
Consider a combined gas–steam power plant that has a net power output of 280 MW. The pressure ratio of the gas-turbine cycle is 11. Air enters the compressor at 300 K and the turbine at 1100 K. The combustion gases leaving the gas turbine are used to heat the steam at 5 MPa to 350°C in a heat exchanger. The combustion gases leave the heat exchanger at 420 K. An open feedwater heater incorporated with the steam cycle operates at a pressure of 0.8 MPa. The condenser pressure is 10 kPa. Assuming isentropic efficiencies of 100 percent for the pump, 82 percent for the compressor, and 86 percent for the gas and steam turbines, determine (a) the mass flow rate ratio of air to steam, (b) the required rate of heat input in the combustion chamber, and (c) the thermal efficiency of the combined cycle.
(a)
The mass flow rate ratio of the air to the steam.
Answer to Problem 82P
The mass flow rate ratio of the air to the steam is
Explanation of Solution
Show the
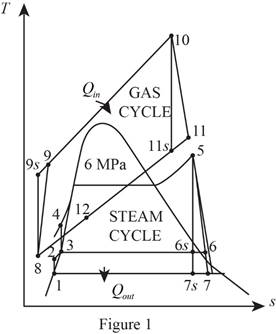
Refer Figure 1.
Consider the gas cycle (topping cycle) and their respective process states such as 8, 9,
At state 8:
The air enters the compressor at the temperature of
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air”.
The enthalpy
Write the relative pressure and absolute pressure relation for the process 8-9-
Here, the relative pressure is
Write the formula for isentropic efficiency of compressor for the process 8-9-
Here, the enthalpy is
At state 10:
The air enters the turbine at the temperature of
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air”.
The enthalpy
Write the relative pressure and absolute pressure relation for the process 10-11-
Write the formula for isentropic efficiency of gas turbine
At state 12: (heat exchanger)
The enthalpy
Refer Figure 1.
Consider the steam cycle (bottoming cycle) and their respective process states such as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
At state 1: (Pump I inlet)
The water exits the condenser as a saturated liquid at the pressure of
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
At state 2:
Write the formula for work done by the pump during process 1-2.
Here, the specific volume is
Write the formula for enthalpy
At state 3: (Pump II inlet)
The water exits the open feed water heater as a saturated liquid at the pressure of
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
At state 4:
Write the formula for work done by the pump during process 3-4.
Here, the specific volume is
Write the formula for enthalpy
At state 5:
The steam enters the turbine as superheated vapour.
Refer Table A-6, “Superheated water”.
The enthalpy
At state
The steam expanded to the pressure of
The quality of water at state
The enthalpy at state
Here, the enthalpy is
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following properties corresponding to the pressure of
The isentropic efficiency of the steam turbine for the process 5-6-
At state
The steam enters the condenser at the pressure of
The quality of water at state
The enthalpy at state
Here, the subscript
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following properties corresponding to the pressure of
The isentropic efficiency of the steam turbine for the process 5-7-
Here, the subscript
Write the general energy rate balance equation.
Here, the rate of energy in is
Consider the heat exchanger operates on steady state. Hence, the rate of change in net energy of the system is zero.
The Equation (XVI) is reduced as follows for the heat exchanger.
Here, the mass flow rate of air is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air”.
The enthalpy
Substitute
Substitute
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air”.
The enthalpy
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (VII).
Substitute
From Figure 1.
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (X).
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (XIII).
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the mass flow rate ratio of the air to the steam is
(b)
The required rate of heat input in the combustion chamber.
Answer to Problem 82P
The required rate of heat input in the combustion chamber is
Explanation of Solution
Refer Equation (XV).
Consider the open feed water heater operates on steady state. Hence, the rate of change in net energy of the system is zero.
Write the energy rate balance equation for open feed water heater.
Rewrite the Equation (XVII) in terms of mass fraction
Here, the mass fraction steam extracted from the turbine to the inlet mass of the boiler
Write the formula for work output of the steam turbine.
Write the formula for net work output of the steam cycle.
Write the formula for net work output of the gas cycle.
Write the formula for the net work output of the gas-steam cycle per unit mass of gas.
Write the formula for mass flow rate of air through the compressor.
Write the formula for rate of heat input to the combustion chamber.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Equation (XVIII).
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (XXIV).
Thus, the required rate of heat input in the combustion chamber is
(c)
The thermal efficiency of the combined cycle.
Answer to Problem 82P
The thermal efficiency of the combined cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula for thermal efficiency.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the thermal efficiency of the combined cycle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Calculate the mean piston speed (in mph) for a Formula 1 engine running at 14,750 rpm with a bore of 80mm and a stroke of 53mm. Estimate the average acceleration imparted on the piston as it moves from TDC to 90 degrees ATDCarrow_forwardCalculate the compression ratio of an engine with a stroke of 4.2inches a bore of 4.5 inches and a clearance volume of 6.15 cubic inches. Discuss whether or not this is a realistic compression ratio for a street engine and what octane rating of fuel it would need to run correctlyarrow_forwardDraw the free-body diagram for the pinned assembly shown. Find the magnitude of the forces acting on each member of the assembly. 1500 N 1500 N C 45° 45° 45° 45° 1000 mmarrow_forward
- An elastic bar of length L spins with angular velocity ω about an axis, as shown in the figure below. The radial acceleration at a generic point x along the bar is a(x) = ω 2 x. Due to this radial acceleration, the bar stretches along x with displacement function u(x). The displacement u(x) is governed by the following equations: ( d dx (σ(x)) + ρa(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = E du dx Hooke’s law (1) where σ(x) is the axial stress in the rod, ρ is the mass density, and E is the (constant) Young’s modulus. The bar is pinned on the rotation axis at x = 0, and it is free at x = L. Determine:1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem.2. The displacement function u(x).3. The stress function σ(x).arrow_forwardWith reference to the given figure: a) Draw a free-body diagram of the structure supporting the pulley. b) Draw shear and bending moment diagrams for both the vertical and horizontal portions of the structure. 48 in. 100 lb 12 in. Cable 27 in. 12-in. pulley radius 100 lb Cablearrow_forwardConsider a standard piston engine . Draw a free body diagram of the piston. Then:a) For an A SI engine with a 100 mm bore at an instantaneous cylinder pressure of 42 bar i. Calculate the level of the combustion gas loading force on the wrist pin in kN. b) Repeat this calculationfor a forced-induction Diesel engine with a 145 mm boreat a cylinder pressure of 115 bararrow_forward
- A punch press with flywheel adequate to minimize speed fluctuation produces 120 punching strokes per minute, each providing an average force of 2000 N over a stroke of 50 mm. The press is driven through a gear reducer by a shaft rotating 200 rpm. Overall efficiency is 80%. a) What power (W) is transmitted through the shaft? b) What average torque is applied to the shaft?arrow_forward1.58 The crankshaft of a single-cylinder air compressor rotates 1800 rpm. The piston area is 2000 mm2 and the piston stroke is 50 mm. Assume a simple “idealized” case where the average gas pressure acting on the piston during the compression stroke is 1 MPa, and pressure during the intake stroke is negligible. The compressor is 80% efficient. A flywheel provides adequate control of the speed fluctuation. a) What motor power (kW) is required to drive the crankshaft? b) What torque is transmitted through the crankshaft?arrow_forward28. The shaft shown in Figure P5-28 is supported by bear- ings at each end, which have bores of 20.0 mm. Design the shaft to carry the given load if it is steady and the shaft is stationary. Make the dimension a as large as pos- sible while keeping the stress safe. Determine the required d 20 mm 5.4 kN d D = ? Length not to scale -α = = -125 mm 20 mm a = -250 mm- FIGURE P5-28 (Problems 28, 29, and 30)arrow_forward
- The motor shown operates at constant speed and develops a torque of 100 lb-in during normal operation. Attached to the motor shaft is a gear reducer of ratio 5:1, that is, the reducer output shaft rotates in the same direction as the motor but at one-fifth motor speed. Rotation of the reducer housing is prevented by the "torque arm" pin-connected at each end as shown. The reducer output shaft drives the load through a flexible coupling. Neglecting gravity and friction, what loads are applied to (a) the torque arm, (b) the motor output shaft, and (c) the reducer output shaft? Motor Gear reducer Flexible coupling (To load) Torque arm- Torque arm Reducer output shaft Motor Reducer Shaft rotationarrow_forwardPlease can you help with ten attatched question?arrow_forwardAn AISI 1018 steel ball with 1.100-in diameter is used as a roller between a flat plate made from 2024 T3 aluminum and a flat table surface made from ASTM No. 30 gray cast iron. Determine the maximum amount of weight that can be stacked on the aluminum plate without exceeding a maximum shear stress of 19.00 kpsi in any of the three pieces. Assume the figure given below, which is based on a typical Poisson's ratio of 0.3, is applicable to estimate the depth at which the maximum shear stress occurs for these materials. 1.0 0.8 Ratio of stress to Pmax 0.4 90 0.6 στ Tmax 0.2 0.5a a 1.5a 2a 2.5a За Distance from contact surface The maximum amount of weight that can be stacked on the aluminum plate is lbf.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





