
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure has to be completed from the skeletal structure given below and the bond angles around the central atoms in the given structure have to be predicted using the VSEPR model.
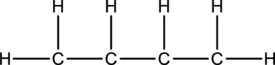
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure is used for predicting the shape of molecules. From the steric number obtained in a Lewis structure, the molecular geometry can be predicted. VSEPR model can predict the shape of molecules considering their Lewis structure. Certain rules has to be followed in for the VSEPR model.
- The molecule will have a shape where there is minimal electrostatic repulsion between the valence‑shell electron pairs.
- The forces of repulsion between two lone pairs of electrons will be higher than the repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of electrons. This in turn will be higher than the bond pair‑bond pair of electrons.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Skeletal structure for the molecule given is shown;
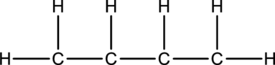
The Lewis structure can be drawn considering the valence electrons in the molecule. Total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
Eighteen electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. One electron pair is added to the terminal carbon atom each. Thus the Lewis structure can be drawn as follows;
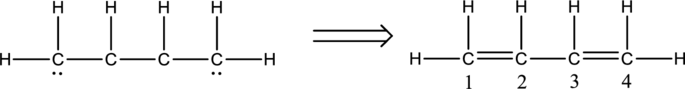
Bond Angles:
Central atoms present in the above structure are four carbon atoms. The bond angles can be predicted using the steric number.
Steric number for carbon atom C-1:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-2:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-3:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-4:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure has to be completed from the skeletal structure given below and the bond angles around the central atoms in the given structure have to be predicted using the VSEPR model.
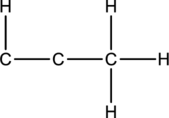
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Skeletal structure for the molecule given is shown;
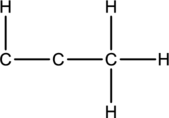
The Lewis structure can be drawn considering the valence electrons in the molecule. Total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
Twelve electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Two carbon atoms are added with a lone pair of electrons. Thus the Lewis structure can be drawn as follows;
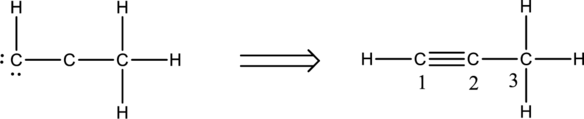
Bond Angles:
Central atoms present in the above structure are three carbon atoms. The bond angles can be predicted using the steric number.
Steric number for carbon atom C-1:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is two. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the arrangement is linear and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-2:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is two. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the arrangement is linear and the bond angle will be
Steric number for carbon atom C-3:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is four. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the arrangement is tetrahedral and the bond angle will be
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure has to be completed from the skeletal structure given below and the bond angles around the central atoms in the given structure have to be predicted using the VSEPR model.
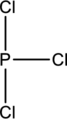
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Skeletal structure for the molecule given is shown;
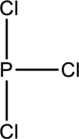
The Lewis structure can be drawn considering the valence electrons in the molecule. Total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
Six electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Three lone pair of electrons are placed on the chlorine atom each and a lone pair of electron is placed over the phosphorus atom. Thus the Lewis structure can be drawn as follows;
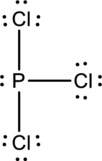
Bond Angles:
Central atom present in the above structure is a phosphorus. The bond angles can be predicted using the steric number.
Steric number for phosphorus:
The number of lone pair of electrons on phosphorus atom is one while the number of atoms that are bonded to phosphorus is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the arrangement is tetrahedral and the bond angle will be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- In what position will 4-methylbenzonitrile be nitrated and what will the compound be called.arrow_forwardIn what position will benzenesulfonic acid be nitrated?arrow_forwardIf compound A reacts with an excess of methyl iodide and then heated with aqueous Ag₂O, indicate only the major products obtained. Draw their formulas. A Harrow_forward
- Explanation Check 1:01AM Done 110 Functional Groups Identifying and drawing hemiacetals and acetals In the drawing area below, create a hemiacetal with 1 ethoxy group, 1 propoxy group, and a total of 9 carbon atoms. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ $ 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Sarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: CI structure CI CI Explanation CI ठ CI Check B ☐ 188 F1 80 name F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 60 F7 2arrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure i HO OH Explanation Check name ☐ ☐arrow_forward
- X 5 Check the box under each molecule that has a total of five ẞ hydrogens. If none of the molecules fit this description, check the box underneath the table. CI Br Br Br 0 None of these molecules have a total of five ẞ hydrogens. Explanation Check esc F1 F2 tab caps lock fn Q @2 A W # 3 OH O OH HO © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility IK F7 F7 F8 TA F9 F10 & 6 28 * ( > 7 8 9 0 80 F3 O F4 KKO F5 F6 S 64 $ D % 25 R T Y U பட F G H O J K L Z X C V B N M H control option command P H F11 F12 + || { [ command optionarrow_forwardAn open vessel containing water stands in a laboratory measuring 5.0 m x 5.0 m x 3.0 m at 25 °C ; the vapor pressure (vp) of water at this temperature is 3.2 kPa. When the system has come to equilibrium, what mass of water will be found in the air if there is no ventilation? Repeat the calculation for open vessels containing benzene (vp = 13.1 kPa) and mercury (vp = 0.23 Pa)arrow_forwardEvery chemist knows to ‘add acid to water with constant stirring’ when diluting a concentrated acid in order to keep the solution from spewing boiling acid all over the place. Explain how this one fact is enough to prove that strong acids and water do not form ideal solutions.arrow_forward
- The predominant components of our atmosphere are N₂, O₂, and Ar in the following mole fractions: χN2 = 0.780, χO2 = 0.21, χAr = 0.01. Assuming that these molecules act as ideal gases, calculate ΔGmix, ΔSmix, and ΔHmix when the total pressure is 1 bar and the temperature is 300 K.arrow_forwarddG = Vdp - SdT + μA dnA + μB dnB + ... so that under constant pressure and temperature conditions, the chemical potential of a component is the rate of change of the Gibbs energy of the system with respect to changing composition, μJ = (∂G / ∂nJ)p,T,n' Using first principles prove that under conditions of constant volume and temperature, the chemical potential is a measure of the partial molar Helmholtz energy (μJ = (∂A / ∂nJ)V,T,n')arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of dichloromethane at 20.0 °C is 58.0 kPa and its enthalpy of vaporization is 32.7 kJ/mol. Estimate the temperature at which its vapor pressure is 66.0 kPa.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





