
Concept explainers
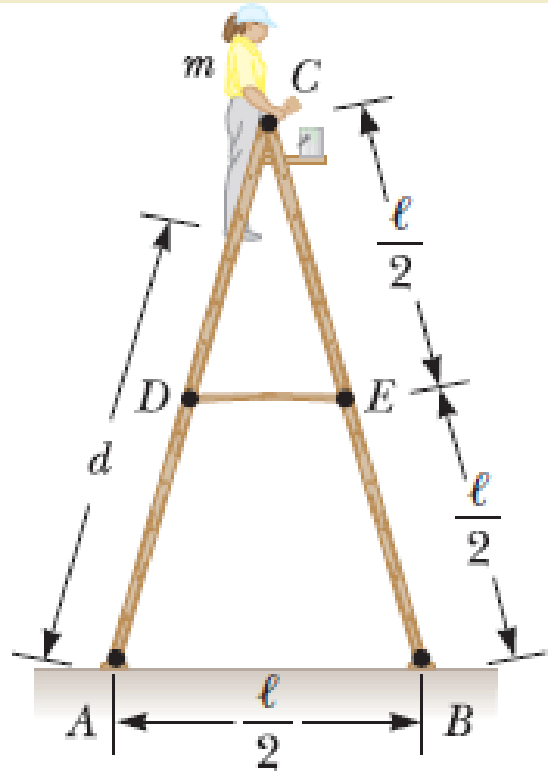
A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = ℓ = 4.00 m. A painter of mass m = 70.0 kg stands on the ladder d = 3.00 m from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately.
(a)
The tension experienced on the horizontal bar
Answer to Problem 73P
The tension experienced on the horizontal bar
Explanation of Solution
From the geometry of the ladder the angle
First of all consider the net torque at the point A which is at the bottom left side of the ladder. The torque experienced at this point is due to the weight of the painter, and the normal force at point B,
Write the expression for the torque at point A.
Here,
The net torque at point A is zero, hence equate equation (I) to zero and obtain an expression for
Now consider the net torque acting at the point B, which is at the bottom right of the ladder. The torque at point B same as A, is due to the weight of the painter and normal force at point A,
Write the expression for the net torque at point B.
The net torque acting at point B will be zero, equate equation (III) to zero, and obtain an expression for
Consider the torque at the point Cat the top of the right half of the ladder. At this point torque is due to the tension,
Write the expression for the torque at point C.
The net torque at point C is zero. Equate equation (III) to zero, and obtain an expression for
Substitute, equation (II) in (VI).
The tension
Write the expression for the force acting along right.
Equate equation (VIII) to zero.
Write the expression for the force acting along
Equate equation (VIII) to zero.
From equation (XI) the reaction force
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the tension experienced on the horizontal bar
(b)
The normal force acting at A, and B.
Answer to Problem 73P
The normal force acting at A is
Explanation of Solution
Use equation (II) and (IV) to obtain the answer.
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Therefore, the normal force acting at A is
(c)
The components of reaction forces at point C.
Answer to Problem 73P
The components of reaction forces at point C are,
Explanation of Solution
Consider equation (IX) and (XI), the
The tension experienced on the horizontal bar
The normal force acting at B is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the components of reaction forces at point C are,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- For each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forwardWhat are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forward
- simple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





