
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To identify the products are formed when 3-methyl-2-cyclohexenone reacts with each of the given reactant.
Concept introduction:
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (
Grignard reagent is reaction with carbonyl compound such as
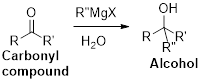
(b)
Interpretation:
To identify the products are formed when 3-methyl-2-cyclohexenone reacts with each of the given reactant.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction:
The nucleophile is reaction with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound (1,4 –addtion) which yield the addition product is called Michael reaction.
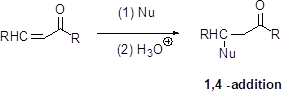
(c)
Interpretation:
To identify the products are formed when 3-methyl-2-cyclohexenone reacts with each of the given reactant.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction:
The nucleophile is reaction with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound (1,4 –addtion) which yield the addition product is called Michael reaction.
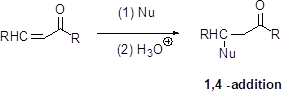
Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: unsymmetrical
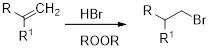
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- 5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward
- 5.arrow_forward9arrow_forwardalekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward
- 0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forwardx + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forwardS: Using a phase diagram leksogi/x/sl.exe/1ou-IgNs kr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZdHYU+80XL-5alyVp O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure se the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the boiling point of X when the pressure on the liquid is 1.6 atm. pressure (atm) 32- 16- solid liquid 0. gas 100 200 temperature (K) 300 Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. 10 Explanation Check § Q Search J 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Researrow_forward
- 151.2 254.8 85.9 199.6 241.4 87.6 242.5 186.4 155.8 257.1 242.9 253.3 256.0 216.6 108.7 239.0 149.7 236.4 152.1 222.7 148.7 278.2 268.7 234.4 262.7 283.2 143.6 QUESTION: Using this group of data on salt reduced tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardResults Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unloc xb Success Confirmation of Q x O Google Pas alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCavJ17dZtpxbFD0Qggd1J O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Gabr 3/5 he pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 101. °C is lowered. At what pressure will the sample sublime? Use the phase diagram of X below to nd your answer. pressure (atm) 24- 12 solid liquid gas 200 400 temperature (K) 600 ote: your answer must be within 0.15 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. atm Thanation Check © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center I Q Search L³ ملةarrow_forward301.7 348.9 193.7 308.6 339.5 160.6 337.7 464.7 223.5 370.5 326.6 327.5 336.1 317.9 203.8 329.8 221.9 331.7 211.7 309.6 223.4 353.7 334.6 305.6 340.0 304.3 244.7 QUESTION: Using this group of data on regular tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


