
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given molecule has to be assigned including the prefix cis- or trans-.
Concept Introduction:
- The suffix –ane has to be replaced with the suffix –ene. This is used to indicate the presence of double bond.
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has to be chosen that contains both carbon atoms of the double bond.
- The parent carbon chain has to be numbered in a way so that the numbering begins at the end near to the double bond. In case if the double bond is equidistant from both ends, then numbering has to be done from the end that is closer to substituents.
- The position of the double bond has to be given a single number which is lower‑numbered carbon atom that is present in the double bond.
- Suffixes like –diene, -triene, -tetrene, and so on are used when the compound contains more than one double bond.
- In case of cycloalkenes which do not have any substitution, the numbering is not needed to locate the double bond because the bond is assumed to be between the carbons 1 and 2.
- In case if substituents are present in cycloalkene, then the double‑bonded carbon
atoms are numbered 1 and 2 in a direction where the substituent gets the lower number. - If the cycloalkenes contain more than one double bond, then one double bond is assigned the numbers 1 and 2 followed by the other double bond so that the lowest number possible is given.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. To indicate a double bond between carbon atom, double line is used.
If stereoisomers are possible for the alkene, the stereoinformation is shown in the IUPAC name by adding prefix cis- or trans- with respect to the groups present on the same side of double bond or opposite side of double bond.
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.49EP
The IUPAC name for the given compound is cis-2-pentene.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
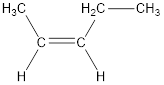
The longest continuous carbon chain present in the given compound is five carbon atoms. Hence, the parent
As the given compound contains a double bond, the suffix –ane is replaced by –ene. Therefore, the name obtained is pentene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the carbon atoms present in the double bond gets the least numbering. Therefore, the name of the given compound is 2-pentene.
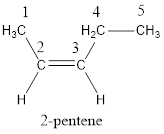
In order to include the stereo information, the groups attached to the double‑bonded carbon atoms are looked into.
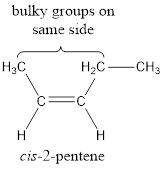
The bulky groups are present on same side of the double bond. Hence, the configuration of the given molecule is cis-. Therefore, the IUPAC name can be given as cis-2-pentene.
IUPAC name for the given molecule is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given molecule has to be assigned including the prefix cis- or trans-.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature for alkene: There are about eight rules to be followed in giving IUPAC name for alkene.
- The suffix –ane has to be replaced with the suffix –ene. This is used to indicate the presence of double bond.
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has to be chosen that contains both carbon atoms of the double bond.
- The parent carbon chain has to be numbered in a way so that the numbering begins at the end near to the double bond. In case if the double bond is equidistant from both ends, then numbering has to be done from the end that is closer to substituents.
- The position of the double bond has to be given a single number which is lower‑numbered carbon atom that is present in the double bond.
- Suffixes like –diene, -triene, -tetrene, and so on are used when the compound contains more than one double bond.
- In case of cycloalkenes which do not have any substitution, the numbering is not needed to locate the double bond because the bond is assumed to be between the carbons 1 and 2.
- In case if substituents are present in cycloalkene, then the double‑bonded carbon atoms are numbered 1 and 2 in a direction where the substituent gets the lower number.
- If the cycloalkenes contain more than one double bond, then one double bond is assigned the numbers 1 and 2 followed by the other double bond so that the lowest number possible is given.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. To indicate a double bond between carbon atom, double line is used.
If stereoisomers are possible for the alkene, the stereoinformation is shown in the IUPAC name by adding prefix cis- or trans- with respect to the groups present on the same side of double bond or opposite side of double bond.
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.49EP
The IUPAC name for the given compound is trans-1-bromo-2-iodoethene.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
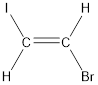
The longest continuous carbon chain present in the given compound is two carbon atoms. Hence, the parent alkane is ethane.
As the given compound contains a double bond, the suffix –ane is replaced by –ene. Therefore, the name obtained is ethene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the carbon atoms present in the double bond gets the least numbering. This is followed by the substituents present in the given molecule. It is found that an iodine atom is present on the second carbon atom and bromine atom is present on the first carbon atom. Therefore, the name of the given compound is 2-pentene.
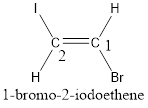
In order to include the stereo information, the groups attached to the double‑bonded carbon atoms are looked into.
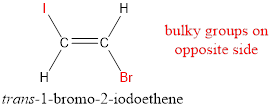
The bulky groups are present on opposite side of the double bond. Hence, the configuration of the given molecule is trans-. Therefore, the IUPAC name can be given as trans-1-bromo-2-iodoethene.
IUPAC name for the given molecule is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given molecule has to be assigned including the prefix cis- or trans-.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature for alkene: There are about eight rules to be followed in giving IUPAC name for alkene.
- The suffix –ane has to be replaced with the suffix –ene. This is used to indicate the presence of double bond.
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has to be chosen that contains both carbon atoms of the double bond.
- The parent carbon chain has to be numbered in a way so that the numbering begins at the end near to the double bond. In case if the double bond is equidistant from both ends, then numbering has to be done from the end that is closer to substituents.
- The position of the double bond has to be given a single number which is lower‑numbered carbon atom that is present in the double bond.
- Suffixes like –diene, -triene, -tetrene, and so on are used when the compound contains more than one double bond.
- In case of cycloalkenes which do not have any substitution, the numbering is not needed to locate the double bond because the bond is assumed to be between the carbons 1 and 2.
- In case if substituents are present in cycloalkene, then the double‑bonded carbon atoms are numbered 1 and 2 in a direction where the substituent gets the lower number.
- If the cycloalkenes contain more than one double bond, then one double bond is assigned the numbers 1 and 2 followed by the other double bond so that the lowest number possible is given.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. To indicate a double bond between carbon atom, double line is used.
If stereoisomers are possible for the alkene, the stereoinformation is shown in the IUPAC name by adding prefix cis- or trans- with respect to the groups present on the same side of double bond or opposite side of double bond.
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.49EP
The IUPAC name for the given compound is tetrafluoroethene.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
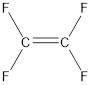
The longest continuous carbon chain present in the given compound is two carbon atoms. Hence, the parent alkane is ethane.
As the given compound contains a double bond, the suffix –ane is replaced by –ene. Therefore, the name obtained is ethene.
In this case, numbering does not make any difference. This is because all the hydrogen atoms are replaced by fluorine atoms. Hence, the IUPAC name can be given as tetrafluoroethene.
Stereoisomers are not possible for the given molecule because same groups are present on the carbon atom that is present on the double bond.
IUPAC name for the given molecule is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given molecule has to be assigned including the prefix cis- or trans-.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature for alkene: There are about eight rules to be followed in giving IUPAC name for alkene.
- The suffix –ane has to be replaced with the suffix –ene. This is used to indicate the presence of double bond.
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has to be chosen that contains both carbon atoms of the double bond.
- The parent carbon chain has to be numbered in a way so that the numbering begins at the end near to the double bond. In case if the double bond is equidistant from both ends, then numbering has to be done from the end that is closer to substituents.
- The position of the double bond has to be given a single number which is lower‑numbered carbon atom that is present in the double bond.
- Suffixes like –diene, -triene, -tetrene, and so on are used when the compound contains more than one double bond.
- In case of cycloalkenes which do not have any substitution, the numbering is not needed to locate the double bond because the bond is assumed to be between the carbons 1 and 2.
- In case if substituents are present in cycloalkene, then the double‑bonded carbon atoms are numbered 1 and 2 in a direction where the substituent gets the lower number.
- If the cycloalkenes contain more than one double bond, then one double bond is assigned the numbers 1 and 2 followed by the other double bond so that the lowest number possible is given.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. To indicate a double bond between carbon atom, double line is used.
If stereoisomers are possible for the alkene, the stereoinformation is shown in the IUPAC name by adding prefix cis- or trans- with respect to the groups present on the same side of double bond or opposite side of double bond.
(d)
Answer to Problem 13.49EP
The IUPAC name for the given compound is 2-methyl-2-butene.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
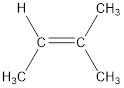
The longest continuous carbon chain present in the given compound is four carbon atoms. Hence, the parent alkane is butane.
As the given compound contains a double bond, the suffix –ane is replaced by –ene. Therefore, the name obtained is butene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the carbon atoms present in the double bond gets the least numbering. Therefore, the name of the given compound is 2-butene. The substituent present on the longest carbon chain is a methyl group that is present on the second carbon atom. Therefore, the name of the given molecule can be given as,
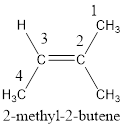
In order to include the stereo information, the groups attached to the double‑bonded carbon atoms are looked into.
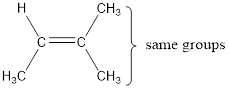
The bulky groups are present on same carbon atom of the double bond. Hence, isomerism is not possible. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given molecule is 2-methyl-2-butene.
IUPAC name for the given molecule is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- Describe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardState two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forwardState three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


