
(a)
The ratio of mass flow rate of air to mass flow rate of steam in the combined power cycle
(a)
Answer to Problem 78P
The ratio of mass flow rate of air to mass flow rate of steam in the combined power cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Draw the T-s diagram for the combined gas-steam power cycle.
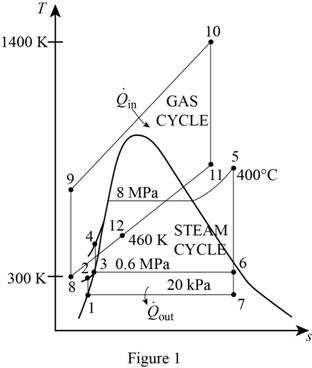
Write the expression for the relation relative pressure and ideal pressure.
Here, the relative pressure at state 9 is
Write the expression for the efficiency of compressor.
Refer to properties table of air, and interpret the value of
Write the expression for the relation relative pressure and ideal pressure.
Here, the relative pressure at state 11 is
Write the expression for the efficiency of turbine.
Write the expression for the specific work input of pump I to the system/
Write the expression for the enthalpy of steam at state 2.
Write the expression for the specific work input of pump II to the system/
Write the expression for the enthalpy of steam at state 4.
Write the expression for the quality of steam at state 6s.
Here, specific entropy of wet steam at 0.6 MPa is
Write the expression for the specific enthalpy of steam at state 6s.
Here, specific enthalpy of wet steam at
Write the expression for the efficiency of turbine.
Write the expression for the quality of steam at state 7s.
Here, specific entropy of wet steam at 20 kPa is
Write the expression for the specific enthalpy of steam at state 7s.
Here, specific enthalpy of wet steam at
Write the expression for the efficiency of turbine.
Write the expression for the energy balance equation for the heat exchanger.
Rewrite Equation (1) and rearrange the terms with mass and enthalpy terms.
Here, mass flow rate of steam is
Conclusion:
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air”, select the relative pressure
Substitute 1.386 kPa for
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air”, interpret the value of the enthalpy
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air”, select the relative pressure
Substitute 450.5 kPa for
Refer Table A-17 “Ideal-gas properties of air , interpret the value of
Refer Table A-5, “saturated water-Pressure table”, select the enthalpy
Substitute
Substitute
Refer Table A-5, “saturated water-Pressure table”, select the enthalpy
Substitute
Substitute
Refer Table A-5, “Superheated water”, select the enthalpy
Since, the entropy at state 5 is equal to state 6s, so the entropy value of
Interpret the value of
Substitute
Refer to steam tables, and interpret the value of
Substitute
Since, the entropy at state 5 is equal to the entropy at state 7, the entropy value of
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”, obtain the value of
Substitute
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”, obtain the value of
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the ratio of mass flow rate of air to mass flow rate of steam in the combined power cycle is
(b)
The rate of heat input in the combustion chamber.
(b)
Answer to Problem 78P
The rate of heat input in the combustion chamber is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the energy balance equation for the open feed water heater.
Rewrite Equation (3) and rearrange the terms with mass and enthalpy terms.
Here, fraction of steam extracted is y.
Write the expression for the specific power output of the turbine.
Write the expression for the specific net work output from the steam.
Write the expression for the specific net work output from the gas stream.
Write the expression for the net work output per unit mass of gas.
Write the expression for the mass flow rate of air.
Write the expression for the rate of heat input to the cycle.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute 0.86 for
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the rate of heat input in the combustion chamber is
(c)
The thermal efficiency of the combined power cycle
(c)
Answer to Problem 78P
The thermal efficiency of the combined power cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the thermal efficiency of the combined power cycle.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the thermal efficiency of the combined power cycle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





