
Concept explainers
For health reasons, public spaces require the continuous exchange of a specified mass of stale indoor airwith fresh outdoor air. To conserve energy during theheating season, it is expedient to recover the thermalenergy in the exhausted, warm indoor air and transferit to the incoming, cold fresh air. A coupled single pass, cross-flow heat exchanger with both fluidsunmixed is installed in the intake and return ducts of aheating system as shown in the schematic. Water containing an anti-freeze agent is used as the workingfluid in the coupled heat exchange device, which iscomposed of individual heat exchangers A and B.Hence, heat is transferred from the warm stale air tothe cold fresh air by way of the pumped water.
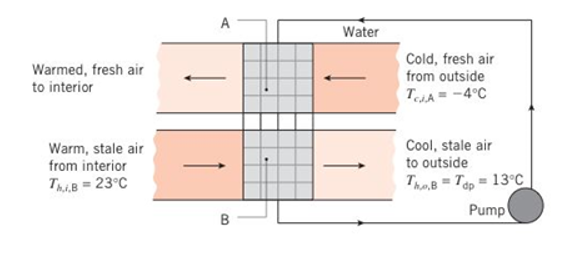
Consider a specified air mass flow rate (ineach duct) of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardaversity of Baoyion aculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023, st Course, 1st Attempt Stage: 3rd Subject: Heat Transfer I Date: 2023\01\23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Q4: A thick slab of copper initially at a uniform temperature of 20°C is suddenly exposed to radiation at one surface such that the net heat flux is maintained at a constant value of 3×105 W/m². Using the explicit finite-difference techniques with a space increment of Ax = = 75 mm, determine the temperature at the irradiated surface and at an interior point that is 150 mm from the surface after 2 min have elapsed. Q5: (12.5 M) A) A steel bar 2.5 cm square and 7.5 cm long is initially at a temperature of 250°C. It is immersed in a tank of oil maintained at 30°C. The heat-transfer coefficient is 570 W/m². C. Calculate the temperature in the center of the bar after 3 min. B) Air at 90°C and atmospheric pressure flows over a horizontal flat plate at 60 m/s. The plate is 60 cm square and is maintained at a…arrow_forwardUniversity of Baby on Faculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023. 1 Course, 1" Attempt Stage 3 Subject Heat Transfer I Date: 2023 01 23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Notes: Q1: • • Answer four questions only Use Troles and Appendices A) A flat wall is exposed to an environmental temperature of 38°C. The wall is covered with a layer of insulation 2.5 cm thick whose thermal conductivity is 1.4 W/m. C, and the temperature of the wall on the inside of the insulation is 315°C. The wall loses heat to the environment by convection. Compute the value of the convection heat-transfer coefficient that must be maintained on the outer surface of the insulation to ensure that the outer-surface temperature does not exceed 41°C. B) A vertical square plate, 30 cm on a side, is maintained at 50°C and exposed to room air at 20°C. The surface emissivity is 0.8. Calculate the total heat lost by both sides of the plate. (12.5 M) Q2: An aluminum fin 1.5 mm thick is placed on a circular tube…arrow_forward
- Solve this and show all of the workarrow_forwardNeed helparrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

