
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 76QRT
For this reaction mechanism,
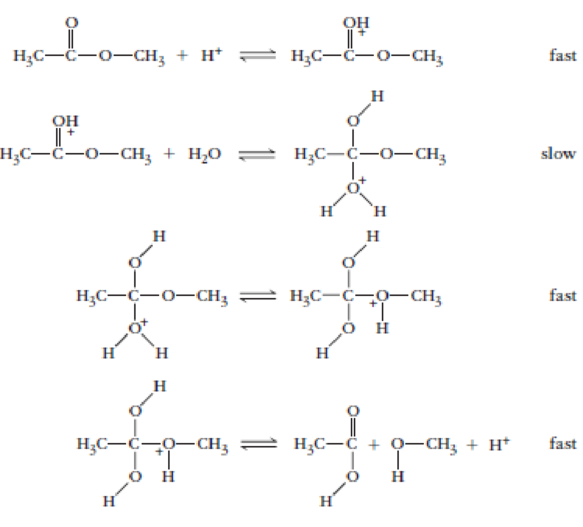
- (a) write the chemical equation for the overall reaction.
- (b) write the rate law for the reaction.
- (c) is there a catalyst involved in this reaction? If so, what is it?
- (d) identify all intermediates in the reaction.
- (e) draw a reaction energy diagram for the reaction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
help me solve this HW
Molecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)
Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Ch. 11.1 - For the reaction of crystal violet with NaOH(aq),...Ch. 11.1 - (a) From data in Table 11.1, calculate the rate of...Ch. 11.1 - For the reaction 4NO2(g)+O2(g)2N2O5(g) (a) express...Ch. 11.1 - Instantaneous rates for the reaction of hydroxide...Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 11.3CECh. 11.2 - Prob. 11.4ECh. 11.2 - Prob. 11.3PSPCh. 11.2 - Prob. 11.5ECh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.4PSPCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.5PSP
Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.6PSPCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.7PSPCh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.6ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.7CECh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.8PSPCh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.8CECh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.9PSPCh. 11.5 - The frequency factor A is 6.31 108 L mol1 s1 and...Ch. 11.6 - Prob. 11.10CECh. 11.7 - Prob. 11.11ECh. 11.7 - The Raschig reaction produces the industrially...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 11.12ECh. 11.8 - The oxidation of thallium(I) ion by cerium(IV) ion...Ch. 11.9 - Prob. 11.11PSPCh. 11.9 - Prob. 11.14CECh. 11 - An excellent way to make highly pure nickel metal...Ch. 11 - Prob. 1QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 2QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 3QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 4QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 5QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 6QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 7QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 8QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 9QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 10QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 11QRTCh. 11 - Cyclobutane can decompose to form ethylene:
The...Ch. 11 - Prob. 13QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 14QRTCh. 11 - For the reaction 2NO2(g)2NO(g)+O2(g) make...Ch. 11 - Prob. 16QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 17QRTCh. 11 - Ammonia is produced by the reaction between...Ch. 11 - Prob. 19QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 20QRTCh. 11 - The reaction of CO(g) + NO2(g) is second-order in...Ch. 11 - Nitrosyl bromide, NOBr, is formed from NO and Br2....Ch. 11 - Prob. 23QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 24QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 25QRTCh. 11 - For the reaction
these data were obtained at 1100...Ch. 11 - Prob. 27QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 28QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 29QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 30QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 31QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 32QRTCh. 11 - For the reaction of phenyl acetate with water the...Ch. 11 - When phenacyl bromide and pyridine are both...Ch. 11 - The compound p-methoxybenzonitrile N-oxide, which...Ch. 11 - Prob. 36QRTCh. 11 - Radioactive gold-198 is used in the diagnosis of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 38QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 39QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 40QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 41QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 42QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 43QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 44QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 45QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 46QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 47QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 48QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 49QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 50QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 51QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 52QRTCh. 11 - For the reaction of iodine atoms with hydrogen...Ch. 11 - Prob. 54QRTCh. 11 - The activation energy Ea is 139.7 kJ mol1 for the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 56QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 57QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 58QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 59QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 60QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 61QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 62QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 63QRTCh. 11 - Which of the reactions in Question 62 would (a)...Ch. 11 - Prob. 65QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 66QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 67QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 68QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 69QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 70QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 71QRTCh. 11 - For the reaction the rate law is Rate=k[(CH3)3CBr]...Ch. 11 - Prob. 73QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 74QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 75QRTCh. 11 - For this reaction mechanism,
write the chemical...Ch. 11 - Prob. 77QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 78QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 79QRTCh. 11 - When enzymes are present at very low...Ch. 11 - Prob. 81QRTCh. 11 - The reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme succinate...Ch. 11 - Prob. 83QRTCh. 11 - Many biochemical reactions are catalyzed by acids....Ch. 11 - Prob. 85QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 86QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 87QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 88QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 89QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 90QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 91QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 92QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 93QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 94QRTCh. 11 - Nitryl fluoride is an explosive compound that can...Ch. 11 - Prob. 96QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 97QRTCh. 11 - For a reaction involving the decomposition of a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 99QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 100QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 101QRTCh. 11 - This graph shows the change in concentration as a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 103QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 104QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 105QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 106QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 107QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 108QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 109QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 110QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 111QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 112QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 113QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 114QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 115QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 116QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 118QRTCh. 11 - Prob. 119QRTCh. 11 - In a time-resolved picosecond spectroscopy...Ch. 11 - If you know some calculus, derive the integrated...Ch. 11 - If you know some calculus, derive the integrated...Ch. 11 - (Section 11-5) A rule of thumb is that for a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.BCPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.CCPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.DCP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forwardWhat characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forward
- For a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forwardDescribe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
- State two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forwardState three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardIn a photochemical reaction, how is the rate of the process related to its quantum yield?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Kinetics: Chemistry's Demolition Derby - Crash Course Chemistry #32; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7qOFtL3VEBc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY