
(a)
Interpretation:
To predict the hybridization and geometry around each indicated atom.
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the three dimensional shape that a molecule in space. It is determine by considering the central atom and the surrounding atom and electron pairs. The shape of the molecule is determined by using Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion method. Some of the most common shapes that can be determined by this method are linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar and pyramidal.
For example.,
Linear (angle = 180o)
Trigonal planar (angle = 120o)
Tetrahedral (angle = 109.5o)
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbital into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the electron pairing to form
Answer to Problem 1.69P
The hybridization and geometry of
![]()
is sp3 and tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
For the hybridization, count the number of groups present around each atom. For example 4 groups = sp3, 3 groups = sp2, 2 groups = sp. And for the geometry count the surrounding atoms and lone pairs.
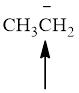
Fig.1
In the given compound (Fig.1), the central atom is carbon. It is surrounding by 3 atoms and a lone pair. So the geometry is tetrahedral. Number of groups present around the carbon atom is 4 so the hybridization is sp3.
The geometry is tetrahedral and the hybridization is sp3.
(b)
Interpretation:
To predict the hybridization and geometry around each indicated atom.
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the three dimensional shape that a molecule in space. It is determine by considering the central atom and the surrounding atom and electron pairs. The shape of the molecule is determined by using Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion method. Some of the most common shapes that can be determined by this method are linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar and pyramidal.
For example.,
Linear (angle = 180o)
Trigonal planar (angle = 120o)
Tetrahedral (angle = 109.5o)
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbital into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the electron pairing to form chemical bonds and valence bonds in other words mixing of two new orbital having same energy and shape. The orbital is called the hybrid orbital and the process is the hybridization. For example mixing s-orbital and p-orbital to form new hybridization is called sp-hybridization.
Answer to Problem 1.69P
The hybridization and geometry of
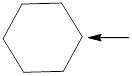
is nitrogen = sp3 and tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
For the hybridization, count the number of groups present around each atom. For example 4 groups = sp3, 3 groups = sp2, 2 groups = sp. And for the geometry count the surrounding atoms and lone pairs.
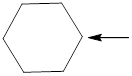
Fig.2
In the given compound (Fig.2), the central atom is carbon. Carbon is surrounding by 4 atoms. So the geometry is tetrahedral. Number of groups present around the nitrogen atom is 4 so the hybridization is sp3.
The geometry of carbon is tetrahedral and the hybridization is sp3.
(c)
Interpretation:
To predict the hybridization and geometry around each indicated atom.
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the three dimensional shape that a molecule in space. It is determine by considering the central atom and the surrounding atom and electron pairs. The shape of the molecule is determined by using Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion method. Some of the most common shapes that can be determined by this method are linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar and pyramidal.
For example.,
Linear (angle = 180o)
Trigonal planar (angle = 120o)
Tetrahedral (angle = 109.5o)
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbital into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the electron pairing to form chemical bonds and valence bonds in other words mixing of two new orbital having same energy and shape. The orbital is called the hybrid orbital and the process is the hybridization. For example mixing s-orbital and p-orbital to form new hybridization is called sp-hybridization.
Answer to Problem 1.69P
The hybridization and geometry of
![]()
is sp3 and tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
For the hybridization, count the number of groups present around each atom. For example 4 groups = sp3, 3 groups = sp2, 2 groups = sp. And for the geometry count the surrounding atoms and lone pairs.
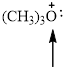
Fig.3
In the given compound (Fig.3), the central atom is oxygen. It is surrounding by 3 atoms and a lone pair. So the geometry is tetrahedral. Number of groups present around the oxygen atom is 4 so the hybridization is sp3.
The geometry is tetrahedral and the hybridization is sp3.
(d)
Interpretation:
To predict the hybridization and geometry around each indicated atom.
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the three dimensional shape that a molecule in space. It is determine by considering the central atom and the surrounding atom and electron pairs. The shape of the molecule is determined by using Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion method. Some of the most common shapes that can be determined by this method are linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar and pyramidal.
For example.,
Linear (angle = 180o)
Trigonal planar (angle = 120o)
Tetrahedral (angle = 109.5o)
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbital into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the electron pairing to form chemical bonds and valence bonds in other words mixing of two new orbital having same energy and shape. The orbital is called the hybrid orbital and the process is the hybridization. For example mixing s-orbital and p-orbital to form new hybridization is called sp-hybridization.
Answer to Problem 1.69P
The hybridization and geometry of
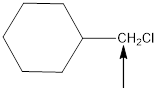
is sp3 and tetrahedral
Explanation of Solution
For the hybridization, count the number of groups present around each atom. For example 4 groups = sp3, 3 groups = sp2, 2 groups = sp. And for the geometry count the surrounding atoms and lone pairs.
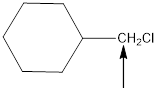
Fig.4
In the given compound(Fig.4), the central atom is carbon. It is surrounding by 4 atoms. So the geometry is tetrahedral. Number of groups present around the carbon atom is 4 so the hybridization is sp3.
The geometry is tetrahedral and the hybridization is sp3.
(e)
Interpretation:
To predict the hybridization and geometry around each indicated atom.
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the three dimensional shape that a molecule in space. It is determine by considering the central atom and the surrounding atom and electron pairs. The shape of the molecule is determined by using Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion method. Some of the most common shapes that can be determined by this method are linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar and pyramidal.
For example.,
Linear (angle = 180o)
Trigonal planar (angle = 120o)
Tetrahedral (angle = 109.5o)
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbital into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the electron pairing to form chemical bonds and valence bonds in other words mixing of two new orbital having same energy and shape. The orbital is called the hybrid orbital and the process is the hybridization. For example mixing s-orbital and p-orbital to form new hybridization is called sp-hybridization.
Answer to Problem 1.69P
The hybridization and geometry of
![]()
is sp and linear
Explanation of Solution
For the hybridization, count the number of groups present around each atom. For example 4 groups = sp3, 3 groups = sp2, 2 groups = sp. And for the geometry count the surrounding atoms and lone pairs.
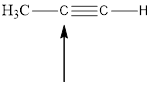
Fig.5
In the given compound (Fig.5), the central atom is carbon. It is surrounding by 2 atoms. So the geometry is linear. Number of groups present around the carbon atom is 2 so the hybridization is sp.
The geometry is linear and the hybridization is sp.
(f)
Interpretation:
To predict the hybridization and geometry around each indicated atom.
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the three dimensional shape that a molecule in space. It is determine by considering the central atom and the surrounding atom and electron pairs. The shape of the molecule is determined by using Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion method. Some of the most common shapes that can be determined by this method are linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar and pyramidal.
For example.,
Linear (angle = 180o)
Trigonal planar (angle = 120o)
Tetrahedral (angle = 109.5o)
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbital into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the electron pairing to form chemical bonds and valence bonds in other words mixing of two new orbital having same energy and shape. The orbital is called the hybrid orbital and the process is the hybridization. For example mixing s-orbital and p-orbital to form new hybridization is called sp-hybridization.
Answer to Problem 1.69P
The hybridization and geometry of
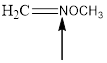
is nitrogen = sp2 and trigonal planar
Explanation of Solution
For the hybridization, count the number of groups present around each atom. For example 4 groups = sp3, 3 groups = sp2, 2 groups = sp. And for the geometry count the surrounding atoms and lone pairs.
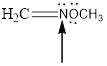
Fig.6
In the given compound (Fig.6), the central atom is nitrogen. Nitrogen is surrounding by 2 atoms and a lone pair. So the geometry is trigonal planar. Number of groups present around the nitrogen atom is 3 so the hybridization is sp2.
The geometry of nitrogen is trigonal planar and the hybridization is sp2.
(g)
Interpretation:
To predict the hybridization and geometry around each indicated atom.
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the three dimensional shape that a molecule in space. It is determine by considering the central atom and the surrounding atom and electron pairs. The shape of the molecule is determined by using Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion method. Some of the most common shapes that can be determined by this method are linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar and pyramidal.
For example.,
Linear (angle = 180o)
Trigonal planar (angle = 120o)
Tetrahedral (angle = 109.5o)
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbital into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the electron pairing to form chemical bonds and valence bonds in other words mixing of two new orbital having same energy and shape. The orbital is called the hybrid orbital and the process is the hybridization. For example mixing s-orbital and p-orbital to form new hybridization is called sp-hybridization.
Answer to Problem 1.69P
The hybridization and geometry of
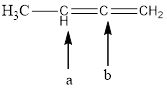
is carbon-a = sp2 and trigonal planar
carbon-b = sp and linear
Explanation of Solution
For the hybridization, count the number of groups present around each atom. For example 4 groups = sp3, 3 groups = sp2, 2 groups = sp. And for the geometry count the surrounding atoms and lone pairs.
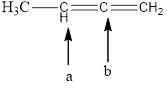
Fig.7
In the given compound (Fig.7), the central atom is carbon. The given structure has two carbons. Carbon-a is surrounding by 3 atoms. So the geometry is trigonal planar. Number of groups present around the carbon atom is 3 so the hybridization is sp2.
Carbon-b is surrounding by 2 atoms. So the geometry is linear. Number of groups present around the carbon atom is 2 so the hybridization is sp.
The geometry of carbon-a is trigonal planar and the hybridization is sp2. The geometry of carbon-b is linear and the hybridization is sp.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forwardWhat is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forwardIndicate the product obtained (formula). F3C. CF3 Br NH2 NH OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forward
- What are the missing intermediates 1, 2, and 3? Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediates and how they occur.arrow_forwardThe following intermediates are to proceed by acetoacetic ester synthesis. What are intermediates 1 and 2 plus the final product 3? Please include a detailed explanation and drawings of the intermediates and how they occurred.arrow_forwardThe chemical formula of "benzimidazole E" is C7H6N2. Draw it.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


