
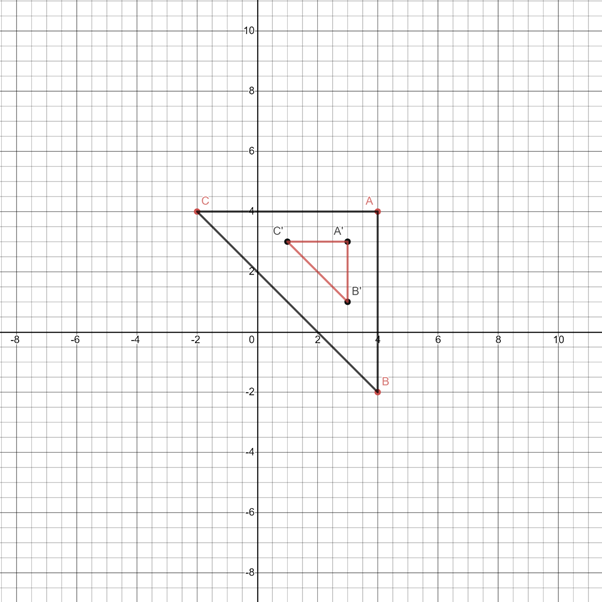
To find:Draw a triangle on grid paper and its image.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
We need to draw image of the triangle after it is moved
Let us take Vertices of the triangle are
When it is moved
Vertices of Dilated Triangle are
Vertices of Dilated Triangle are
Graph of Dilated triangle is
Chapter 11 Solutions
Glencoe Math Accelerated, Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Using and Understanding Mathematics: A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (6th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
- 3:59 m s ☑ D'Aniello Boutique | Fashion VOLTE danielloboutique.it/asia SUBSCRIBE NOW: 10% OFF TO USE ANYTIME YOU WANT d'aniello NEW IN WOMEN NEW IN MEN WINTER SALE: 50% OFF on FW24 SHOP WOMEN SHOP MENarrow_forwardJOB UPDATE EMERSON GRAD ENGINEER (FRESHERS) SOFTWARE ENGG NEW RELIC BROWSERSTACK (FRESHERS) SOFTWARE ENGG FULL STACK DATA ENGINEER GENPACT + PYTHON CARS24 WORK FROM HOME #vinkjobs TELE PERFORMANCE Vinkjobs.com CUSTOMER SUPPORT Search "Vinkjobs.com" on Googlearrow_forwarddo question 2 pleasearrow_forward
- question 10 pleasearrow_forward00 (a) Starting with the geometric series Σ X^, find the sum of the series n = 0 00 Σηχη - 1, |x| < 1. n = 1 (b) Find the sum of each of the following series. 00 Σnx", n = 1 |x| < 1 (ii) n = 1 sin (c) Find the sum of each of the following series. (i) 00 Σn(n-1)x^, |x| <1 n = 2 (ii) 00 n = 2 n² - n 4n (iii) M8 n = 1 շոarrow_forward(a) Use differentiation to find a power series representation for 1 f(x) = (4 + x)²* f(x) = 00 Σ n = 0 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = (b) Use part (a) to find a power series for f(x) = 1 (4 + x)³° f(x) = 00 Σ n = 0 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = (c) Use part (b) to find a power series for f(x) = x² (4 + x)³* 00 f(x) = Σ n = 2 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWERarrow_forward
- answer for question 4 pleasearrow_forward(3) (20 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (y, z, x²z). Define E = {(x, y, z) | x² + y² ≤ z ≤ 1, x ≤ 0}. (a) (2 points) Calculate the divergence V. F. (b) (4 points) Let D = {(x, y) | x² + y² ≤ 1, x ≤ 0} Without calculation, show that the triple integral √ (V · F) dV = √ 2²(1. = x²(1 − x² - y²) dA. Earrow_forward(2) (22 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (x sin y, cos y, ―xy). (a) (2 points) Calculate V. F. (b) (6 points) Given a vector field is everywhere defined with V G₁(x, y, z) = * G2(x, y, z) = − G3(x, y, z) = 0. 0 0 F(x, y, z) = (F₁(x, y, z), F₂(x, y, z), F(x, y, z)) that F = 0, let G = (G1, G2, G3) where F₂(x, y, y, t) dt - √ F³(x, t, 0) dt, * F1(x, y, t) dt, t) dt - √ F Calculate G for the vector field F(x, y, z) = (x sin y, cos y, -xy).arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √ √(x + y) A R R = {(x, y) | 25 < x² + y² ≤ 36, x < 0} Hint: The integral and Region is defined in rectangular coordinates.arrow_forwardFind the volume of the solid that lies under the paraboloid z = 81 - x² - y² and within the cylinder (x − 1)² + y² = 1. A plot of an example of a similar solid is shown below. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). Volume using Double Integral Paraboloid & Cylinder -3 Hint: The integral and region is defined in polar coordinates.arrow_forwardEvaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √4(1–2² 4(1 - x² - y²) dA R 3 R = {(r,0) | 0 ≤ r≤ 2,0π ≤0≤¼˜}. Hint: The integral is defined in rectangular coordinates. The Region is defined in polar coordinates.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





