
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The spatial arrangement for the
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and
Saturated hydrocarbons are
Alkane has general molecular formula as
Considering the geometry of carbon atoms, the carbon atoms that have double bonds will have trigonal planar geometry. The carbon atoms that have only single bonds attached to it will have tetrahedral geometry. The carbon atoms that have a triple bond attached to it will have a linear geometry.
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.37EP
The spatial arrangement is identified as tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
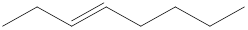
Looking into the left most carbon atom present in the given structure, it is not bonded to any double bonds or triple bond. This carbon atom has only four single bonds (three with hydrogen and one with carbon atom). Therefore, the spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is tetrahedral.
The spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is identified.
(b)
Interpretation:
The spatial arrangement for the chemical bonds in the left‑most carbon atom in the given structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Saturated hydrocarbons are alkanes. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are alkene, alkyne and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Alkane has general molecular formula as
Considering the geometry of carbon atoms, the carbon atoms that have double bonds will have trigonal planar geometry. The carbon atoms that have only single bonds attached to it will have tetrahedral geometry. The carbon atoms that have a triple bond attached to it will have a linear geometry.
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.37EP
The spatial arrangement is identified as tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
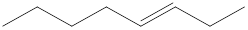
Looking into the left most carbon atom present in the given structure, it is not bonded to any double bonds or triple bond. This carbon atom has only four single bonds (three with hydrogen and one with carbon atom). Therefore, the spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is tetrahedral.
The spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is identified.
(c)
Interpretation:
The spatial arrangement for the chemical bonds in the left‑most carbon atom in the given structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Saturated hydrocarbons are alkanes. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are alkene, alkyne and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Alkane has general molecular formula as
Considering the geometry of carbon atoms, the carbon atoms that have double bonds will have trigonal planar geometry. The carbon atoms that have only single bonds attached to it will have tetrahedral geometry. The carbon atoms that have a triple bond attached to it will have a linear geometry.
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.37EP
The spatial arrangement is identified as trigonal planar.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
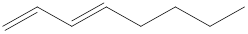
Looking into the left most carbon atom present in the given structure, it is bonded to one double bond. This carbon atom has only two single bonds with hydrogen and a double bond with carbon atom. Therefore, the spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is trigonal planar.
The spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is identified.
(d)
Interpretation:
The spatial arrangement for the chemical bonds in the left‑most carbon atom in the given structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Saturated hydrocarbons are alkanes. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are alkene, alkyne and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Alkane has general molecular formula as
Considering the geometry of carbon atoms, the carbon atoms that have double bonds will have trigonal planar geometry. The carbon atoms that have only single bonds attached to it will have tetrahedral geometry. The carbon atoms that have a triple bond attached to it will have a linear geometry.
(d)
Answer to Problem 13.37EP
The spatial arrangement is identified as tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
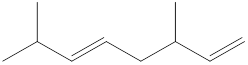
Looking into the left most carbon atom present in the given structure, it is not bonded to any double bonds or triple bond. This carbon atom has only four single bonds (three with hydrogen and one with carbon atom). Therefore, the spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is tetrahedral.
The spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is identified.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- in the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forwardMolecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forward
- Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forward
- What characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forwardFor a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





