3 (b) Page 1 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 Recitations b. Draw all the possible radical products for 2-methylbutane, and determine which bond is most likely to be broken.arrow_forwardA 5-m³ rigid tank contains 5 kg of water at 100°C. Determine (a) the pressure, (b) the total enthalpy, and (c) the mass of each phase of water.arrow_forwardQ8. Draw the mechanism for this halogenation reaction. Show all steps including initiation, propagation, and recombination. Cl₂, hv CI Br Br2, hv, heatarrow_forward
- Q6. Given the following alkanes, draw the most likely product to form upon monohalogenation with Br2 (keep in mind that this may not be the only product to form though). If the reaction was performed with Cl2 would there be more or less selectivity in the desired product formation? Why? (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardQ4. Radicals a. For the following indicated bonds, rank them in order of decreasing AH° for homolytic cleavage. Based on your answer, which bond would be most likely to break homolytically? (c) CH3 CH3 H3C CH3 (a) CH3 (b)arrow_forwardQ1. (a) Draw equations for homolytic and heterolytic cleavages of the N-H bond in NH3. Use curved arrows to show the electron movement. (b) Draw equations for homolytic and heterolytic cleavages of the N-H bond in NH4*. Use curved arrows to show the electron movement.arrow_forward
- ohing Quantitative Relationships 425 The specific heats and atomic masses of 20 of the elements are given in the table below. Use a graphical method to determine if there is a relationship between specific heat and the atomic mass. a. b. C. d. e. If your graphs revealed relationship between specific heat and atomic revealed a mathematical mass, write down an equation for the relationship. Comment on the usefulness of the determination of specific heat as a method for identifying an element. Would specific heat alone give you much confidence with regard to the identity of the element? If you think measurement of another property would be needed to support an identification, what property would you measure and why? The elements listed in the table are all selected metals. The values for nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine and neon are 1.040, 0.918, 0.824 and 1.030 J/g K respectively. Do these elements fit your equation? element atomic mass specific heat (almol) (Jig K) magnesium 24.305 1.023…arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand rating and don't use Ai solutionarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning


