
Concept explainers
Phono Company manufactures a plastic toy cell phone. The following standards have been established for the toys materials and labor inputs:
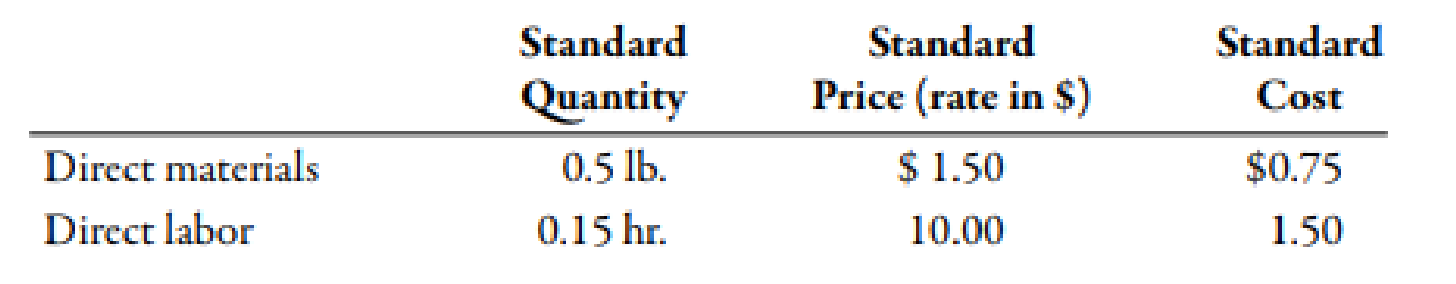
During the first week of July, the company had the following results:
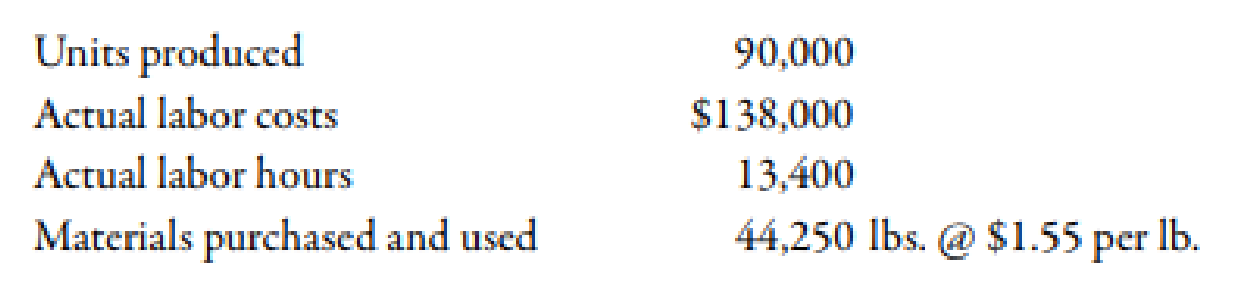
The purchasing agent located a new source of slightly higher-quality plastic, and this material was used during the first week in July. Also, a new manufacturing layout was implemented on a trial basis. The new layout required a slightly higher level of skilled labor. The higher-quality material has no effect on labor utilization. Similarly, the new manufacturing approach has no effect on material usage. (Note: Round all variances to the nearest dollar.)
Required:
- 1. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compute the materials price and usage variances. Assuming that the materials variances are essentially attributable to the higher quality of materials, would you recommend that the purchasing agent continue to buy this quality, or should the usual quality be purchased? Assume that the quality of the end product is not affected significantly.
- 2. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compute the labor rate and efficiency variances. Assuming that the labor variances are attributable to the new manufacturing layout, should it be continued or discontinued? Explain.
- 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Refer to Requirement 2. Suppose that the industrial engineer argued that the new layout should not be evaluated after only one week. His reasoning was that it would take at least a week for the workers to become efficient with the new approach. Suppose that the production is the same the second week and that the actual labor hours were 13,200 and the labor cost was $132,000. Should the new layout be adopted? Assume the variances are attributable to the new layout. If so, what would be the projected annual savings?
1.
Calculate the value of material price variance and material usage variance. Identify whether the plant manger could continue to purchase this quality product or purchase the usual quality.
Explanation of Solution
Variance:
The amount obtained when actual cost is deducted from budgeted cost is known as variance. Variance is calculated to find whether the cost is over applied or under applied.
Use the following formula to calculate material price variance:
Substitute $1.55 for actual price, 44,250 units for actual quantity and $1.50 for standard price in the above formula.
Therefore, the material price variance is $2,213(U).
Use the following formula to calculate material usage variance:
Substitute $1.50 for standard price, 44,250 units for actual quantity and 45,000 for standard quantity in the above formula.
Therefore, the material usage variance is $1,125(F).
The total variance is $1,088(U)
Working Note:
1. Calculation of standard quantity:
2.
Calculate the value of labor rate variance and labor efficiency variance. Identify whether the labor variances are attributable to the new manufacturing process should be continued or discontinued.
Explanation of Solution
Use the following formula to calculate labor rate variance:
Substitute $138,000 for actual cost, 10,800 hours for actual hours and $10 for standard rate in the above formula.
Therefore, the labor rate variance is $4,000(U).
Use the following formula to calculate labor efficiency variance:
Substitute $10.00 for standard rate, 13,400 hours for actual hours and 13,500 hours for standard hours in the above formula.
Therefore, the labor efficiency variance is $1,000(F).
The total labor variance is $3,000 (U)
Working Note:
1. Calculation of standard hours:
3.
Calculate the value of labor rate variance and labor efficiency variance. Identify whether the new process should be adopted.
Explanation of Solution
Use the following formula to calculate labor rate variance:
Substitute $132,000 for actual cost, 13,200 hours for actual hours and $10 for standard rate in the above formula.
Therefore, the labor rate variance is $0.
Use the following formula to calculate labor efficiency variance:
Substitute $10 for standard rate, 13,200 hours for actual hours and 13,500 hours for standard hours in the above formula.
Therefore, the labor efficiency variance is $3,000(F).
The total labor variance is $3,000 (F)
Working Note:
1. Calculation of standard hours:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
- Silver Star Manufacturing has $20 million in sales, an ROE of 15%, and a total assets turnover of 5 times. Common equity on the firm's balance sheet is 30% of its total assets. What is its net income? Round the answer to the nearest cent.arrow_forwardHi expert please give me answer general accounting questionarrow_forwardprovide (P/E ratio)?arrow_forward
- What was xyz corporation's stockholders' equity at the of marcharrow_forward???arrow_forwardHorizon Consulting started the year with total assets of $80,000 and total liabilities of $30,000. During the year, the business recorded $65,000 in service revenues and $40,000 in expenses. Additionally, Horizon issued $12,000 in stock and paid $18,000 in dividends. By how much did stockholders' equity change from the beginning of the year to the end of the year?arrow_forward
- х chat gpt - Sea Content Content × CengageNOW × Wallet X takesssignment/takeAssignmentMax.co?muckers&takeAssignment Session Loca agenow.com Instructions Labels and Amount Descriptions Income Statement Instructions A-One Travel Service is owned and operated by Kate Duffner. The revenues and expenses of A-One Travel Service Accounts (revenue and expense items) < Fees earned Office expense Miscellaneous expense Wages expense Required! $1,480,000 350,000 36,000 875,000 Prepare an income statement for the year ended August 31, 2016 Labels and Amount Descriptions Labels Expenses For the Year Ended August 31, 20Y6 Check My Work All work saved.arrow_forwardEvergreen Corp. began the year with stockholders' equity of $350,000. During the year, the company recorded revenues of $500,000 and expenses of $320,000. The company also paid dividends of $30,000. What was Evergreen Corp.'s stockholders' equity at the end of the year?arrow_forwardEvergreen corp.'s stockholders' equity at the end of the yeararrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning



