
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure is used for predicting the shape of molecules. From the steric number obtained in a Lewis structure, the molecular geometry can be predicted. VSEPR model can predict the shape of molecules considering their Lewis structure. Certain rules has to be followed in for the VSEPR model.
- The molecule will have a shape where there is minimal electrostatic repulsion between the valence‑shell electron pairs.
- The forces of repulsion between two lone pairs of electrons will be higher than the repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of electrons. This in turn will be higher than the bond pair‑bond pair of electrons.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
The total number of valence electrons present in
The skeletal structure can be drawn considering the formula as shown below;
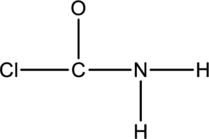
Ten electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Among the remaining fourteen valence-electrons, six are placed over chlorine atom and six are placed over oxygen atom. Two electrons are placed over nitrogen atom.
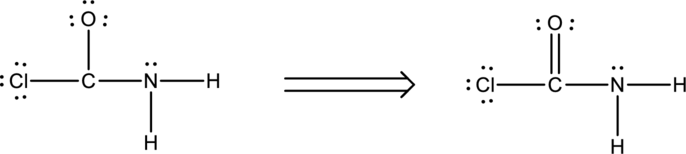
Thus the Lewis structure of
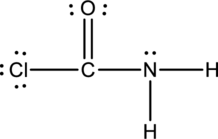
Bond Angles:
There is a carbon atom and a nitrogen atom as central atom in the Lewis structure. The steric number of the central atom can be used to predict the bond angles of the central atoms.
Steric number for carbon
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, and only bonding pair of electrons are present, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
Steric number for nitorgen atom:
The number of lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom is one while the number of atoms that are bonded to nitrogen is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the arrangement is tetrahedral and the bond angle will be
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
The total number of valence electrons present in
The skeletal structure can be drawn considering the formula as shown below;
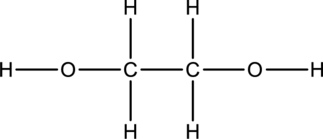
Eighteen electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Among the remaining eight valence-electrons, four are placed over oxygen atom each. Thus the Lewis structure for
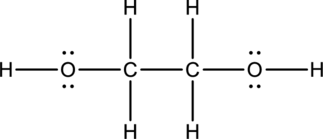
Bond Angles:
There are two carbon atoms as central atoms in the Lewis structure. The steric number of the central atom can be used to predict the bond angles of the central atoms.
Steric number for carbon atom:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is four. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the arrangement is tetrahedral and the bond angle will be
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
The total number of valence electrons present in
The skeletal structure can be drawn considering the formula as shown below;
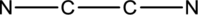
Six electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Among the remaining twelve valence-electrons, six are placed over nitrogen atom each. Thus the Lewis structure for

Bond Angles:
There are two carbon atoms as central atoms in the Lewis structure. The steric number of the central atom can be used to predict the bond angles of the central atoms.
Steric number for carbon atom:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is two. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the arrangement is linear and the bond angle will be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- Search Results Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unlo x b Success Confirmation of Q aleks.com/alekscgi/x/sl.exe/10_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTIOHz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCav States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 0. 32- 16 solid liquid gas 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Дос Xarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to answer the following questions: Acetoacetic ester can be prepared by the Claisen self-condensation reaction of ethyl acetate. 1. NaOEt, EtOH H&C OCH CH3 2 H30 H3C CH2 OCH2CH3 A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures. B. Ethyl acetate can be prepared from ethanol as the only organic starting material. Show all reagents and structures for all intermediates in this preparation. C. Give the structures of the ester precursors for the following Claisen condensation product and formulate the reaction. OEtarrow_forwardUse the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 32 16 solid liquid gas 0 0 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Шос ☑ كarrow_forward
- Starting from bromoethane, how could you prepare the following compounds: a. Ethanol. b. Acetaldehyde f. Acetone. e. 2-Propanol i. Acetoacetic ester. d. 2-Bromoacetic acid. c. Acetic acid g. Acetamide. j. Ethylmalonate k. Gama ketoacid. h. Ethyl magnesium bromide.arrow_forward- The pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 60. °C is raised. At what pressure will the sample melt? Use the phase diagram of X below to find your answer. pressure (atm) 02 0.4 solid Hliquid gas 0 0 200 400 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 0.025 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. ☐ atmarrow_forward15. What is the order of decreasing reactivity towards nucleophilic acyl substitution for the carboxylic acid derivatives? (most reactive first) 0 O H3C COC CH3 H₂C C N(CH3)2 H3C C OCH3 A. a. I, 11, 111, b. I, III, IV, II C. II, IV, III, I ° (CH3)2CH C OCH3 IV d. II, I, III, IV B. R COCR 0 0 0 13= RC NH2 RC OR RC CI === IV a. I, III, II, IV b. II, III, I, IV C. III, II, I, IV d. IV, I, III, IIarrow_forward
- Draw the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Tallose with bromine water.arrow_forwardChoose the best reagent(s) for carrying out the following conversions from the list below. Place the letter corresponding to the best choice in the blank to the left of the conversion. a. KMnO4, H3O+ b. Tollens' Reagent [oxidizing reagent] C. NaBH4, ethanol d. 1. BH3 2. H3O+ e. 1. CH3MgBr, ether 2. H3O+ f. CrO3, H2SO4, H₂O g. 1. Mg, ether 2. CO2 3. H3O+ h. 1. NaCN 2. H2SO4, H2, heat i. O3, then Zn and HOAC j. CH₂I A. B. C. CH CH=CHCH2COOH Br CEN CH COOH + HOOCCH COOH COOH 010 CH3arrow_forwardDraw the structures for each of the intermediates in the boxes provided for the synthesis below. OCH3 Fe HO HNO (CHOO pynding H₂504 LHNO2 NACH-I Fa H₂O HCL HNO 180arrow_forward
- Provide structure(s) for the starting material(s), reagent(s) or the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry [three only] A. o 11 (CH3)CH — C— C ether (CH3)2CH-C-O-C-CH3 B. CH3 CHy CI Staf OH C. HC OCHS + H₂Oarrow_forwardConsider the reaction sequence below to answer the following questions: EtO Compound X 1. NaOEt, EtOH OEt Br CO₂Et NaOEt, EtOH Compound Z CO₂Et Compound Y A. Compound X, diethyl propanedioate, is more commonly known as a. ethyl acetoacetate b. acetoacetic ester C. oxalic ester d. malonic ester 3. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the conversion of Compound X into Compound Y. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures.arrow_forwardClassify each of the following nitrogen atoms in the following compounds as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary [three only] CH3 HO-CHCHNHCH3 A. B. C. H&C CH3 D. HO phedrine CH2CHCH3 amphetamine NH₂ mepiquat chloride faxofenadine OH H&C CH CO₂Harrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
