
Anethole, the major constituent of anise oil, is used in licorice-flavored sweets and flavored brandy. Answer the following questions using the ball-and-stick model of anethole.
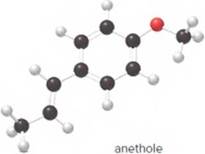
- What is the molecular formula of anethole?
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula of anethole should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The numbers and kinds of atoms present in a molecule of a compound are given by a formula said to be a molecular formula. This formula of a molecule gives the definite number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
Answer to Problem 19P
The molecular formula of anethole is C10H12O.
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-and-stick model of anethole is:
In ball-and-stick model, the black ball represents carbon, C atom, white ball represents hydrogen, H atom, and red ball represents oxygen, O atom.
The number of each atom in the ball-and-stick model is:
Carbon atoms = 10
Hydrogen atoms = 12
Oxygen atom = 1
Thus, the molecular of anethole is C10H12O.
(b)
Interpretation:
The functional group(s) in anethole should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
A group of atoms or an atom which is responsible for the characteristic reactions of a particular compound is said to be the functional group. Every functional group shows distinctive chemical properties irrespective to the moiety to which it is attached.
Answer to Problem 19P
The functional group(s) in anethole is ether.
Explanation of Solution
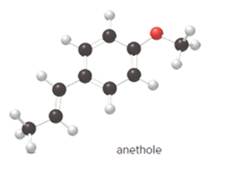
The given ball-and-stick model of anethole is:
When the oxygen atom is connected to two alkyl or aryl groups with general formula R-O-R' such class of compounds is known as ether.
Since, in anethole compound the oxygen atom is bonded to an aryl and an alkyl group so, the functional group(s) in anethole is ether.
(c)
Interpretation:
The carbon-carbon double bond in anethole should be labeled as cis or trans.
Concept Introduction:
The molecule with same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in spatial arrangements of atoms in the molecule are said to be geometric isomers of each other.
Answer to Problem 19P
The carbon-carbon double bond in anethole is labeled as trans.
Explanation of Solution
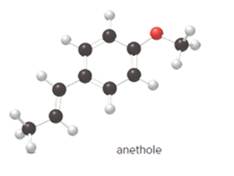
The given ball-and-stick model of anethole is:
Geometric isomerism, or cis-trans, isomerism is most common in alkenes. The two forms exist due to no free rotation about carbon-carbon double bond. It exists only when the double bonded carbon atoms are joined to two different groups or atoms.
In cis- isomer, the two identical groups or atoms are close to each other whereas in trans- isomer two identical groups or atoms are farther apart.
Since, in the given molecule the groups attached to carbon-carbon double bonded are farther apart from each other so, the carbon-carbon double bond in anethole is trans.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of anethole should be drawn and each carbon should be labeled as trigonal planar or tetrahedral.
Concept Introduction:
In structural formula, the bonding and type of bonds which holds the atoms in molecule together are shown.
Answer to Problem 19P
The structure of anethole is:
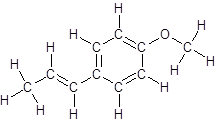
Labelling of each carbon is:
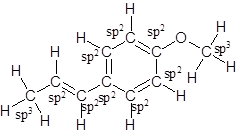
Explanation of Solution
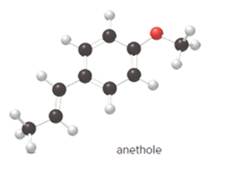
The given ball-and-stick model of anethole is:
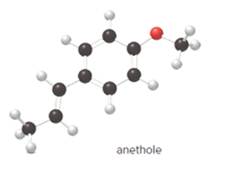
In ball-and-stick model, the black ball represents carbon, C atom, white ball represents hydrogen, H atom, and red ball represents oxygen, O atom.
So, the structure of anethole is:
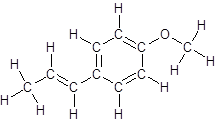
In the structure of anethole, there are 10 C atoms, 2 of which them are in CH3- groups which has four electron groups around the central carbon atom, so the electron group arrangement is tetrahedral, sp3hybridized. The 8 carbon atoms have three electron groups around the central carbon atom, so the electron group arrangement is trigonal planar, sp2hybridized.
Thus, the electron group arrangement of all the 10 carbon atoms in anethole is:
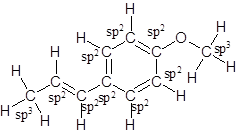
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- Predict the major organic product(s), if any, of the following reactions. Assume all reagents are in excess unless otherwise indicated.arrow_forwardHow many signals would you expect to find in the 1 H NMR spectrum of each given compound? Part 1 of 2 2 Part 2 of 2 HO 5 ☑ Х IIIIII***** §arrow_forwardA carbonyl compound has a molecular ion with a m/z of 86. The mass spectra of this compound also has a base peak with a m/z of 57. Draw the correct structure of this molecule. Drawingarrow_forward
- Can you draw this using Lewis dot structures and full structures in the same way they are so that I can better visualize them and then determine resonance?arrow_forwardSynthesize the following compound from cyclohexanol, ethanol, and any other needed reagentsarrow_forwardFor a titration of 20.00 mL of 0.0500 M H2SO4 with 0.100 M KOH, calculate the pH at each of the following volume of KOH used in the titration: 1) before the titration begin; 2) 10.00 mL; 3) 20.00 mL; 4) 30.00 mL. Ka2 = 1.20×10-2 for H2SO4.arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s) Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps Problem 73 of 10 Drawing Amows ro HO Donearrow_forward12. Synthesize the following target molecules (TMs) using the specified starting materials. .CI a) HO3S SM TM b) HO- SMarrow_forwardFor a titration of 20.00 mL of 0.0500 M H2SO4 with 0.100 M KOH, calculate the pH at each of the following volume of KOH used in the titration: 1) before the titration begin; 2) 10.00 mL; 3) 20.00 mL; 4) 30.00 mL. Ka2 = 1.20×10-2 for H2SO4.arrow_forward
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure name show work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardA Elschboard Part of SpeechT-D Alt Leaming App app.aktiv.com Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided resonance structures, draw the curved electron- pushing arrows to show the interconversion between resonance hybrid contributors. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Include all lone pairs and formal charges in the structures. Problem 45 of 10 I Select to Add Arrows N Please selarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





