
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Constitutional isomer possible for
Concept introduction:There are three ways of representation of molecular structures. The hashed and wedged formulas have three types of bonds. The bond above the plane is represented by bold hash while bonds behind the plane are represented by wedge. The bonds in plane are represented by normal bonds.
Bond-line formula depicts the zig-zag framework of carbon chain with attached substituents. The terminal position represents a methyl while the non-terminal is for methylene group. For instance, the propane is written in this notation as follows:
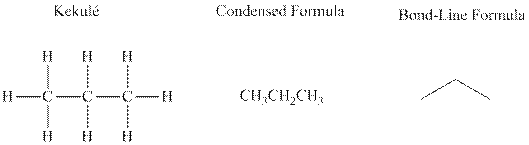
Molecules that possess identical molecular formula but vary in the manner of their connectivity of the bonds are referred to as structural isomers. These are essentially found in
For instance, the smallest branched alkane possible is

The two compounds, in fact, constitute a pair of constitutional isomers. These kinds of isomers are formed by cleavage and replacement of bonds, unlike the conformational isomers that result due to rotation around the bond.The structural isomers possible for a given alkane increase rapidly with a number of carbon atoms. This is justified as for alkanes higher than propane more ways exist to connect the carbon atoms.
(b)
Interpretation: Constitutional isomer possible for
Concept introduction:There are three ways of representation of molecular structures. The hashed and wedged formulas have three types of bonds. The bond above the plane is represented by bold hash while bonds behind the plane are represented by wedge. The bonds in plane are represented by normal bonds.
Bond-line formula depicts the zig-zag framework of carbon chain with attached substituents. The terminal position represents a methyl while the non-terminal is for methylene group. For instance, the propane is written in this notation as follows:
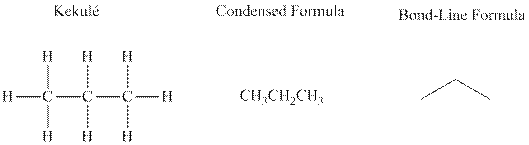
Molecules that possess identical molecular formula but vary in the manner of their connectivity of the bonds are referred to as structural isomers. These are essentially found in alkanes that can be branched by removal of
For instance, the smallest branched alkane possible is

The two compounds, in fact, constitute a pair of constitutional isomers. These kinds of isomers are formed by cleavage and replacement of bonds, unlike the conformational isomers that result due to rotation around the bond.The structural isomers possible for a given alkane increase rapidly with a number of carbon atoms. This is justified as for alkanes higher than propane more ways exist to connect the carbon atoms.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-PACKAGE
- Need help with these problems...if you can please help me understand problems E & F.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve these problems. Thank you in advance.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O N IN A N + H2O + HCI ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. 田 C + Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- 6. For each of the following, fill in the synthesis arrows with reagents and show the intermediates. You DO NOT need to use the same number of arrows that are shown (you may use more or less), but the product must be formed from the reactant. Then write the mechanism of one step in the synthesis (you can choose which step to write the mechanism for), including all reagents required, clearly labeling the nucleophile and electrophile for each step, and using curved arrows to show the steps in the mechanism. a. b. OHarrow_forwardDraw the productsarrow_forwardDraw the correct productsarrow_forward
- E Organic Chemistry Maxwell Draw the correct products, in either order, for the ozonolysis reaction: 1) O3, CH2Cl2, -78 °C Product 1 + Product 2 2) Zn, HOAc Draw product 1. Select Draw Templates More C H O presented by M Draw product 2. Erase Select Draw Templates M / # # carrow_forward✓ edict the products of this organic reaction: ---- ။ A CH3–C−NH–CH2–C−CH3 + KOH ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. C 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibiliarrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: A HO-C-CH3 + CH3NH2 P+ H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. marrow_forward
- H 1) OsO4, pyridine 2) Na2SO3 or NaHSO3 in H₂O 2 productsarrow_forward● Biological Macromolecules Naming and drawing cyclic monosaccharides Your answer is incorrect. • Row 1: Your answer is incorrect. Row 3: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 4: Your answer is incorrect. Try again... 0/5 Give the complete common name, including anomer and stereochemistry labels, of the following molecules. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS resource. CH2OH OH OH H H I H OH OH H] H CH2OH H OH ẞ-L-sorbose HOCH2 OH OH H HOCH2 H OH OH H OH H H CH2OH OH H H OH H I- H OH H OH Explanation Recheck W E R % 25 α B Y X & 5 D F G H McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Pr Parrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? + R -A HO IN + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax

