
Convert the following models into line drawings (black = C; white = H; red = O: blue = N):
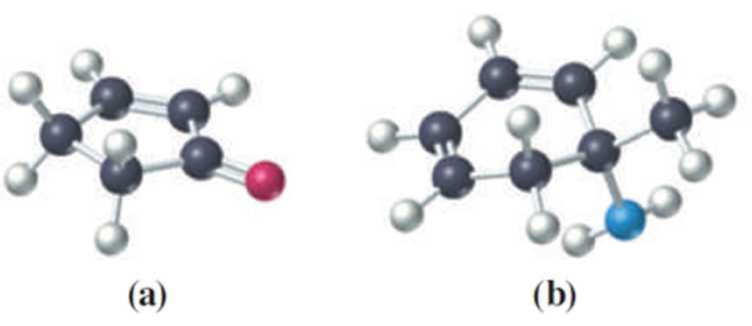
(a)
Interpretation:
The given ball and stick model has to be drawn in line structure.
Concept Introduction:
- The ball and stick model is a molecular model of the chemical substance that represent the 3-D position of the atoms and bonds between them. The atoms are typically represented by spheres, joined by rods which represent the bonds.
- Line structure is a simple and quick way to represent organic molecules without showing carbons and hydrogens present.
Answer to Problem 12.22UKC
The line structure for the given molecule is given below,
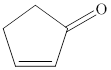
Explanation of Solution
Given black is C; white is H and red is O in the structure below,
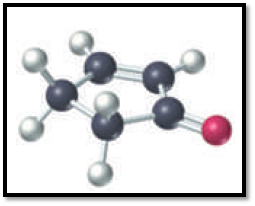
Figure 1
So the structure has five carbons, five hydrogens and oxygen. Out of the five carbons, two carbons in the ring are connected by double bond. One carbon is connected to oxygen by other double bond. Since all carbon is connected together we can conclude it as cyclopentane. So the structure representing the given ball and stick model is given below,

(b)
Interpretation:
The given ball and stick model has to be drawn in line structure.
Concept Introduction:
- The ball and stick model is a molecular model of the chemical substance that represent the 3-D position of the atoms and bonds between them. The atoms are typically represented by spheres, joined by rods which represent the bonds.
- Line structure is a simple and quick way to represent organic molecules without showing carbons and hydrogens present.
Answer to Problem 12.22UKC
The line structure for the given molecule is given below,
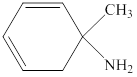
Explanation of Solution
Given black is C; white is H and blue is N in the structure below,
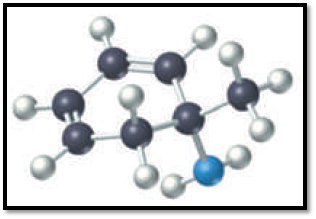
Figure 2
So the structure has seven carbons, eleven hydrogens and nitrogen. Out of the seven carbons, four carbons in the ring are connected by two double bonds. One carbon is connected to nitrogen by a single bond, which in turn is connected with two hydrogens. Since all carbon except one is connected together we can conclude it as cyclohexane. So the structure representing the given ball and stick model is given below,

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H H ⚫OH HO- -H H- -OH H- -OH CH2OH Ag*, NH4OH, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H₂O -OH H ⚫OH HO H HO- CH2OH Cu2+ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H、 H -OH H ⚫OH H -OH CH2OH Fehlings' solution ⑤ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO C=0 H ⚫OH H ⚫OH HO- H HO H CH2OH Tollens' solution Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H-C=O HO H HO H H- ⚫OH HO H CH2OH HNO3, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO HO- HO H HO ∙H HO CH2OH NaBH4, CH3OH Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Но сво HO H HO H H OH H -OH CH2OH H2 Pd Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection for Gulose-ẞ-1,6-sorbose and answer the following questions. (Gulose will be in the pyranose form and Sorbose will be in the furanose form) a. Label the reducing and nonreducing ends of the disaccharide b. Label the glycosidic bond c. Circle the anomeric carbons and label them as hemiacetals or acetals. d. Can this disaccharide undergo mutarotation?arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H OH HO HO HO ·H H OH H OH excess CH3CH2I KOHarrow_forward
- Draw the Haworth structures for the following: a. α-D-Gulopyranose b. ẞ-D-Sorbofuranose c. The two possible isomers of a-D-altrose (furanose and pyranose forms)arrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO H ⚫OH HO- ∙H H- -OH H ⚫OH CH2OH HNO3, H2Oarrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO CH2OH OH OH OH excess CHзI Ag2Oarrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning





